Implementing total quality management (TQM) manually is a struggle for most organizations. Paper-based inspections, scattered spreadsheets, and inconsistent reporting make it nearly impossible to maintain compliance, track progress, or foster a culture of continuous improvement. Without real-time visibility, managers risk poor process control, missed defects, and regulatory non-compliance. That’s where total quality management software comes in. It helps organizations move beyond manual processes by digitizing inspections, automating workflows, and ensuring every employee, from executives to frontline staff, is aligned with quality objectives.
This article will explore the key features and benefits of TQM software, as well as practical steps and free checklists to implement a TQM program and principles.
- What is Total Quality Management Software?
- Factors to Consider When Choosing the Best TQM Software
- What is a Total Quality Management System?
- Total Quality Control vs Total Quality Management
- Approaches to Total Quality Management System: What is the Main Purpose of TQM?
- Steps to Implement a Total Quality Management Program
- How Different Industries Use TQM Software to Implement a TQM System
- FAQs
What is Total Quality Management Software?
Total quality management (TQM) software is a specialized digital solution designed to help organizations implement, automate, and sustain the core principles and practices of total quality management in their daily operations.
TQM itself is a management philosophy and approach focused on long-term success through customer satisfaction, continuous improvement, employee involvement, and process optimization.
Key Features and Benefits of TQM Software
Key features commonly offered by modern TQM software include:
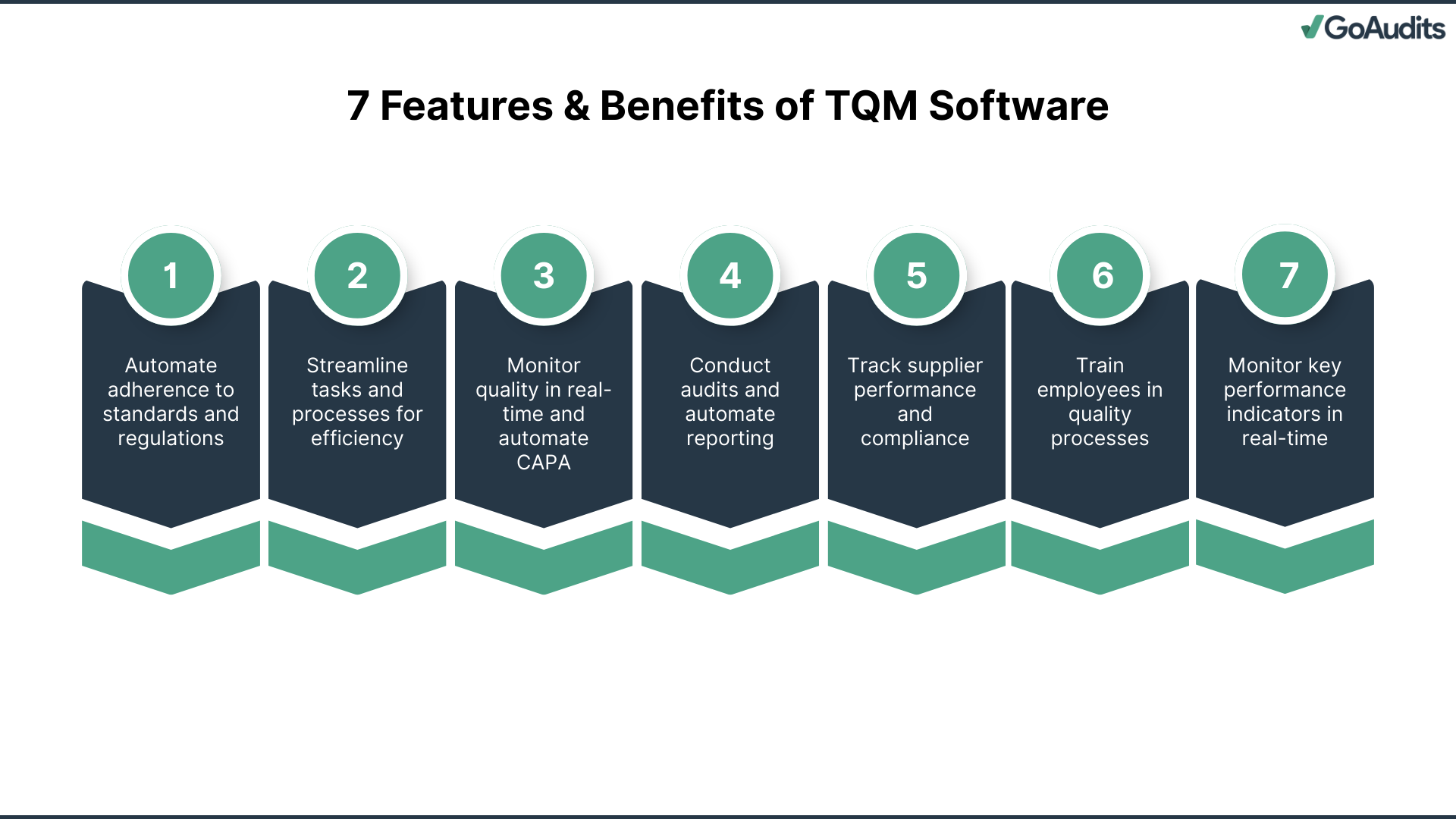
- Compliance and Risk Management: Automate compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 and FDA regulations while integrating risk assessment and mitigation workflows. This reduces non-compliance risks and ensures audit readiness.
- Process Automation, Efficiency, and Continuous Improvement: Streamline workflows, automate repetitive quality tasks, and embed improvement cycles, reducing errors, shortening lead times, and fostering operational excellence.
- Quality Control, Assurance, and CAPA: Monitor quality in real time, ensure adherence to standards, and provide automated corrective and preventive action workflows for lasting quality improvements.
- Audits, Inspections, and Document Management: Schedule and conduct digital audits with automated reporting while centralizing documents with version control and secure access for complete traceability.
- Supplier and Customer Quality Management: Track supplier compliance and performance, integrate procurement processes, and manage customer complaints with fast, structured resolution workflows to strengthen relationships.
- Training, Competency, and Change Management: Assign and monitor employee training, ensure competency in quality processes, and manage controlled changes with full impact assessments.
- Dashboards, Analytics, and Integration: Deliver real-time KPI tracking, AI-driven insights, and seamless integration with ERP, CRM, PLM, and IoT systems for unified, data-driven decision-making.
👉 GoAudits quality inspection software helps organizations digitize their entire quality management and auditing lifecycle, from inspections to corrective actions. With ready-to-use industry templates, mobile and offline functionalities, instant reporting, and real-time analytics, GoAudits makes TQM practical, efficient, and sustainable.
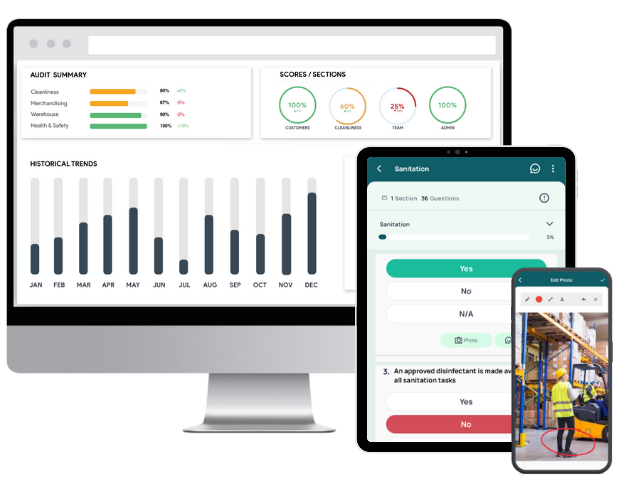
- Access industry-specific templates or build your own from scratch. Send us your existing checklists, and we’ll digitize them at no additional cost.
- Perform inspections on any mobile device, even offline. Capture photos, signatures, timestamps, and geo-location directly from your device.
- Automatically generate & share professional reports after each inspection, with evidence, scores, and corrective actions.
- Assign issues to the right personnel during inspections. Define priorities, deadlines, and responsibilities to ensure timely resolution and accountability.
- Automate notifications, escalations, approvals, and reminders. Maintain control with centralized task dashboards and track completion by assignee, location, or due date.
- Monitor audit scores, recurring issues, and performance trends. Drill down from high-level views to specific inspections for deep insights and informed decision-making.

Factors to Consider When Choosing the Best TQM Software
To make an informed decision, consider these specific, high-impact factors:
Budget-Friendly Without Hidden Costs
Begin with a clear budget to avoid overspending. Compare pricing models (subscription, one-time purchase, or tiered plans) against the features offered. A budget-friendly solution should provide essential TQM functionalities without forcing you to pay for unnecessary extras. Look for transparent pricing and avoid software with hidden charges for updates or additional users.
Reliable and Responsive Customer Support
Quality management issues often require immediate attention. Choose a vendor known for responsive and knowledgeable support. Check availability across multiple channels, such as live chat, email, and phone. Review service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure quick resolution times and assess whether support is available during your business hours or 24/7.
Intuitive and User-Friendly Interface
A complex interface slows adoption and increases training costs, while an intuitive one reduces errors. Opt for software with a clean layout, logical navigation, and clear instructions. Run usability tests with your team to ensure workflows are straightforward and align with your processes.
Robust Data Security Measures
TQM systems often handle sensitive operational and compliance data. Ensure the software uses robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls. Verify the vendor’s compliance with relevant regulations, such as ISO 27001, GDPR, etc. Regular security audits and data backup protocols are essential for minimizing risk.
Free Trials and Comprehensive Demos
Before committing, take advantage of free trials or live demos. This allows you to test real-world scenarios, check integration with existing systems, and confirm ease of use. Trials also reveal performance under your organization’s typical workload, helping you make a data-driven choice.
What is a Total Quality Management System?
A total quality management system is an organization-wide management approach focused on continuous improvement of processes, products, and services, with the primary aim of meeting or exceeding customer expectations. TQM involves every employee, from executives to frontline workers, working collaboratively to enhance quality and drive long-term success.
Key attributes and principles include:
- Customer focus
- Employee involvement
- Process approach
- Integrated system
- Data-driven decision making
- Continual improvement
- Effective communication
We have discussed these approaches to total quality management in detail below.
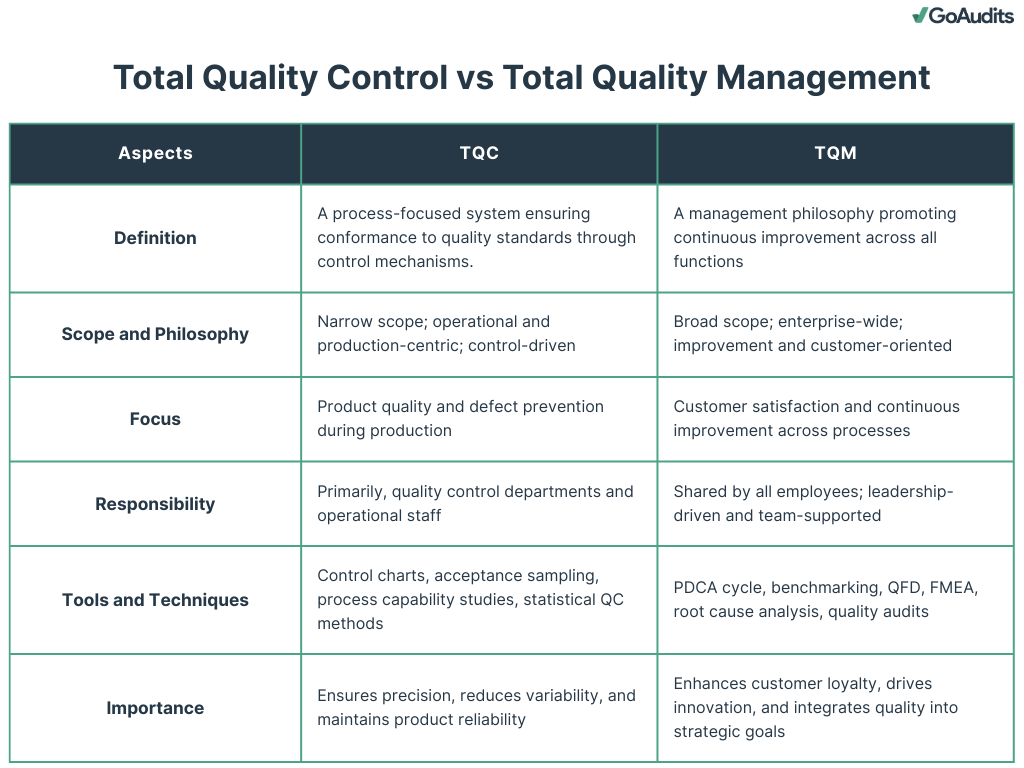
Total Quality Control vs Total Quality Management
Understanding the difference between total quality control (TQC) and total quality management is essential when aiming to establish an effective quality strategy. Both concepts aim to ensure superior product and service quality, but their scope, approach, and implementation differ significantly.
Definition
TQC is a comprehensive system for achieving optimal quality by controlling all production and service processes. It focuses on process-centered control through stringent monitoring, inspection, and compliance. TQC emphasizes detecting and eliminating defects during the production process.
TQM is a management philosophy centered on continuous improvement across all organizational functions. It promotes quality as a shared responsibility and integrates it into corporate culture, involving everyone from top leadership to frontline employees.
Scope and Philosophy
The scope of TQC is mainly operational. It centers on manufacturing, engineering, and product development. The philosophy is control-oriented, aiming to maintain conformance to standards through rigorous checks and statistical methods.
TQM has a broader scope, encompassing customer service, human resources, finance, and strategic planning. Its philosophy is holistic and system-wide, aiming to build quality into every function and process.
Focus
In TQC, the focus is on product quality. It seeks to reduce variability and ensure consistency through inspection and process control.
The focus shifts to customer satisfaction in TQM. TQM prioritizes understanding customer needs, enhancing experience, and fostering long-term relationships through proactive quality improvements.
Responsibility
In TQC, responsibility for quality largely rests with the quality control department and operational personnel. It follows a hierarchical structure where accountability is siloed.
Responsibility is shared across all levels in TQM. Senior management leads the initiative, but every employee is empowered and accountable for maintaining and improving quality.
Tools and Techniques
TQC involves the use of statistical tools, primarily during production stages, including:
- Control charts
- Acceptance sampling
- Cause-and-effect diagrams
- Process capability analysis
TQM combines TQC tools with strategic management tools such as:
- Benchmarking
- Quality function deployment (QFD)
- Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA)
- Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle
Importance
TQC ensures product reliability, reduces defects, and maintains compliance with standards. It is critical in industries where process stability and precision are paramount, such as automotive or pharmaceuticals.
TQM builds a culture of excellence, drives customer loyalty, and enhances organizational agility. TQM enables you to align quality with business goals, resulting in sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Approaches to Total Quality Management System: What is the Main Purpose of TQM?
Here’s a breakdown of key TQM principles and how each contributes to sustained operational excellence:
- Customer Focus: Identify, meet, and exceed customer expectations by collecting feedback, monitoring satisfaction, and aligning processes to deliver consistent value.
- Leadership: Provide a clear vision and foster a culture of quality at all levels; remove barriers, set performance standards, and ensure resources support quality goals.
- Total Employee Involvement: Encourage active participation from all staff through idea-sharing, ownership of processes, training, and recognition.
- Process-Centered Approach: Treat all activities as value-adding processes; document workflows, set metrics, and reduce variation to prevent defects at the source.
- Integrated Systems: Align all departments and functions toward common quality objectives, ensuring transparency, collaboration, and accountability.
- Strategic and Systematic Approach: Embed quality improvement into the business strategy with measurable objectives, efficient resource allocation, and progress monitoring.
- Effective Communication: Maintain open channels, share performance data, and provide feedback loops to build trust and keep quality top-of-mind.
- Continuous Improvement: Use tools like PDCA, Six Sigma, and Lean to identify inefficiencies, test solutions, and sustain operational gains.
- Fact-Based Decision-Making: Base decisions on accurate data, KPIs, and root cause analysis to ensure focused, effective, and measurable improvements.
Steps to Implement a Total Quality Management Program
Follow these defined steps to ensure effective implementation:
1. Secure Top Management Commitment
Begin by gaining unwavering support from top leadership. Without executive buy-in, TQM efforts will lack direction and authority. Management must actively participate, allocate resources, and model quality-driven behavior.
2. Establish a Clear Quality Vision and Mission
Define a focused quality vision aligned with your business objectives. Craft a mission statement that reflects long-term quality goals and customer satisfaction as a core value. Ensure it’s specific, measurable, and communicated across all departments to provide strategic clarity.
3. Form a Quality Management Team
Assemble a cross-functional team responsible for planning and executing TQM initiatives. Include members from various departments to encourage collaboration and shared accountability. Assign defined roles and empower the team to make data-driven decisions.
4. Assess Current Processes
Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing processes, systems, and workflows to guide future improvements. Use tools like process mapping, flowcharts, and gap analysis to identify inefficiencies and areas that fall short of quality standards.
5. Define Critical Success Factors and KPIs
Identify the factors that are crucial for your TQM program’s success, such as customer satisfaction, defect rates, or process efficiency. Develop precise key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure these factors. Make sure the metrics are actionable, relevant, and tied directly to your objectives.
👉 Find out how GoAudits can help you track and improve KPIs across different industries: Restaurant KPIs, manufacturing KPIs, hotel KPIs, retail KPIs, healthcare quality metrics, and health and safety KPIs.
6. Develop a Strategic Quality Plan and Quality Management System (QMS)
Create a detailed strategic quality plan that outlines objectives, timelines, responsibilities, and resources. Integrate a formal QMS tailored to your operational needs. Ensure the QMS covers documentation, standard operating procedures, and audit mechanisms.
7. Train and Educate Employees
Provide targeted training for all employees, from entry-level staff to senior management. Cover TQM principles, specific quality tools, and the use of the QMS. Reinforce training with regular workshops, on-the-job coaching, and updated learning modules to build lasting competence.
8. Promote a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Embed continuous improvement into daily operations. Encourage feedback, reward quality contributions, and support innovation. Use frameworks like PDCA or Kaizen to make incremental, ongoing enhancements to processes and products.
9. Implement Quality Tools and Techniques
Use proven quality management tools to diagnose issues and improve processes. Examples include:
- Pareto Analysis to prioritize problems
- Fishbone Diagrams for root cause analysis
- Control Charts to track process stability
- Six Sigma to reduce variation and defects
Select tools based on the specific challenges identified in your assessments.
10. Monitor Progress and Adjust
Track performance continuously using your KPIs. Review the data regularly through audits, dashboards, and team reviews. Identify gaps between targets and outcomes, then adjust strategies or resources accordingly. Responsiveness is essential to maintain momentum.
11. Sustain the TQM System
Ensure long-term success by integrating quality objectives into strategic planning and daily operations. Institutionalize best practices, standardize procedures, and keep the QMS updated. Regularly revisit the vision, retrain employees, and refresh improvement targets to keep the system dynamic.
How Different Industries Use TQM Software to Implement a TQM System
Here’s a closer look at how TQM software is used across five distinct industries:
TQM in Manufacturing
TQM software helps manufacturers standardize quality checks, prevent defects, and monitor KPIs like defect rates, cycle times, and equipment efficiency. Integrated analytics support root cause analysis and continuous improvement through methods such as Six Sigma or Kaizen.
👉 Free Resources
GoAudits offers a wide range of ready-to-use and customizable manufacturing audit checklists to help you ensure product quality, workplace safety, and compliance at every stage of manufacturing.
→ ISO 9001:2015 Supplier Audit Checklist
→ Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Audit
→ Manufacturing Process Audit Checklist
→ Production Quality Control Checklist for Manufacturing
→ Quality Control Audit Checklist
→ Manufacturing Quality Control Checklist
→ Vendor Quality Audit Checklist
Total Quality Management in the Food Industry
TQM software helps comply with stringent food safety standards and maintain product consistency. It enables you to document and track every step of the production process, from raw material sourcing to packaging, ensuring traceability and regulatory compliance with standards like HACCP, GMP, SQF, BRCGS, FSSC, IFS, and more.
👉 Free Resources
GoAudits offers comprehensive food safety and quality checklists that help you meet regulatory standards, maintain hygiene, and safeguard customer health.
→ Food Quality Control Checklist
→ HACCP-Based SOP Templates
→ BRC Audit Checklists
→ Food Safety Checklists & Audit Templates
→ GMP Audit Checklist & Templates
→ SQFI Quality Checklist
Total Quality Management Principles in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use TQM systems to improve patient safety, track incidents, and meet accreditation standards. By digitizing protocols and monitoring clinical KPIs, TQM software reduces errors, ensures compliance, and facilitates cross-department communication.
👉 Free Resources
GoAudits offers a wide range of healthcare audit checklists to ensure compliance with clinical protocols, maintain patient safety, and support continuous quality improvement.
→ Patient Care Checklist
→ Patient Satisfaction Survey Template
→ Care Home Audit Checklist
→ Equality and Diversity in Healthcare Checklist
→ Healthcare Employee Training Checklist
→ Nursing Home Safety Checklist
Total Quality Management in the Hospitality Industry
TQM software helps hotels and resorts deliver consistent guest experiences by tracking cleanliness, service quality, and brand standards across multiple sites. Analytics highlight trends in guest satisfaction and service delivery.
👉 Free Resources
GoAudits provides a variety of hotel inspection & audit checklists to maintain service quality, cleanliness, and compliance with health and safety regulations across all locations.
→ Hotel Safety Checklist
→ Hotel Housekeeping Checklists
→ Hotel Maintenance Checklists
→ Hotel Front Desk Checklist
→ Room Inspection Checklist
→ Hotel Operations Manager Checks
Laboratories
TQM software ensures you maintain accuracy, reliability, and compliance with testing standards. It enables you to manage sample tracking, calibration schedules, and testing workflows, minimizing the risk of human error. You can generate audit-ready reports, manage corrective and preventive actions, and ensure compliance with ISO 17025 or similar standards. Eventually, you can identify inefficiencies, improve turnaround times, and maintain high testing integrity.
FAQs
The main purpose of TQM is to ensure that all aspects of an organization are focused on continually meeting or exceeding customer expectations by improving the quality of processes, products, and services.
The seven tools of TQM are cause-and-effect diagrams, check sheets, control charts, histograms, Pareto charts, scatter diagrams, and flowcharts. Each tool serves a specific purpose in identifying, analyzing, and improving quality-related issues. For instance, cause-and-effect diagrams help trace problems to their root causes, while control charts monitor process stability. Using these tools enables you to make data-driven decisions, reduce variability, and enhance process performance across different functions.
TQM enhances customer satisfaction by embedding quality at every stage of production or service delivery. By continuously improving processes, minimizing errors, and responding proactively to customer feedback, you ensure products and services meet or exceed expectations. This builds trust, loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth. From a business standpoint, TQM reduces operational inefficiencies, lowers costs, and improves employee engagement, contributing to long-term profitability and competitive advantage.
Traditional TQM software focuses on documentation, compliance, and isolated quality control tasks. It often lacks real-time data integration and advanced analytics. In contrast, modern TQM software leverages cloud computing, automation, AI, and machine learning to provide real-time monitoring, predictive insights, and cross-functional collaboration. It integrates seamlessly with other enterprise systems, enabling faster decision-making and a more proactive approach to quality management.





