In the food industry, safety isn’t a box to tick on a compliance checklist. Food safety is essential for both consumers and the food establishments involved in its production. Ensuring product safety and top-notch quality demands compliance with food safety standards by manufacturers, retailers, and suppliers. BRC standards and BRC audits are industry-best practice frameworks that help all types of businesses achieve that.

Established in 1992, the British Retail Consortium (BRC) aimed to support the food industry amidst evolving landscapes and the regulatory frameworks of UK and EU food safety laws. Subsequently, the BRC Global Standards (BRCGS) is a pivotal global benchmark, shaping safety and quality programs worldwide. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of BRC audits and provide several useful tools to help you succeed in your BRC certification.
Understanding BRC Global Standards (BRCGS)
BRC Global Standards is a leading safety and quality certification program for food products. Originally, the standards were developed by the British Retail Consortium, a trade association representing the UK retail industry. However, the LGC Group acquired the BRC standards in 2016.
👉 In 2019, the British Retail Consortium (BRC) rebranded as BRCGS (Brand Reputation through Compliance of Global Standards).
The BRC Global Standards has become a widely recognized and respected food safety certification program, with over 30,000 certified suppliers in more than 130 countries. Though BRCGS is currently in its 9th edition, it was the first standard to introduce food safety culture requirements, define food fraud, and be benchmarked by GFSI.
BRCGS covers a wide range of food safety and quality issues, including food safety management systems, product safety, packaging, storage, and distribution. It also provides a framework for product safety, quality, legality, and operational controls in the food and food ingredient manufacturing, processing, and packing industry. It has improved consumer safety by identifying and correcting 185,000 non-conformities each year.

BRC Version 9
The BRC standards are regularly updated to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
👉 The BRC’s Issue 9 was published on August 1, 2022, and is effective for audits from February 1, 2023.
BRC Issue 9 has two core themes, including developing a food safety culture and building core competencies.
The updated standards are structured around nine core sections. These 9 sections represent the series of requirements for the BRC audit certification:
- Senior Management Commitment: It emphasizes the crucial role of top leadership in fostering a culture of food safety throughout the organization.
- The Food Safety Plan – HACCP: The updated HACCP requirements focus on a more preventative and risk-based approach, aligning with the Codex Alimentarius principles.
- Food Safety and Quality Management System: It reinforces the importance of integrating food safety into the core business management system.
- Site Standards: Hygiene and sanitation requirements are enhanced, with stricter guidelines for pest control, cleaning validation, and temperature control.
- Product Control: Product specifications, traceability, and recall procedures are given greater emphasis to ensure product safety at every stage.
- Process Control: Process validation and monitoring are strengthened to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure product consistency.
- Personnel: Training and competency requirements for food handlers are expanded, promoting a knowledgeable and responsible workforce.
- Production Risk Zones: Specific controls are outlined for production areas, including high-risk, high-care, and ambient high-care, handling particularly vulnerable or sensitive products.
- Requirements for Traded Products: It addresses the growing complexity of global food chains, ensuring the safety of traded products.
Adopting BRC Standards
The BRC program has helped improve the safety and quality of food products by setting high standards. BRC certification has become a requirement for many retailers and suppliers, which has helped raise the bar for food safety across the industry. By adhering to these benchmarks, BRC-certified sites effectively mitigate the risk of food safety incidents, ensuring consumer confidence in the products they purchase. Moreover, BRC audit certification has become an indispensable requirement for many retailers and suppliers.
Adopting BRC Standards offers several benefits, including the following:
- Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements: BRC certification ensures that your business complies with all relevant food safety laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Competitive Advantage: BRC audit certification sets your business apart by demonstrating your commitment to food safety and quality. This can be a significant differentiator when vying for contracts with major retailers and suppliers.
- Improved Reputation: BRC certification enhances your brand reputation as a responsible and trustworthy food producer. Consumers are increasingly discerning about the safety and quality of the food they consume, and BRC audit certification gives them peace of mind.
- Reduced Risk of Food Safety Incidents: By implementing the rigorous BRC standards, you significantly reduce the likelihood of food safety incidents occurring within your facility. This not only protects consumers but also safeguards your business from potential financial losses and legal repercussions.
- Reduced Costs: While achieving BRC certification may require an initial investment, it can lead to long-term cost savings by minimizing product recalls, rework, and waste. Efficient processes and adherence to best practices can enhance overall operational efficiency.
What is a BRC Audit & What You Should Expect from It
A BRC audit evaluates a company’s compliance with the BRC Global Standards. It is an assessment of the food safety management system, processes, and procedures for the organization. It is conducted by an independent BRC-accredited certification body to ensure that the company meets the requirements of the BRC Global Standard for food safety.
BRCGS audit is relevant for companies that:
- Process or work with open food
- Ingredient suppliers that supply retailers with ingredients and other food products
- Manufacture consumer products and handle non-food items
- Buy, sell, or facilitate the trade of products, but do not manufacture, process, or store the products
There are four key components of every BRCGS audit, including the following:
- Documentation review: This involves reviewing the company’s food safety documentation to ensure that it is complete and accurate. This documentation includes the company’s food safety manual, procedures, and records.
- Site inspection: This involves conducting a thorough inspection of the company’s production facilities, equipment, and premises. It includes identifying any conditions that could pose a risk to food safety, such as poor sanitation, inadequate pest control, or improper storage of food.
- Employee interviews: Employees are interviewed to assess their understanding and adherence to food safety practices. It also included reviewing their roles and responsibilities, their training, and their knowledge of food safety procedures.
- Product testing: This includes testing finished products to verify their safety and quality. Microbiological testing, chemical testing, and sensory testing are some common types of product testing that form part of BRC audits.
There are two main types of BRC audits:
- Full (Announced) BRC audit
- Unannounced audit
Both these BRC audits result in an official grade decided by the auditor, based on specific criteria.
BRC Grading Systems
BRCGS audits are graded on the number and type of non-conformances. These can either be minor, major, or critical.
👉 The BRC grading system is based on a scale of AA, as the highest, to Uncertified. Unannounced audits have a ‘+’ after their grades.
The grades are based on the company’s performance in the following areas:
- Food safety
- Quality management
- Compliance with legal requirements
- Continuous improvement
| Announced | Unannounced | Non-Conformances |
| AA | AA+ | Lesser than 5 errors |
| A | A+ | 5 to 10 errors |
| B | B+ | 11 to 16 minors, or 1 major, and up to 10 minors |
| C | C+ | 17 to 24 minors, or 1 major and up to 16 minors, or 2 majors and up to 10 minors |
| D | D+ | 25 and 30 minors, or 1 major and up to 24 minors, or 2 majors and up to 16 minors |
| Uncertified | Uncertified | 1 or more critical, 31 or more minors, 1 major and 25 or more minors, 2 majors and 17 or more minors, or 3 or more majors |
How to Prepare For a BRC Audit?
Here’s a comprehensive guide on conducting a BRCGS audit:
Step 1: Preparation Phase
- Gather comprehensive documentation: Assemble all necessary documents demonstrating consistent food safety management, including policies, procedures, records, plans, reports, certificates, licenses, and training materials. Make sure your documents are accurate, traceable, and easily available.
- Conduct thorough internal audits: Identify potential gaps and areas for improvement before the official audit. You can do so by conducting thorough internal audits. For internal audits, your team should be comprised of members who have in-depth knowledge and experience in BRC standards and the overall food industry.
- Use BRC audit checklists: Use BRC internal audit checklists to ensure thorough coverage of all audit criteria and track progress.
- Train personnel: Educate your staff on BRC standards and audit procedures to ensure preparedness and compliance. The audit procedures can include assessment, testing, sampling, verification, reporting, and more.
Step 2: Audit Execution Phase
- Pre-audit briefing: Holding a pre-audit briefing with the auditor will help you establish the expectations, scope, and timelines of the audit.
- Documentation review: The auditor meticulously examines documentation for compliance with BRC standards. Documentation review will also enable the auditor to assess your company’s other documentation, including food safety plans, quality manuals, procedures, and records.
- On-site inspection: The auditor will conduct an on-site inspection of your premises, including production areas, storage facilities, and equipment. A thorough walkthrough of the facility will enable the auditor to observe practices, conditions, and potential risks.
- Evidence evaluation: The auditor will evaluate the evidence gathered during the documentation review and on-site inspection to assess compliance with BRC standards.
Step 3: Reporting and Follow-up Phase
- Document audit findings: The auditor meticulously documents all audit findings, including non-conformities and areas for improvement.
- Root cause analysis: It involves identifying the underlying causes of non-conformities. Conducting a thorough investigation to identify the underlying causes of non-conformities will prevent them from recurring.
- Corrective action plan: It outlines the steps to address and prevent the non-conformities from happening again. The corrective plan should also include clear timelines, accountable parties, and verification techniques.
- Continuous improvement suggestions: The auditor may offer recommendations for continuous improvement to enhance your food safety and quality and food safety management system.
- Post-audit activities: You must implement the corrective actions as per the agreed timelines. Monitor the effectiveness of the corrective actions and make necessary adjustments. Continuously review and improve your food safety and quality management systems to maintain compliance with BRC standards.
Though the above process might look daunting, BRC software can help you prepare for and conduct a successful BRCGS audit. It can provide you with a structured approach to assessing compliance with the BRC standard and help you identify areas for improvement.
BRC Certification
BRC audit certification shows that a food business adheres to the BRC Global Standards of food safety and quality management system, and is committed to providing safe food to consumers. In addition to guaranteed food safety, other benefits of BRC certification include operational efficiency, access to global markets, and increased customer confidence.
A BRC audit certificate is issued by a BRCGS-approved certification body.
Auditors who issue a certificate against any global food standard must work for a certification body. An independent auditor cannot issue a BRCGS audit certificate. The auditor writes a full report once the BRC audit is complete. The certification body then reviews the audit report and the actions taken by your company to correct identified non-conformities. Eventually, it approves or declines the BRC audit certification.
The requirements for BRC audit certification vary depending on the type of food business. However, some of the general requirements include:
- Food safety management system: You must have a documented food safety management system that is based on the principles of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points).
- HACCP plan: You must have a HACCP plan that identifies and controls food safety hazards. HACCP software can help automate and streamline the process of creating and managing HACCP plans, while HACCP checklists can be used to verify that critical control points are being met.
- Internal audits: You must conduct regular internal audits to verify that the food safety management system is effective.
- Continuous review: You must conduct regular management reviews to assess the effectiveness of the food safety management system.
The BRC audit certification process involves the following steps:
- Application: A food business must submit an application to a BRC-approved certification body.
- Assessment: The certification body will conduct an assessment of the food business to verify that it meets the requirements of the BRC Global Standard for Food Safety.
- Certification: If your food business meets the requirements of the standard, it will be issued with a BRC certificate.
BRC Certification Bodies
BRC Certification Bodies are independent organizations that are accredited to conduct audits and issue certificates against the BRC Global Standards. They are responsible for assessing whether your business’s food safety, quality, and operational management systems meet the requirements of the relevant BRC Standard.
Streamline Audits with BRC Software
GoAudits’ all-in-one BRC audit software enables you to conduct self-assessments and audits more efficiently and effectively, using digital BRC audit checklists. GoAudits works on any electronic device, such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones (iOS or Android), saving valuable time and reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
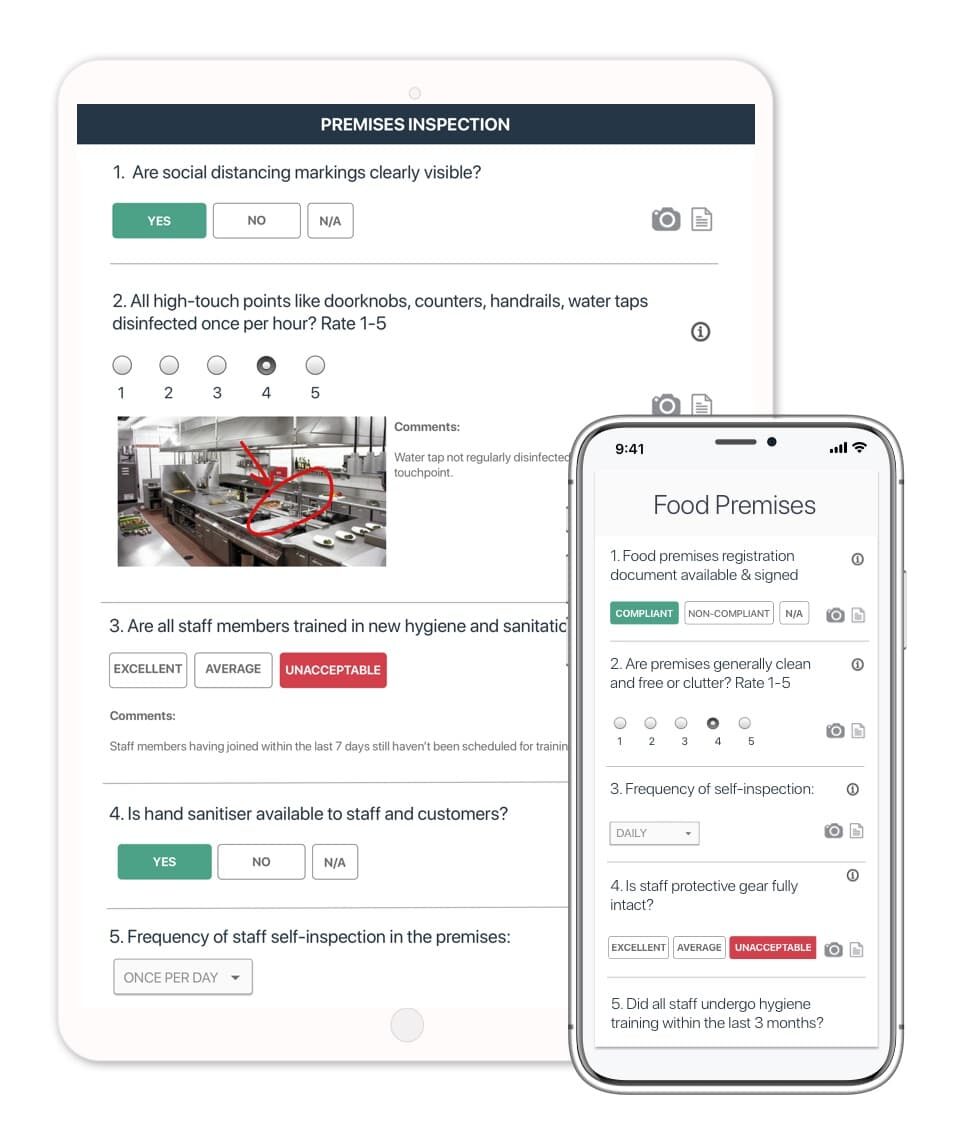
With GoAudits, you get:
- Efficient mobile inspections
- Instant reports and analytics
- Issue and task tracking
- 5x faster inspections
“Spend time where it matters. GoAudits has allowed us to spend 95% of our time where it matters – watching the floor and coaching the team, rather than filling forms and preparing reports. Seeing historical data without digging out and comparing past reports, has helped us spot trends & issues.” – said Jason Hunt – Domino’s
Digital inspections with GoAudits BRC software also increase transparency and accountability. All results, images, and comments are automatically bundled in a digital report. Auditors can provide real-time updates and communicate with the team and management more easily.
This can help to build trust and confidence in the audit process and ensure that all parties have access to the same information.
Free BRC Audit Checklists
👉 Access our library of free and customizable BRC audit checklists.
- BRC Management Commitment Checklist (Clause 1)
- BRC Food Safety Plan HACCP Checklist (Clause 2)
- BRC Food Safety & Quality Management System Checklist (Clause 3)
- BRC Audit Site Standards Checklist (Clause 4)
- BRC Audit Product Control Checklist (Clause 5)
- BRC Audit Process Control Checklist (Clause 6)
- BRC Personnel Checklist (Clause 7)
- BRC Production Risk Zones Checklist (Clause 8)
- BRC Audit Traded Products Checklist (Clause 9)
Additional Food & Safety Inspection Checks
In our checklist template library, you will also find dozens of food safety checklists, some examples include:
- Food Safety & Hygiene Checklist
- Hygiene Standard Checklist
- Food Allergen Checklist
- Hygiene Checklist for Food Industry
- Food Hygiene Audit Checklist
BRC audits are crucial for ensuring food safety and quality in the food industry. With GoAudits, you can streamline your BRCGS audit processes, improve efficiency, and enhance compliance. With GoAudits, you can effectively manage audit schedules, assign tasks, collaborate with team members, and generate detailed reports.


