The food industry’s complex supply chain involves numerous stakeholders, from farms and food manufacturers to retailers and restaurants or hotels. Implementing robust food safety management systems is essential to food businesses, to ensure the safety and quality of their products, as well as to meet all the requirements for food safety compliance. However increasingly, companies large and small find it necessary to achieve a widely recognized international food safety certification, to strengthen their reputation or to access wider markets.
The industry’s many safety certifications and acronyms can seem complex and difficult to interpret. In this article, we will discuss some of the most widely recognized food safety standards and certifications (GMP, HACCP, ISO 22000, BRC, SQFI, FSSC 22000, IFS). We will explain what they are, the differences between them, and how to conduct effective digital audits using a food safety software for easier food safety compliance and successful certification.
Levels of food safety compliance and certifications
To simplify, we can think of the different food safety & quality programs as climbing up the stairs. Each step includes additional requirements to obtain a certification:
At the most basic level, to have permission to operate companies have to ensure compliance with their local food safety laws and regulations. Examples include the FDA Food Code in the US, the SFCR in Canada or the Food Standards Act from the UK’s Food Standards Agency. Food safety regulations typically require having a Food Safety Management System (FSMS), with documentation of a Food Safety Plan following GMP or HACCP principles.
Companies that want to go beyond the basic regulatory requirements can obtain their certification in voluntary food safety programs. This requires getting audited and certified by a third-party. The next level in food safety includes certification to non-benchmarked standards such as GMP, HACCP and ISO. Non-benchmarked essentially means that each certification agency writes and approves their own standard without specific external oversight.
Finally, the highest level of food safety compliance comes with GFSI-recognized certifications. GFSI is an international industry body that aims to harmonize food safety standards by setting stringent norms. It recognizes only a limited number of certification programs and certification bodies. The most widespread programs include BRC, SQF, FSSC 22000 and IFS. Obtaining one of these certifications is often a prerequisite to get access to international markets.
By understanding the nuances between standards, certifications, different organizations and how they interact, you will be able to determine the right type of food safety audit for your business.
No-Benchmark Standards
“Non-benchmark” standards are not accredited or benchmarked by any external body. Each certification agency writes and approves their own standard without external oversight or approval. The brand recognition of the chosen certification body will determine how widely accepted the food safety certification will be.
There are 3 main categories of standards that aren’t benchmarked:
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices)
To ensure the production and preparation of safe food, GMPs lay the foundation in various aspects such as pest control, sanitation and employee hygiene. GMPs can be thought of as a preliminary step to HACCP. Read more: Learn How to Digitize your GMP audit checklists
- HACCP (The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points)
HACCP is a methodology for the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling, to manufacturing, distribution and consumption of the finished product. In addition to the GMP practices, HACCP adds requirements for risk mitigation around products and ingredients, as well as traceability requirements. An HACCP certification recognizes that a food business has developed, documented and implemented systems and procedures in accordance with HACCP.
- ISO 22000 (International Organization for Standardization)
ISO 22000 is a global food safety management system standard that covers the entire food supply chain. It combines the principles of HACCP and ISO 9001 (quality management) to help companies build a robust food safety and quality management system. It is one of the most popular worldwide standards with more than 300,000 certifications to ISO 14001 in 171 countries around the world.
Despite the fact that ISO 22000 and HACCP are highly regarded food safety management systems, GFSI does not explicitly recognize them. Many of the recognized certification programs under GFSI, including FSSC 22000 and BRC, integrate their principles and practices, but benchmarking is a process by which GFSI evaluates and recognizes third-party certification programs rather than specific individual food safety management systems.
GFSI-Recognized Certification Programs
What is GFSI and how does its benchmark work?
GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative) is a collaboration between some of the world’s leading food safety experts from the food industry, international organizations, and other stakeholders to provide a framework for benchmarking food safety standards for the food supply chain.
Founded in 2000 to restore trust after many food safety crises occurred over many years, the GFSI compiled and harmonized existing food safety management requirements to establish a benchmark. GFSI doesn’t conduct food safety audits or certify food businesses. The auditing and food safety certification process is managed by Certification Program Owners (CPOs). In order to be recognised by GFSI, CPOs must verify that they meet the Benchmarking Requirements.
It recognizes and supports a range of food safety certification programs that meet its benchmark criteria. For food industry organizations, this recognition implies “once certified, worldwide recognized.” GFSI-recognized certifications include over a dozen certification schemes offered by COPs:

However, it’s important to note that not all of the standards offered by these CPOs are recognized by GFSI.
GFSI’s most popular food safety certification schemes are:

- The British Retail Consortium (BRC) Standards
BRC Global Standards is a leading quality and food safety certification program for food products developed in 1992 by the British Retail Consortium, a trade association representing the UK retail industry.
The BRC Global Standards has become a widely recognized and respected food safety certification program, with over 30,000 certified sites in more than 130 countries. It is one of the most used standards in food industry and is particularly well established in the UK, Europe and USA/Canada.
A BRC food safety audit is an independent assessment of the food safety management system, processes, and procedures for the organization based on the BRC Global Standards. Read more on BRC standards and how to prepare your BRC certification with internal audits.
- The Safe Quality Food (SQF) program
The Safe Quality Food (SQF) Institute is a leading global provider of food safety and quality assurance certification programs. SQFI offers certification based on their comprehensive SQF Code which includes food safety and quality requirements from farm to fork. The latest SQF Code Edition 9 in effect for audits since May 2021. First developed in Australia in 1994, it gained its popularity in the USA with the major acceptance by Walmart for their supplier registration.

While the auditing process for SQF and BRC differs, one of the main differences between these standards stands in their approach to food safety. SQF is a comprehensive food safety and quality management system that focuses on the entire supply chain, including food production, packaging, storage, and distribution. BRC, on the other hand, is primarily focused on the manufacturing and processing of food products.
In this article on Tips and Best practices to prepare SQF audits, we elaborate on the differences between the two standards and how to prepare for your SQF certification with a food safety software.
- The Food Safety System Certification (FSSC22000)

FSSC is another globally recognized food safety certification scheme that combines ISO 22000 and ISO/TS 22002-1 requirements with additional FSSC requirements. FSSC certification is critical for companies seeking to demonstrate their commitment to food safety management and compliance with international standards.
Read more on FSSC and how to Conduct efficient FSSC 22000 internal inspections with GoAudits.
In terms of scope, FSSC is a generic food safety standard that can be applied to any type of food product, while SQF and BRC are both more specific to certain sectors of the food industry. Also, there are some differences in the way the standards are structured and assessed.
For example, SQF and BRC both use a scoring system to assess compliance, while FSS does not. Additionally, the requirements for certification and recertification may vary between these standards.
- The International Featured Standards (IFS)
IFS is a globally recognized standard for certification of food and non-food products that was founded in 1983. IFS offers robust quality management systems, including HACCP, traceability, and documentation measures. IFS certification is widely accepted by major retailers worldwide, but is especially used in Western Europe including Germany and France.
BRC, SQF, FSSC and IFS are all globally recognized food safety and quality standards. These certifications are all based on international food safety standards and regulations, and they provide a comprehensive approach to ensure food safety and quality.
However there are some differences between them. For example the FSSC and BRC are both widely recognized in the retail industry; IFS is more prevalent in Europe while BRC is more commonly used in the UK. FSSC requirements include additional emphasis on environmental sustainability and social responsibility, while SQF has additional requirements for food defense and fraud prevention.
GFSI’s program is renowned for its comprehensive and rigorous standards, ensuring that all areas and elements of food safety are appropriately addressed. In this regard, aside from its most popular certifications, GFSI’s benchmark also includes specialized certifications covering a wide range of aspects and areas of food safety, for example: the use of Good Agricultural Practices and Seafood (The Global Seafood Alliance), Food Safety for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables (CanadaGAP), Global Red Meat Standard (GRMS), EFI (Equitable Food Initiative), JFSM (Japan Food Safety Management Association), GLOBALG.A.P, PrimusGFS and Freshcare.
It is imperative that any plan takes into account the time, money, and resources required for certification. It is common for certification processes to be lengthy and expensive, but the rewards are well worth the effort. If you wish to succeed in the certification process, you must be proactive and prepare for internal and external audits beforehand.
The right software for your food safety audits
You should carefully evaluate which standard is the most appropriate for your business needs, customer requirements and choose the best food safety software to help you with this process and with your food safety inspections without paperwork and heavy admin workload. Our comprehensive food safety software helps you automate many of the manual tasks involved in the food safety inspections process:
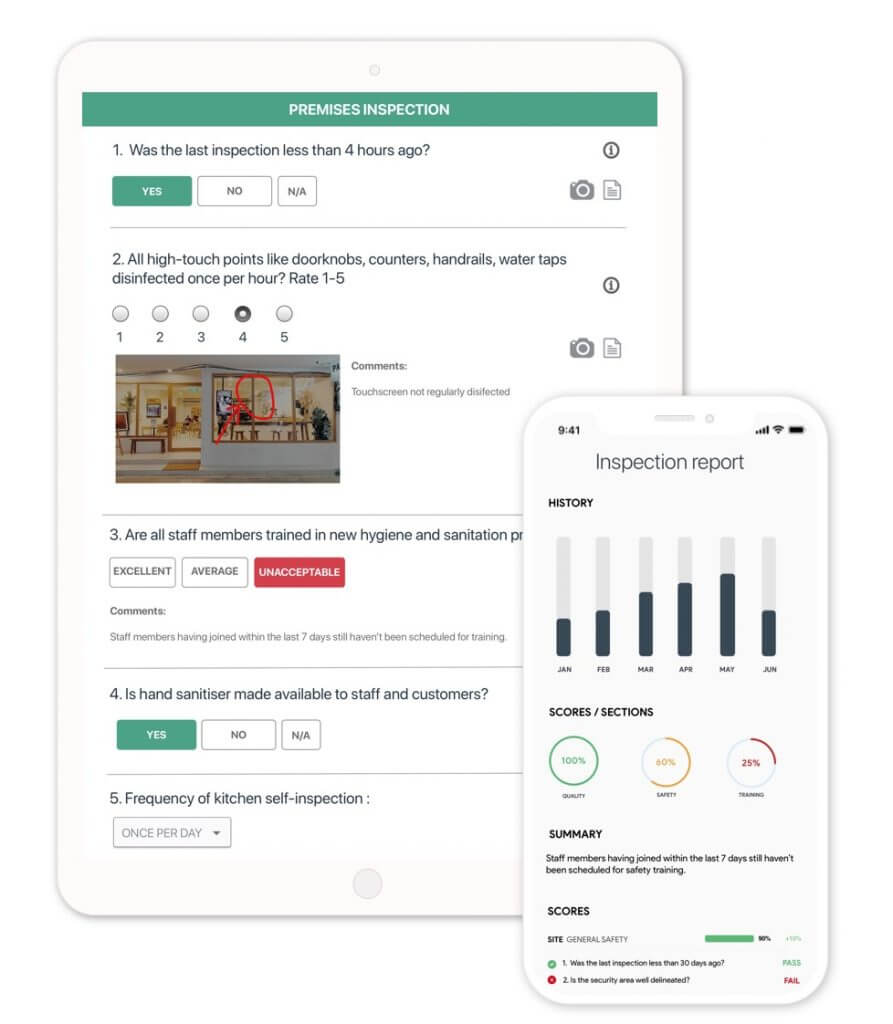
- easier data collection in the field with smart forms
- instant reporting to share audit information quickly, pinpointing every non-conformances or highlighting critical non-conformances
- smart dashboards for real-time analysis
- Corrective actions that can be assigned to specific team members, internally or externally
- vast library of audit checklist templates which can be customised, to get started as quickly as possible.
Both your company and the external auditors will be able to access up-to-date information about the performance of your inspections at any time.
The best part? This whole process can be automated. With a food safety software, you can rest assured that your certification audit will go through without a hitch and that you’ll receive the certificate in no time.
FREE Checklists for Food Safety
BRC – Food Safety Checklists
- Food Safety Hygiene Checklist
- BRC Management Commitment Checklist (Clause 1)
- BRC Food Safety Plan HACCP Checklist (Clause 2)
- BRC Food Safety & Quality Management System Checklist (Clause 3)
- BRC Audit Site Standards Checklist (Clause 4)
- BRC Audi Product Control Checklist (Clause 5)
- BRC Audit Process Control Checklist(Clause 6)
- BRC Personnel Checklist (Clause 7)
- BRC Production Risk Zones Checklist (Clause 8)
- BRC Audit Traded Products Checklist (Clause 9)
SQF – Checklists for food safety
- SQFI Quality Checklist
- SQFI Food Packaging Checklist
- SQFI Food Manufacturing Audit Checklist
- SQFI Storage And Distribution Checklist
- SQFI Primary Plant Production Checklist
- SQFI Primary Animal Production Checklist
- SQFI Aquaculture Checklist
- SQFI Pet Food Manufacturing Checklist
- SQFI Animal Product Manufacturing Checklist
- SQFI Manufacturing of Food Packaging Checklist
- Find more Food Safety Checklists in our checklist library
Discover more about the GoAudits food safety inspection app.



