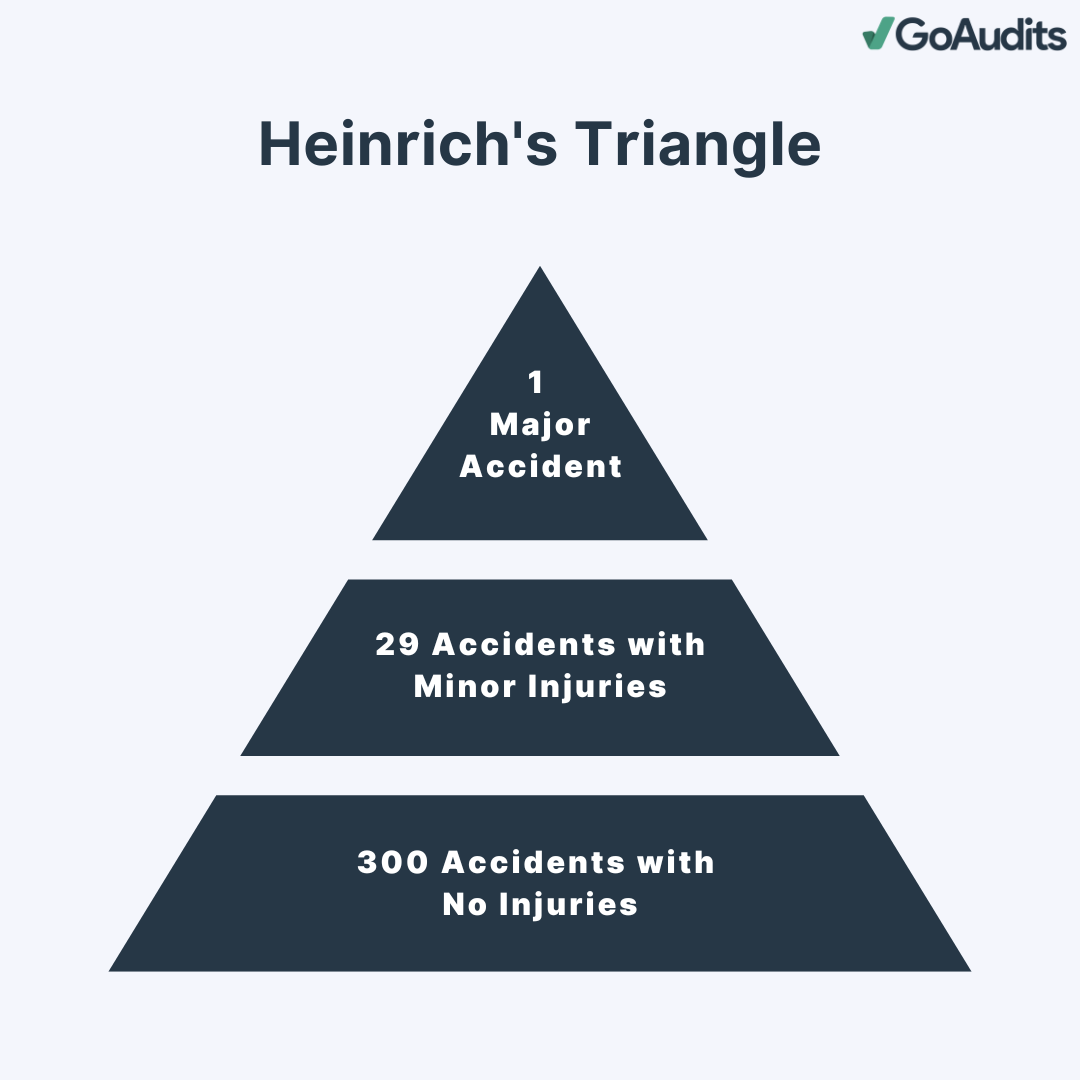
Near miss incident reporting is essential to ensure workplace safety. In that regard, Heinrich’s Triangle (also known as Heinrich’s Pyramid) is a foundational concept in workplace health and safety. Introduced by Herbert William Heinrich in 1931, this theory establishes a link between minor and major accidents: for every major injury accident, there are 29 minor injury accidents and 300 no-injury accidents. Focusing on and reducing the number of minor accidents can significantly decrease the occurrence of major accidents. Though this approach is simple and straightforward, a majority of near miss incidents go unreported even when a worker has sustained an injury in the workplace.
Today, we explore how this proactive approach to reporting and addressing minor incidents will prevent major accidents in the future.
- What is Near Miss Incident Reporting?
- Why is Near Miss Incident Reporting Important?
- Near Miss Incident Examples in the Workplace
- What is the Near Miss Reporting Procedure?
- How to Improve Near Miss Incident Reporting for Your Employees?
- Report Near-Miss Incidents & Accidents in Real-Time with GoAudits
- FREE & Customizable Health & Safety Checklists
- Near Miss Programs: An Overview
What is Near Miss Incident Reporting?
Near miss incident reporting is a proactive safety management practice. It involves identifying, documenting, and analyzing incidents that could have resulted in injury, damage, or loss but were narrowly avoided. These incidents, often referred to as ‘close calls,’ provide valuable insights into potential hazards and risks within an organization. Effectively reporting and addressing near misses can prevent future accidents, enhance workplace safety, and improve operational efficiency.
The concept of near miss incident reporting revolves around the principle that every near miss represents an opportunity for improvement. Identifying and recording these near miss incidents helps you fix problems before they result in a genuine accident. It involves a systematic process where employees report these incidents as soon as they occur, even if no harm is done.
👉 How does OSHA define and handle near-miss incidents?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) defines a near-miss incident as an unplanned event that did not result in injury, illness, or damage but had the potential to do so. These incidents reveal underlying safety issues that, if not addressed, could lead to more severe accidents in the future.
OSHA encourages reporting and investigating near-misses to identify and rectify unsafe conditions or behaviors. Addressing the root causes of near-misses through thorough investigations and corrective actions is essential for creating a safer work environment.
What are Near-Miss Incidents?
Near miss incidents are often brushed off since no immediate harm was observed or injury was narrowly avoided. However, these incidents highlight potential hazards that could lead to severe consequences if not addressed. They are also indicative of underlying organizational safety issues that need addressing.
👉 What is the difference between near misses, incidents, and accidents in a workplace?
Near misses, incidents, and accidents differ primarily in their outcomes. A near miss is an event where no injury or damage occurs, but it has the potential to do so. An incident is a broader term that includes any unplanned event that could lead to an accident, injury, or damage, but it may or may not result in harm. An accident, on the other hand, is an event that results in injury, illness, or property damage.
Near miss incidents often stem from various causes, such as human error, equipment failure, or environmental factors. Human error can include mistakes due to fatigue, lack of training, or inattention. Equipment failure might involve malfunctioning tools or outdated machinery. Environmental factors could be slippery floors, poor lighting, or obstructions in walkways.
Key Components of Near Miss Incident Reporting
To effectively manage near miss incidents, it’s essential to understand the key components of the reporting process:
- Identify: Recognition of a near miss event is the most crucial aspect. Employees should be able to recognize and differentiate between a routine task and a potential hazard that narrowly avoided becoming an incident.
- Report: Once identified, the near miss incident must be immediately reported. Creating an easy and accessible reporting system encourages prompt reporting. Reports should be detailed, noting the time, location, and circumstances of the near miss, along with any potential causes.
- Investigate: Investigating the near miss is crucial to understand not just what happened, but why it happened. This involves analyzing the event to identify the root cause and any contributing factors.
- Intervene: Based on the findings of the investigation, appropriate interventions should be implemented. This could range from modifying existing safety protocols, introducing new training programs, or updating equipment.
- Review: It involves reviewing the effectiveness of the intervention and the near miss reporting process itself. This should be an ongoing process with adjustments made as necessary to improve both safety outcomes and the reporting process itself.
Let’s look at some examples of near misses in workplaces.
Why is Near Miss Incident Reporting Important?
Let’s look at some reasons why near miss event reporting is important.
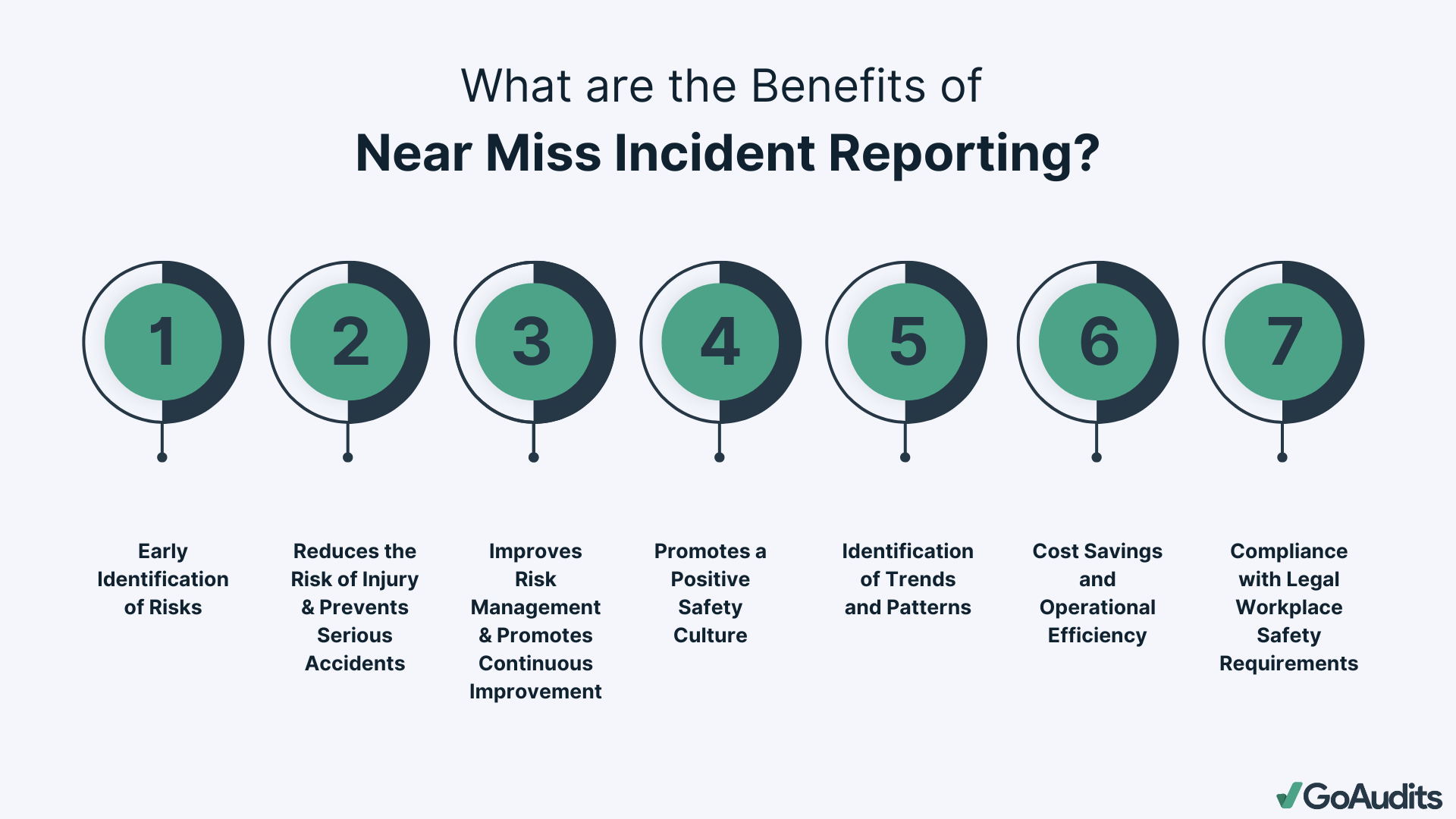
- Early Identification of Risks
Near miss incident reporting is crucial for the early identification of risks and the implementation of preventive measures. By documenting near misses, you capture incidents that had the potential to cause harm but didn’t, allowing you to recognize hazards before they lead to serious accidents and safeguarding your employees and work environment.
- Reduces the Risk of Injury and Prevents Serious Accidents
Consistently reporting near misses helps you reduce injuries, take corrective actions, and prevent serious accidents. It helps mitigate the chances of future incidents, making your workplace safer for everyone.
- Improves Risk Management and Provides Data for Continuous Improvement
Effective risk management relies on accurate data. Near miss reporting offers valuable information for internal assessments and continuous improvement. By analyzing these reports, you can identify patterns and trends, understand the root causes of potential accidents, and develop targeted strategies to mitigate risks.
- Promotes a Positive Safety Culture
Encouraging near miss reporting promotes a positive safety culture within your organization. When employees feel comfortable reporting near misses without fear of blame, it fosters an environment where safety is a shared responsibility.
- Identification of Trends and Patterns
Near miss reports are invaluable for identifying trends and patterns in workplace safety. Systematically analyzing these reports helps you detect recurring issues and address them proactively.
- Operational Cost Savings
Implementing a near miss incident reporting system can prevent accidents before they happen, reducing costs associated with injuries, legal liabilities, and lost productivity. Additionally, addressing safety issues early minimizes equipment damage and maintenance expenses.
- Compliance with Legal Workplace Safety Requirements
Near miss incident reporting also helps you comply with legal and regulatory workplace safety requirements. Many regulations mandate the reporting and analysis of near misses to ensure a safe working environment.
Near Miss Incident Examples in the Workplace
Here are some common examples of near miss incidents that can occur across various work environments:
| Slips and Trips | Slips and trips are frequent near miss incidents in many workplaces. | For instance, an employee might slip on a wet floor that hasn’t been marked with a warning sign, catching themselves just in time to avoid a fall. Similarly, tripping over an improperly stored item, such as a loose carpet edge or cable, can be a near miss if no injury occurs. |
| Equipment Malfunctions | Near misses often involve equipment malfunctions. A worker might narrowly escape injury when a piece of machinery suddenly breaks down or malfunctions. | For example, a forklift operator could lose control due to a mechanical failure, nearly hitting a coworker or causing property damage. |
| Falling Objects | In warehouses or construction sites, falling objects pose significant risks. | Imagine a heavy box falling from a high shelf and landing close to a worker, or tools being accidentally dropped from a height. |
| Electrical Hazards | Electrical hazards are another common example of near misses. | For instance, an employee finds a damaged electrical cord lying in a pool of water, which could lead to electrocution if not noticed in time. |
| Chemical Spills | In environments where chemicals are used, such as laboratories or manufacturing plants, near miss incidents can occur if containers are not properly sealed or stored. | For example, a chemical spill might be narrowly avoided when a container is found leaking but is promptly secured. |
| Signage and Communication Failures | Lack of proper signage and communication can lead to near misses. | For instance, workers might nearly collide in a warehouse due to missing signs, or an area under construction might not be marked, leading to workers unknowingly entering a hazardous zone. |
| Risky Behavior | Unsafe behavior is often a cause of near miss incidents. | Examples include employees operating machinery without proper training, handling hazardous materials without personal protective equipment (PPE), or engaging in risky behavior that nearly results in an accident. |
What is the Near Miss Reporting Procedure?
Let’s explore the near miss incident reporting procedure:
- Identify Hazards & Where the Near Miss Incidents Occurred
Since near miss incidents are early warnings of potential accidents, you should start by identifying unsafe conditions and behaviors in your workplace. Encourage employees to report any near misses, no matter how minor they may seem.
Precisely locate where the near miss occurred. Understanding the environment helps in identifying specific hazards associated with that area. Detailed location information aids in implementing targeted corrective measures and preventing similar incidents in the future.
- Include All Employees When Performing the Risk Assessment
Conduct a thorough risk assessment immediately after a near miss is reported. Evaluate the severity and likelihood of potential risks. It helps prioritize actions to address the most critical safety concerns, ensuring resources are effectively allocated to mitigate these risks.
Involve all employees who witnessed or were part of the near miss incident in the reporting process. Their insights are invaluable in understanding the circumstances leading to the near miss. Engaging employees fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for workplace safety.
- Determine and Analyze the Root Cause
Identify the root cause of the near miss through a detailed analysis. Look beyond immediate causes to uncover underlying issues. The 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram are the most common ways of understanding the root cause of any problem for implementing effective preventive measures.
👉 Did You Know?
The 5 Whys
The 5 Whys technique is a straightforward yet effective method for identifying the root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking the question ‘Why?’ The process typically involves asking ‘Why?’ five times, but it can vary depending on the complexity of the issue.
Fishbone Diagram
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a visual tool used to systematically identify and present potential causes of a problem. Shaped like a fishbone, this diagram helps organize thoughts and facilitate a thorough exploration of potential root causes. To create a Fishbone Diagram, identify the problem, determine major categories, brainstorm possible causes, and finally, analyze the diagram.
- Inform the Management
Keep management informed about the incident and the findings from the initial assessment. Transparent communication ensures that necessary resources and support are available to address identified risks.
- Implement Corrective Actions
Develop and implement corrective actions based on the findings from your risk assessment and root cause analysis. These actions should address both immediate and long-term safety concerns.
- Document Findings & Implement Risk Minimizing Strategies
Document all findings from the near miss incident, including identified hazards, risk assessments, root cause analyses, and implemented corrective actions. It helps track and monitor trends, provide a reference for future safety improvements, and comply with safety regulations.
Develop and implement strategies to minimize risks proactively. This might include revising safety protocols, enhancing employee training programs, or upgrading equipment.
- Regularly Review & Monitor the Process
Continuously review and monitor your near miss incident reporting procedure. Regular workplace inspections can help identify gaps or areas for improvement.
How to Improve Near Miss Incident Reporting for Your Employees?
Here’s how you can encourage your employees to report near miss incidents.

- Define a Clear Reporting Process
Creating a clear, straightforward process for reporting near misses is the foundation of an effective incident reporting system. Begin by defining what constitutes a near miss and provide examples to clarify this for all employees. Develop a step-by-step guide that outlines how and when to report these incidents, ensuring the process is easily accessible and understood by everyone. Visual aids, such as flowcharts, can help simplify the process further.
- Train Your Employees to Recognize Incidents
Training is essential to help employees understand what constitutes a near miss and how to report it. Conduct regular training sessions using real-life scenarios and role-playing exercises to make the learning experience practical and engaging. Provide refresher courses to keep the information fresh and address any new challenges or updates in the reporting process.
- Encourage Your Employees to Report All Incidents
A culture that values safety and transparency encourages more consistent near miss reporting. Emphasize the importance of reporting in safety meetings and training sessions. Highlight how reporting can prevent future accidents and improve overall workplace safety. Recognizing and rewarding employees who report near misses can also motivate others to participate.
👉 How many near miss incidents should be reported?
There isn’t a set number of near miss incidents that should be reported, but the goal is to report every near miss. Reporting all near misses allows you to identify patterns, address potential hazards before they lead to more serious incidents, and improve safety protocols.
- Make it Easy to Report Incidents Anytime
Simplifying the reporting process increases the likelihood of employees reporting near misses. Provide multiple channels for reporting, such as mobile apps, online forms, and paper forms, to accommodate different preferences. Ensure these channels are user-friendly and available at all times. The process should be quick and straightforward, ideally taking less than a minute to complete.
- Use a Near Miss Incident Reporting Software
Implement a near miss incident reporting software to streamline the process and make it more efficient. They can automate workflows, provide real-time data, and generate insightful reports. Features like mobile access, user-friendly interfaces, and customizable templates can tailor the software to your organization’s needs. Analyzing the data collected helps you achieve complete transparency, implement learning, and prevent future incidents.
Report Near-Miss Incidents & Accidents in Real-Time with GoAudits
Safety is paramount. GoAudits safety inspection software enables you to report near-miss incidents and accidents in real-time.
Here’s how GoAudits helps you streamline the process and maximize safety within your organization:
- Report incidents instantly from anywhere, anytime, using the user-friendly GoAudits mobile app. No need to wait until you’re back at your desk.
- You can report incidents and capture crucial details even without an internet connection. GoAudits automatically syncs all the data once you’re back online.
- Create tailored checklists specific to your industry and needs, ensuring you capture all relevant information about the near-miss or accident.
- GoAudits’ analytics tools allow you to analyze historical data, identify recurring issues, and proactively address potential hazards before they escalate.
- Assign corrective actions directly within the app, ensuring prompt resolution of identified issues and preventing future incidents.
- Generate comprehensive reports automatically, including photos, timestamps, and geolocation data, providing a clear record of the incident.
- Gain real-time insights into your safety performance with GoAudits’ interactive dashboards, enabling you to monitor trends and take immediate action.
FREE & Customizable Health & Safety Checklists
Explore our extensive library of free audit checklists for health and safety:
- Near Miss Incident Report
- Office Hazards Checklist
- HSE COSHH Assessment Template
- Chemical Risk Assessment Template
- Accident Investigation Checklist
- Manual Handling Risk Assessment Checklist
- Office Safety Inspection Checklist
- JSA Form – Job Safety Analysis Checklist
- EHS Audit checklist
- Hazardous Material Inspection Checklist
- Equipment Inspection Form
- Fire Prevention Inspection Checklist
- Ergonomic Risk Assessment Template
- Worksite Incident Report Checklist
- Chemical Safety Checklist – COSHH
Near Miss Programs: An Overview
A near miss program is a structured initiative within organizations aimed at identifying, reporting, and analyzing near-miss incidents—events that could have led to injury, illness, or damage but did not, either by chance or timely intervention. The primary purpose of such programs is to proactively address potential hazards, prevent future accidents, and enhance the overall safety culture.
👉 What is the difference between a near-miss program and near-miss reporting?
Near-miss reporting is a critical component of a near miss program. It involves the process by which employees or stakeholders document and communicate near-miss incidents. This reporting serves as the foundation for analysis and subsequent safety improvements. While near-miss reporting focuses on the documentation aspect, a near miss program encompasses the entire lifecycle—from identification and reporting to analysis, corrective action implementation, and monitoring.
Key Components & Steps to Implement Near Miss Safety Programs
The following key components and steps are crucial for establishing an effective near miss safety program:
- Define Near Misses Clearly
A near miss is an unplanned event that did not result in injury, illness, or damage but had the potential to do so. Clearly defining what constitutes a near miss ensures that all employees have a uniform understanding, which is vital for consistent reporting and analysis.
- Establish a Reporting System
Develop a straightforward and accessible reporting system that allows employees to report near misses easily. This system can be digital or paper-based, depending on the organization’s resources, and should ensure confidentiality to encourage participation.
- Educate and Train Employees
Conduct comprehensive training sessions to educate employees about the importance of near miss reporting, how to identify potential hazards, and the procedures for reporting. Regular training reinforces the significance of the program and keeps safety at the forefront of daily operations.
👉 What are some reasons near miss incidents go unreported?
Several factors contribute to near miss incidents going unreported. Employees might fear blame or disciplinary action. There could be a lack of awareness about the importance of reporting near misses. Sometimes, the reporting process is cumbersome or time-consuming, discouraging employees from reporting. Additionally, a workplace culture that doesn’t prioritize safety can lead to underreporting.
- Investigate and Act on Reports
Upon receiving a near miss report, conduct a thorough investigation to identify root causes and contributing factors. Implement corrective actions to address identified hazards, thereby preventing potential accidents.
- Analyze Data and Provide Feedback
Regularly analyze collected data to identify trends and common hazards. Share findings with the workforce to keep them informed and engaged. Providing feedback demonstrates that reports are taken seriously and lead to tangible improvements.
Best Practices for Sustaining a Near Miss Program
To ensure the program’s effectiveness and longevity, consider the following best practices:
- Foster Open Communication and Leadership Involvement
Cultivate a safety culture where employees feel comfortable reporting near misses without fear of blame or repercussions. Leadership should actively participate, demonstrating commitment to safety and encouraging transparent communication.
- Implement User-Friendly Reporting Tools and Multiple Channels
Simplify the reporting process by providing intuitive tools accessible to all employees. Offer various reporting channels—such as digital tools or forms—to accommodate different preferences and ensure inclusivity.
- Investigate Reports Thoroughly and Implement Corrective Actions
Once you have investigated reports, implement appropriate corrective actions to prevent recurrence, demonstrating to employees that their reports lead to tangible safety improvements. Root cause analysis helps in understanding the defect in the system that resulted in the error.
- Establish a Feedback Loop
Provide timely feedback to employees who report near misses, informing them of investigation outcomes and corrective measures taken. This reinforces the value of reporting and encourages ongoing participation.
- Monitor and Evaluate Reporting Effectiveness
Regularly assess the Near Miss Program’s performance by tracking reporting rates, response times, and the implementation of corrective actions. Use this data to make informed adjustments, ensuring continuous improvement and sustained effectiveness.




