International Featured Standards (IFS) Food, particularly its latest version 8, is a globally recognized certification standard aimed at ensuring food safety and quality throughout the supply chain. IFS Food Version 8, which became mandatory for audits from January 2024, introduces updated requirements to further enhance the safety and integrity of food products. It focuses on areas such as food safety culture, risk management, and continuous improvement. The standard also emphasizes the importance of a proactive approach to food safety, encouraging food manufacturers, processors, retailers, wholesalers, distributors, etc., to integrate food safety practices into their corporate culture.
Let’s find out how IFS audits ensure compliance with these standards and help businesses involved in food processing enhance their credibility in the global marketplace.
What is an IFS Audit?
An IFS food audit is a comprehensive assessment conducted to ensure that food production businesses adhere to the IFS Food Standard, recognized globally and benchmarked by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). An IFS food audit helps evaluate how well a company manages its processes to guarantee the safety, quality, and legality of its food products.
IFS audits assess various aspects of food production, including quality management, food safety management systems, resource management, and overall production processes. It also looks into hygiene practices, manufacturing facility design, and the company’s approach to continuous improvement in food manufacturing processes. The objective of IFS audits is to ensure compliance with IFS food safety standards.
Who Conducts IFS Audits?
IFS audits are carried out by accredited certification bodies authorized by IFS to ensure that audits are impartial and follow consistent, global standards. These certification bodies employ experienced auditors who specialize in food safety management systems. They conduct thorough assessments of manufacturing facilities and processes to evaluate compliance with IFS food standards. Companies can search for a certification body directly through the IFS database to find one.
👉 What is the IFS food audit duration?
The duration of an IFS food audit can vary depending on the size and complexity of the food production facility. Typically, the minimum duration for an IFS Food audit is around two days. During the IFS audit, a significant portion of the time is dedicated to field inspections, where auditors examine the physical processes, hygiene practices, and operational procedures in place. After the IFS audit, it usually takes another half day to compile the report. The final report is typically received within two weeks of the IFS audit.
Types of IFS Food Audits
Here’s an overview of the key types of IFS Food audits:
- Initial Audit
This is the first comprehensive IFS audit conducted to assess a company’s adherence to the IFS Food standards. It is essential for companies seeking IFS certification for the first time. It covers all relevant aspects of the production process, including food safety management systems, quality control measures, and compliance with regulatory requirements. A successful initial audit results in the company receiving its IFS certification.
- Recertification Audit
This IFS audit occurs periodically, typically annually, to ensure that the certified company continues to meet the IFS Food standards. The recertification audit is similar in scope to the initial audit but focuses on verifying the maintenance and improvement of the food safety management system. The recertification process is essential for maintaining the IFS certification and identifying any areas for improvement.
- Follow-up Audit
If non-conformities are identified during the initial or recertification audits, a follow-up audit may be required. This IFS food audit specifically addresses the corrective actions taken by the company to rectify the identified issues. The focus is on ensuring that all non-conformities have been effectively resolved and that the company now fully complies with the IFS standards.
- Extension Audit
Occasionally, a certified company may expand its operations or introduce new products or processes. In such cases, an extension audit is necessary to assess these changes and ensure they meet the IFS Food standards. This IFS food audit focuses on the specific areas affected by the expansion and evaluates whether the existing certification can be extended to cover the new scope.
👉 Are IFS Food audits announced in advance?
IFS Food audits can be conducted in two formats: announced and unannounced.
Announced audits mean the company is informed in advance about the audit date. This allows them to prepare and ensure that all documentation and processes are in order. Announced IFS audits are the standard approach and are often preferred by companies as they allow for thorough preparation.
Unannounced audits occur without prior notice to evaluate the company’s compliance with IFS standards under normal operating conditions. It provides a more realistic assessment of a company’s everyday practices. Unannounced audits ensure that food safety and quality protocols are consistently followed, not just during a scheduled inspection.
How to Prepare for an IFS Food Audit
Here’s how you can ensure your organization is fully prepared for the IFS food audit:
- Understand the IFS Food Standard Requirements
Start by thoroughly understanding the IFS food standard. This involves the latest version of the standard and familiarizing yourself with its detailed requirements. Pay special attention to the core areas like food safety management, product quality, and compliance procedures. Ensure you understand what is expected for each criterion to align your processes accordingly.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
A gap analysis is essential to identify discrepancies between your current practices and the IFS requirements. It allows you to document areas needing improvement. Evaluate all aspects of your food safety and quality management systems to ensure they meet the standard.
- Develop and Implement Action Plans
Based on the gaps identified, develop a detailed action plan. Prioritize tasks based on their impact on compliance and set clear deadlines for each action. Assign responsibilities to team members, ensuring everyone knows their role in implementing necessary changes.
- Train Your Team
All employees should be well-versed in the updated procedures and their specific roles in maintaining compliance to prepare for an IFS audit. Regular training sessions and refreshers ensure that everyone is aligned with the new standards, fostering a culture of food safety.
- Review and Update Documentation
Review all your food standard operating procedures (SOPs), policies, and records to ensure they reflect the latest IFS standards. Updated documentation should be thorough, easily accessible, and consistently maintained to demonstrate compliance during the IFS audit.
- Internal Audits and Mock Audits
Conduct regular internal audits to assess your readiness. These audits simulate the official audit environment and help identify any lingering issues. Mock audits, in particular, provide a practical rehearsal, helping staff prepare for the actual audit day. Use the findings from these internal audits to refine your systems and processes further.
👉 Use this IFS Audit Checklist – Food Standard V8 to conduct internal audits and ensure compliance with the IFS Food Version 8 requirements.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions
Address any non-conformities identified during internal audits with robust corrective and preventive actions. These actions should be timely and well-documented, ensuring that similar issues do not recur. Demonstrating a proactive approach to problem-solving is vital for a successful audit outcome. An audit checklist app can help you stay organized and demonstrate this proactive approach during the official audit.
- Ensure Facility Readiness
Your facility should be audit-ready at all times. This means maintaining cleanliness, organization, and adherence to safety protocols. Ensure that all areas of your facility comply with IFS standards, from production to storage. Regular facility checks can help maintain a high level of readiness.
- Engage with the Auditor
Engage with auditors before the IFS audit to understand their expectations and any specific focus areas. On the audit day, ensure that all relevant personnel are available, and be prepared for interviews.
Preparing for IFS food audits can be challenging. However, a digital auditing tool like GoAudits can help streamline the process significantly.
Streamline Internal IFS Food Audits with an Auditing App & Software
GoAudits food safety software is an all-in-one platform for comprehensive inspections, audits, and compliance.
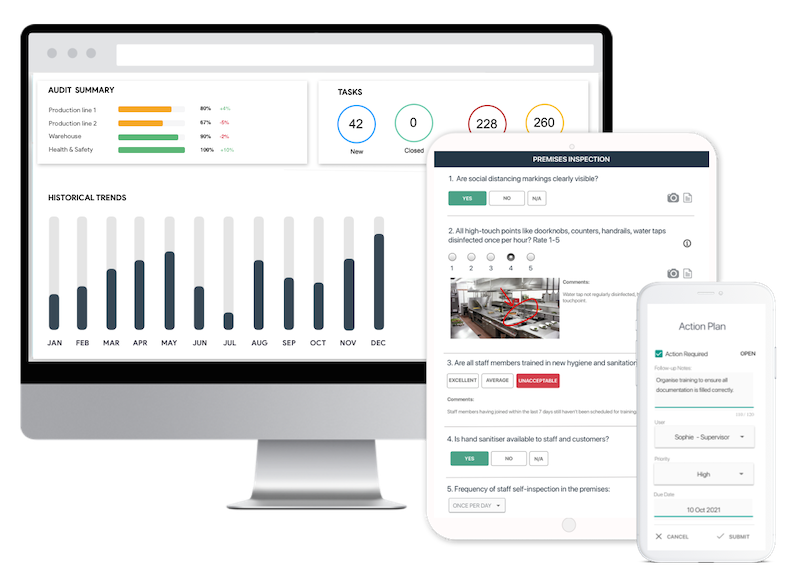
Here’s how you can use GoAudits to streamline internal IFS food audits.
- Conduct audits up to 5 times faster on your preferred device, even offline. Capture photos, annotations, and e-signatures for detailed documentation.
- Generate detailed reports automatically after each audit, pre-populated with attached photos, assigned actions, time stamps, and geo-location.
- Review and automatically share reports with relevant stakeholders for review.
- Assign corrective actions, set deadlines, and track progress to ensure timely resolution of non-conformances. Demonstrate evidence of this proactive improvement loop to external auditors.
- Gain real-time insights into your performance, monitor audit progress, identify trends, and track performance with interactive, smart dashboards.
- Access pre-built IFS audit checklists or create your own customized templates.
Free & Customizable Food Safety Checklists
GoAudits offers the following food safety checklists. You can sign up for free and start using these checklists to conduct inspections effectively and ensure compliance with food safety standards.
- Food Safety & Hygiene Checklist
- ISO 22000 Food Safety Checklist (FSMS)
- ISO 9001:2015 Supplier Audit Checklist – Manufacturing
- Plan for HACCP
- Food Manufacturing Hygiene Audit
- Food Manufacturing SOP
- Hygiene Checklist for Food Industry
- Food Hygiene Inspection Checklist
- Food Facility Self-Inspection Checklist
- Food Safety Self-Inspection Checklist
- Food Safety Inspection Checklist
What Happens After the IFS Audit?
Here’s what happens once the IFS food audit is complete.
Action Plan
Once the audit concludes, you will receive a preliminary action plan from your auditor, usually within a few days. It outlines any deviations or non-conformities identified during the IFS food audit. You are required to develop and implement corrective actions to address these issues. Corrections should be prompt, focusing on immediate fixes, while corrective actions aim to resolve the root causes for long-term compliance. The completed action plan must be submitted to the certification body within four weeks, including evidence of these corrections. If you miss this deadline, a full re-audit may be necessary, potentially delaying your certification.
Issuing the IFS Certificate and Certification Cycle
Once your action plan is approved and all non-conformities are resolved, the certification body will issue the IFS certificate, which is valid for one year. Your organization must undergo a re-certification audit typically halfway through the certification cycle to maintain it. The certification cycle operates continuously, requiring an annual re-audit to renew the certification.
Distribution and Storage of the Audit Report
The final audit report, which includes details on the findings and the corrective actions taken, is distributed to relevant stakeholders within your organization and possibly shared with clients, depending on your agreements. The report must be securely stored not only to maintain transparency but also to facilitate future audits. This ensures that all corrective actions are properly documented and accessible for reference.
IFS Scoring System
The IFS Scoring System provides a clear, structured way for companies to understand their level of compliance and identify areas for improvement.
The IFS scoring system uses a grading scale that includes different levels of compliance:
- A (Full compliance): No deviations from the standard.
- B (Point of attention): A minor issue that is not yet a deviation but could become one.
- C (Deviations): Significant non-compliance with certain requirements.
- D (Major deviations): Non-compliance that requires immediate corrective action.
- Knock-Out (KO) Requirements: Failure in any of the 10 critical criteria results in automatic non-certification.
The audit grades are based on the percentage score achieved:
- Higher Level: A score above 95%, indicating a high level of compliance.
- Foundation Level: A score between 75% and 95%, meaning that the company meets the basic requirements but has some room for improvement.
- No Certification: A score below 75% or failure in any KO requirement means no certification is granted.
The IFS scoring system directly influences the grades assigned in an audit. Each score corresponds to a level of compliance that contributes to the overall percentage. A company’s final score (as a percentage) will determine whether they receive a Foundation or Higher level certification, or no certification at all.
👉 While the scoring system evaluates individual areas of compliance, the grades represent the overall outcome of the audit based on these scores.
IFS Food Certification Process
The IFS Food Certification process includes several key steps:
- Preparation
Before the audit, companies should conduct a thorough internal review to ensure that all processes, documentation, and practices meet the IFS requirements. It involves gap analysis, staff training, and updating all relevant documents.
- The Initial Audit
Conducted by an accredited third-party auditor, it involves a detailed evaluation of the company’s compliance with the IFS standards. They review processes, inspect facilities, and evaluate records.
- Scoring and Reporting
Next, the auditor assigns scores based on the findings. Non-conformities are documented, and a detailed report is provided to the company. The report includes an action plan for addressing any issues identified during the audit.
- Corrective Actions
If non-conformities are found, the company must implement corrective actions within a specified timeframe. Minor non-conformities may only require documentation of corrective measures, while major non-conformities might necessitate a re-audit.
- Certification Decision
Once the corrective actions are verified, the certification body reviews the audit report and determines whether to grant certification. If granted, the certification is valid for one year, after which the company must undergo a re-certification audit to maintain certification.
- Re-certification
The re-certification process is similar to the initial audit and ensures that the company continues to meet the IFS standards.
FAQs
What is the difference between IFS and BRC food standards?
IFS and the British Retail Consortium (BRC) are both food safety standards recognized by the GFSI, but they have different scopes and focuses. IFS is designed to ensure transparency and safety across the entire supply chain, particularly for private labels and food manufacturers. It places significant emphasis on process-oriented quality and food safety management systems. BRC, on the other hand, is more prescriptive, with detailed requirements for process controls and product specifications. It’s particularly stringent on food safety practices, legal compliance, and quality management.
Is IFS a GFSI audit?
Yes, IFS is a GFSI-recognized food safety standard. The GFSI benchmarks various food safety standards to ensure they meet the global requirements for food safety.
Share this article


