In the food industry, there’s no room for guesswork. Whether you’re managing a restaurant, running a food production facility, or catering for an event, every step in the process must meet high standards. Food standard operating procedures (SOPs) are the foundation of safe and consistent food practices. They provide clear instructions for everything from handling raw ingredients to maintaining equipment. By following these food SOPs, you can ensure food quality, keep your business compliant with regulations, and protect your customers.
Let’s dive into the nitty gritty of standard operating procedures that every food business should implement.
- Food Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): An Overview
- How to Develop and Implement SOPs in the Food Industry?
- Food Safety SOP Templates & Inspection Checklists
- Use a Food Safety & Inspection App to Digitize Your Food SOPs
- Types of SOPs in the Food Industry
- Benefits of Implementing Food Safety SOPs
- Challenges Facing the Food Establishments in Following SOPs
Food Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): An Overview
Food standard operating procedures (SOPs) are detailed, step-by-step instructions outlining how specific tasks should be performed in food-related operations. They ensure consistency, safety, and quality in food handling, preparation, and service. SOPs cover various aspects, including hygiene, equipment maintenance, and compliance with food safety standards, making them a cornerstone of any food safety management system.
Food SOPs are essential for any entity involved in food production, preparation, or service, including:
- Restaurants: From food preparation to waste management, SOPs guide restaurant staff in maintaining cleanliness and safety.
- Food Manufacturers: Food SOPs help ensure safe production practices, covering equipment sanitization, raw material handling, and packaging.
- Catering Services: For event caterers, SOPs streamline logistics and food safety practices in dynamic environments.
- Schools, Hospitals, and Care Facilities: These institutions use food SOPs to manage large-scale food preparation and ensure compliance with health standards.
How to Develop and Implement SOPs in the Food Industry?
Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating and executing effective food SOPs:
1. Define the Scope and Purpose
Begin by clearly identifying the objective and applicability of each SOP. Specify the intended outcomes, such as ensuring proper sanitation, receiving fresh produce, or handling allergens. Outline the scope by detailing the tasks, departments, or locations the SOP applies to.
2. Assemble an SOP Team
Bring together a team of experts, including food safety professionals, managers, and operational staff, to develop the food safety SOPs.
3. Conduct a Thorough Assessment
Analyze current food handling and operational practices to identify gaps or areas that require standardization. Focus on critical areas like receiving, storing, preparing, cooking, cleaning, and sanitation to ensure all aspects of food safety are covered.
4. Provide Step-by-Step Instructions
Create detailed, easy-to-follow instructions for every procedure. Use clear and concise language, supplemented with visuals like diagrams or flowcharts to enhance understanding, especially for complex tasks. Be sure to list all necessary resources, such as equipment, materials, and personnel, to ensure consistency in execution.
5. Identify Hazards and Implement Control Measures
Incorporate hazard identification and control into your food safety SOPs to align with HACCP principles. Address potential risks such as cross-contamination, improper storage temperatures, or insufficient cleaning practices. Define control measures like maintaining specific temperature ranges, using personal protective equipment, or enforcing hygiene protocols to mitigate these risks.
6. Train and Educate Employees
Effective implementation requires employee buy-in and understanding. Provide thorough training to ensure that employees know their responsibilities, the importance of compliance, and how to execute the procedures correctly.
7. Monitor and Verify Compliance
Establish systems for monitoring and verifying compliance with SOPs in the food industry. This may include scheduled audits, observational checks, or employee self-reporting. Verification methods such as temperature logs, product testing, and data analysis help assess the effectiveness of control measures.
8. Review and Update Regularly
Schedule regular reviews to ensure SOPs remain relevant, effective, and compliant with changing regulations, industry practices, or new technology. Make necessary updates and communicate changes promptly to all staff.
Food Safety SOP Templates & Inspection Checklists
Checklists are a fundamental tool for implementing and maintaining standard operating procedures in the food industry.
GoAudits offers a range of food inspection checklists to ensure quality and safety compliance. Here are some food safety SOP templates to get you started:
- HACCP-Based SOPs
- Food Manufacturing SOP
- Kitchen SOP Checklist
- SQFI Quality Checklist
- ISO 22000 Food Safety Checklist (FSMS)
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Checklist
- Canteen Hygiene Inspection
- Bar Service SOP
- Food Safety & Hygiene Checklist
- Restaurant Safety Checklist
- Food Safety Inspection Checklist
- HACCP Food Safety Checklist
Use a Food Safety & Inspection App to Digitize Your Food SOPs
GoAudits’ all-in-one food safety software is designed to help you digitize and streamline your internal food safety & quality audits, ensuring compliance and driving continuous improvement.
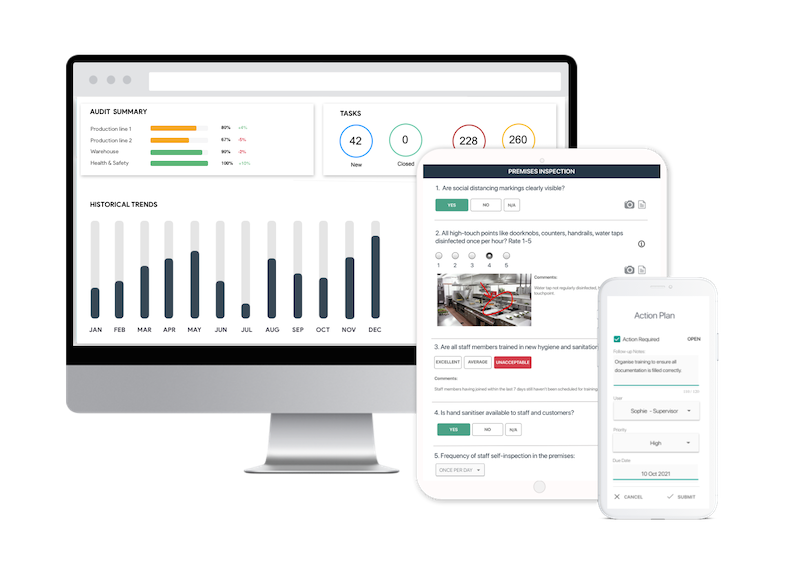
- Replace paper forms with comprehensive digital documentation including photos, annotations, and comments across all devices, online or offline.
- Generate analytics-rich reports instantly to understand operations beyond just scores. Identify recurring weaknesses or risks using advanced analytics.
- Log issues, assign tasks, and track status through an interactive dashboard, ensuring accountability and completion.
- Digitize audits, including hygiene, process & quality reviews, restaurant visits, etc. Standardized checklists make inspections up to 5x faster, meeting food safety standards like HACCP, BRC, FSSC, or ISO.
- Requires no complex training. With GoAudits HACCP software, you get free customization assistance, enabling you to tailor the checklists.
- Gain insights across sites, teams, and operations through trend reports and real-time dashboards. Identify recurring issues and make data-driven decisions to enhance food standards and service levels.
Types of SOPs in the Food Industry
Different types of SOPs address various aspects of food handling, processing, and service. They can differ among various establishments. For instance, restaurant standard operating procedures will vary from those applied in food manufacturing facilities or grocery stores. However, some food SOPs remain consistent across different food-related businesses.
Food Service SOPs
They focus on the processes involved in preparing, packaging, handling, and delivering food. For food production or manufacturing facilities, they also cover tasks like portioning, batch processing, and packaging. They ensure uniformity in service and reduce errors while maintaining quality and food safety.
Food Safety SOPs
Critical for mitigating risks, food safety SOPs include detailed guidelines for
- Cleaning and sanitation procedures for maintaining the hygiene of equipment, utensils, and contact surfaces.
- Preventive strategies and corrective actions to manage pest risks in food facilities.
- Allergen management with instructions for proper labeling, storage, and handling to avoid cross-contact.
- Personal hygiene standards for employee cleanliness, such as handwashing and protective gear.
- Kitchen hygiene covering daily tasks for waste disposal, ventilation, and cleaning schedules.
HACCP-Based SOPs
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) systems involve identifying food safety hazards and establishing controls at critical points in the production process. SOPs based on HACCP principles include monitoring CCPs, documenting safety checks, and ensuring corrective actions for deviations.
Quality Control and Compliance SOPs
SOPs for quality control in the food industry define standards for maintaining quality throughout food processing. They include:
- Raw material specifications to ensure quality inputs
- Product evaluation
- Compliance with food safety regulations like FDA or local guidelines.
Waste Management SOPs
Detailed procedures for segregating, storing, and disposing of food waste in compliance with environmental regulations. They also outline steps for reducing waste through recycling or donation of safe surplus food.
Recall SOPs
In the event of contamination or non-compliance, these food safety SOPs guide the recall process, including communication with stakeholders, removing affected products, and investigating the root cause to prevent recurrence.
Benefits of Implementing Food Safety SOPs
Here are some of the key benefits of SOPs in the food industry:
- Food SOPs establish clear guidelines for food handling, storage, and preparation, reducing the risks of contamination and cross-contamination. It minimizes the likelihood of foodborne illnesses, ensuring public safety and protecting your brand from potential legal and financial fallout.
- They demonstrate your commitment to meeting regulatory requirements, such as those outlined by the USDA and FDA. They streamline audits and ensure consistent compliance with laws and industry standards.
- SOPs in the food industry reduce the risk of workplace accidents and contamination. This safeguards employees, prevents product recalls, and saves the organization from significant losses in revenue and reputation.
- Well-documented food safety SOPs facilitate smooth regulatory inspections and internal audits. They provide proof of adherence to food safety and hygiene standards, reducing the time and resources needed to prepare for such reviews.
- They standardize food preparation and service processes, ensuring that every dish meets the same high standards. It builds customer trust and satisfaction, reflecting positively on your brand’s reliability.
- SOPs equip employees with the knowledge to execute their roles effectively. This reduces errors, fosters a culture of food safety, and ensures operational efficiency across all shifts.
Challenges Facing the Food Establishments in Following SOPs
Here are some of the most common challenges food facilities face in implementing and maintaining food SOPs:
Development and Implementation
- Time and resources: Creating and implementing comprehensive SOPs requires significant time and resources, especially for large or complex operations.
- Expertise: Developing effective SOPs often requires input from various departments, including food safety, production, and quality assurance, which necessitates collaboration and expertise.
- Training and awareness: Ensuring all employees understand and follow food safety SOPs effectively requires regular training and awareness programs.
- Technology limitations: Paper-based SOPs can be cumbersome to manage and update. Electronic SOP systems can be expensive and require ongoing maintenance.
Maintaining and Updating
- Continuously changing regulations: The food industry is subject to constantly evolving regulations, necessitating frequent updates to SOPs to remain compliant.
- Adapting to new technologies and processes: Changes in technology and processes can quickly render existing SOPs outdated, requiring adaptation and revision.
- Version control and accessibility: Maintaining proper version control and ensuring all employees have access to the latest version of each SOP can be challenging.
Compliance and Enforcement
- Auditing and verification: Regularly auditing and verifying compliance with food safety SOPs can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Addressing non-compliance: Effectively addressing and resolving instances of non-compliance with SOPs is crucial for maintaining food safety and quality.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly reviewing and updating SOPs based on performance data and feedback is essential for continuous improvement.
- Difficulty measuring effectiveness: It can be difficult to measure the effectiveness of SOPs in the industry and ensure they are achieving their intended goals.
GoAudits food safety and inspection software can help you overcome these challenges.




