Workplace injuries cost US businesses over $1 billion every single week. Beyond the financial drain, these incidents impact productivity, morale, and lives. The good news? Many of these workplace incidents can be prevented by identifying risks before they cause severe damage. A crucial tool of this proactive approach is safety observation reports.
This blog will explore the importance of reporting safety observations, best practices and ready-to-use templates for making reporting quick and effective, and more.
- What are Safety Observations?
- Types of Safety Observations (with Examples)
- Best Practices for an Effective Safety Observation System
- Safety Observation Reports & Their Importance
- Safety Observation Report: Key Components & Steps
- Safety Observation Report Sample
- Use Software for Safety Observations & Reporting (+ Free Templates)
- Free Checklists to Conduct Safety Observations
What are Safety Observations?
Proactively managing workplace safety involves safety observations – the practice of methodically identifying and documenting safe actions alongside unsafe conditions or behaviors. Everyone has a part to play: frontline employees might spot hazards during daily tasks, while supervisors or safety officers typically perform formal observations and compile detailed reports. Conducting these regular observations helps organizations fix risks before accidents happen, stay compliant, and build an environment where safety is prioritized.
👉 In 2023, there were 1,875 inspectors to inspect 11.5 million workplaces that fall under the jurisdiction of OSHA. It means each workplace would be inspected only once every 186 years on average. Relying solely on external, regulatory audits is not enough. Internal safety observation programs are essential for proactive risk management.
Here are some key benefits of safety observations:
- Detect and address potential risks before they lead to accidents or injuries.
- Involve employees in safety processes, fostering a culture of shared responsibility.
- A safer work environment reduces disruptions and enhances operational efficiency.
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations (e.g., OSHA) to avoid legal penalties and liabilities.
- Minimize workplace incidents by identifying unsafe conditions and behaviors early.
- Encourage vigilance and proactive safety measures among employees.
- Reduce expenses related to workers’ compensation, medical claims, and equipment damage.
- Prevent downtime due to accidents, ensuring smooth business operations.
- Reinforce a strong safety culture where employees prioritize and value workplace safety.
Types of Safety Observations (with Examples)
Below are key types of safety observations, along with some examples:
Unsafe Acts
Unsafe acts involve behaviors that increase the likelihood of accidents or injuries. Examples include:
- Operating machinery without proper training or using tools in a manner not intended by the manufacturer.
- Disregard for personal protective equipment (PPE) and failing to wear required gear such as gloves, safety glasses, or helmets. It’s essential to follow PPE SOPs to ensure compliance with safety protocols. GoAudits offers a wide range of free PPE checklists to verify proper usage, storage, disposal, and more.
Unsafe Conditions
Unsafe conditions pertain to environmental factors that pose risks. Examples include:
- Placing materials or equipment in walkways, leading to potential trip hazards.
- Unaddressed spills or inadequate cleaning leading to slip incidents.
- Accumulation of unnecessary items causing disorganization and potential hazards.
- Poor illumination in work areas, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Blocked or improperly secured access points hindering emergency evacuations.
Near Misses
Near misses are incidents that could have resulted in injury or damage but did not, often due to chance.
Examples include:
- Tools or materials falling near workers without causing harm.
- Losing footing on a wet surface but avoiding a fall.
- Two forklifts narrowly avoiding a collision.
👉 Find out how near miss reporting software can simplify the process of documenting and reporting near misses in workplaces.
GoAudits offers a free near miss incident reporting template. You can use this checklist to document workplace hazards and prevent future occurrences.
At-Risk Behavior
At-risk behaviors are actions that may not immediately cause harm but increase the potential for accidents. Examples include:
- Skipping safety checks to complete work faster.
- Ignoring safety procedures due to familiarity or routine.
- Performing multiple tasks simultaneously, leading to reduced focus on safety.
Ergonomic Hazards
Ergonomic hazards relate to physical factors that can cause musculoskeletal injuries. Examples include:
- Employees adopting awkward positions during tasks.
- Continuous repetitive motions without adequate breaks leading to strain injuries.
👉 Use this ergonomic risk assessment template to identify workplace setup, determine injury risks, and implement improvements for safer work environments.
Process Deviations
Process deviations occur when safety standard operating procedures are not followed. Examples include:
- Skipping pre-operation inspections of equipment.
- Modifying a process without proper approval or assessment.
- Failing to record process steps or safety measures taken during operations.
Best Practices for an Effective Safety Observation System
Implementing an effective safety observation system is crucial for identifying and mitigating potential hazards before they escalate into serious incidents. Consider the following best practices:
Prepare and Set Clear Objectives
Begin by defining the specific goals of your safety observation system. Whether aiming to reduce workplace incidents, enhance employee engagement in safety protocols, or comply with regulatory standards, these objectives provide direction, ensure all stakeholders understand their purpose, and enhance your safety observation system’s design and implementation.
Train and Encourage Employees
Educate employees on the importance of safety observations, how to conduct them, and the correct procedures for reporting. Encourage positive reinforcement by emphasizing it’s designed to promote a safe working environment, creating a supportive atmosphere.
Use Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Develop and implement safe operating procedures to standardize the observation and reporting processes. Standardization and clearly documented procedures ensure consistency, help train new employees, make it easier to analyze data and identify trends, and maintain the integrity of the safety observation system.
Leverage Technology
Transitioning from manual reporting methods, such as paper forms and spreadsheets, to digital solutions can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your safety observation system. Manual systems are often time-consuming, prone to errors, and hinder real-time data analysis. Digital solutions like GoAudits facilitate immediate reporting, trend analysis, and data accessibility, enabling the implementation of corrective actions and informed decision-making.
👉 GoAudits helps you simplify and improve safety observations and report them. With its mobile app, you can conduct inspections and document safety concerns instantly using customizable digital checklists, even when you’re offline. Attach photos with annotations and add time stamps, geolocation, and e-signatures to provide visual evidence.
It also helps you streamline documentation and reporting, automatically generating reports after each inspection. You can track recurring issues, monitor trends, and analyze safety performance across teams or locations using smart dashboards. You can also assign corrective actions during inspections to ensure timely resolution. GoAudits can help enhance compliance, improve accountability, and create a proactive safety culture that reduces workplace accidents.
Act on Observations Promptly
Timely response to safety observations is critical. Implement corrective actions as soon as possible and communicate these measures to the workforce to maintain trust and encourage ongoing participation.
Regularly Evaluate and Update
Regularly assess the performance of the safety observation system by analyzing collected data, soliciting employee feedback, reviewing incident reports, and engaging employees to gain valuable perspectives. Use these insights to update procedures, enhance training programs, and implement new strategies to address emerging safety challenges.
Safety Observation Reports & Their Importance
A safety observation report is a formal document used to record observations related to safety practices within a workplace. These reports record systematic observation of the work environment, equipment, safety processes and practices, etc., with an aim to
- Identify hazards and risks
- Assess employee behaviour
- Implement corrective actions
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations and best practices
- Enhance safety culture
Safety inspections are structured, formal evaluations that assess compliance with established safety regulations, standards, and procedures. They involve systematic examinations of the workplace, equipment, and processes to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety protocols.
Safety observations are informal, ongoing assessments that focus on monitoring and improving daily work practices and behaviors. They involve employees at all levels and encourage the reporting of hazards as they are identified to address potential issues quickly and establish a proactive safety culture.
Why are Safety Observation Reports Important?
Here are some reasons why they’re important:
- Safety observation reports formally document safety concerns, providing a systematic approach to identifying and addressing workplace hazards. This ensures corrective actions are effectively implemented.
- Detailed records help allocate resources efficiently to mitigate potential risks, improving overall workplace safety.
- Regular collection and review of safety observation reports help identify recurring safety issues, allowing organizations to implement targeted interventions.
- Well-maintained safety observation reports demonstrate a commitment to safety and compliance, acting as evidence during audits and inspections.
- Proper documentation of safety observations can help organizations avoid legal liabilities by proving due diligence in hazard mitigation.
- Measurable data from these reports enable organizations to assess safety improvements over time and compare them against industry standards.
- Regular safety observations establish a proactive safety culture, ensuring ongoing enhancements in workplace safety protocols.
Safety Observation Report: Key Components & Steps
Below are the steps you must take to prepare a safety observation report.
1. Identify What to Observe
Begin by determining the specific areas and elements to monitor. Common focus points include:
- Assess the work environment, including housekeeping, lighting, ventilation, and ergonomics.
- Inspect fire extinguishers, including their availability, condition, etc. Use fire safety audit checklists to inspect fire doors, emergency exits, alarm systems, and other risks associated with fire.
- Ensure appropriate PPE is available, in good condition, and correctly used by employees by performing regular PPE inspections.
- Inspect for exposed wiring, overloaded circuits, and proper grounding of equipment.
- Verify proper labeling, storage, and handling of chemicals, along with accessible material safety data sheets (MSDS). GoAudits offers a free chemical risk assessment template and chemical safety checklist – COSHH to help you assess chemical handling, storing, and disposal procedures.
2. Record Basic Information
Document essential details to provide context for your observations:
- Date and Time: Specify when the observation takes place.
- Location: Indicate the exact area within the facility.
- Observer Information: Include your name, department, and title.
3. Describe the Observation in Detail
Provide a comprehensive account of the observed situation:
- Classify the safety observation as a practice, at-risk behavior, or a near-miss incident.
- Clearly detail what was observed, including specific behaviors, conditions, and any equipment involved.
- Collect supporting materials such as photographs, physical evidence, or training records to substantiate your observations.
4. Assess the Risk Levels
Evaluate the severity and likelihood of potential harm:
- Determine the possible impact on personnel, property, or operations if the hazard leads to an incident.
- Estimate the probability of the hazard causing an incident.
- Use a risk matrix to prioritize issues that require immediate attention.
5. Recommend Corrective Actions
Suggest practical measures to mitigate identified risks:
- Outline immediate actions and steps taken to address hazards promptly.
- Propose strategies to eliminate or control hazards, such as revising procedures, providing additional training, or upgrading equipment.
6. Review, Submit, and Follow Up
Finalize and communicate your findings:
- Ensure the report is accurate, comprehensive, and free from errors.
- Forward the report to the appropriate personnel or department responsible for safety management.
- Monitor the implementation of corrective actions and assess their effectiveness over time. Regular follow-ups demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement and reinforce the importance of safety within the organization.
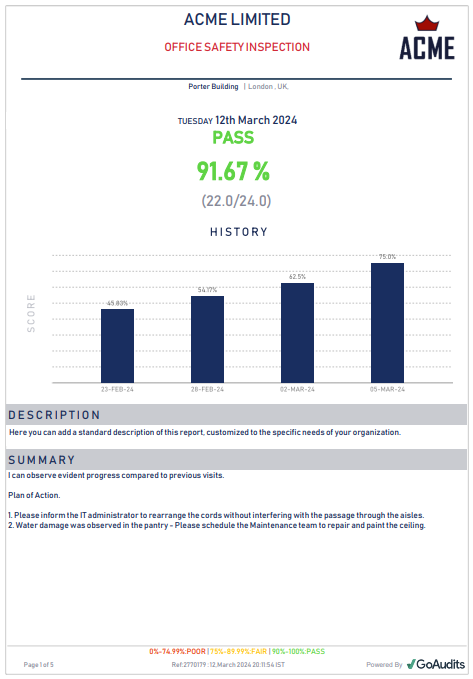
Safety Observation Report Sample
Here’s a safety observation report example generated using GoAudits.
Use Software for Safety Observations & Reporting (+ Free Templates)
Maintaining workplace safety requires efficient inspections, accurate reporting, and streamlined workflows. Traditional safety audits can be time-consuming and prone to errors. GoAudits safety inspection software can simplify safety observations, improve compliance, and drive proactive risk management. It’s an all-in-one platform for audits, inspections, and compliance with a user-friendly interface that eliminates paperwork and enhances real-time visibility.
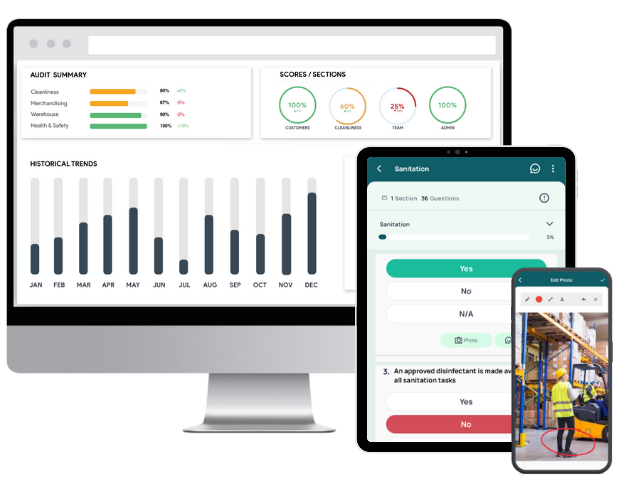
- Conduct comprehensive safety audits and inspections using customizable checklists, even when offline.
- Capture real-time safety observations with photos, annotations, and comments.
- Generate professional reports instantly after each inspection, pre-populated with attached photos, assigned actions, time stamps, and geolocation. Customize these safety reports and share them with relevant stakeholders.
- Assign corrective actions directly from the app during an inspection, set deadlines and track progress, and ensure accountability with automatic notifications and escalations.
- Review audit scores and performance, identify trends, patterns, and recurring safety issues, and benchmark against industry standards with smart dashboards.
Culham Consultancy, a UK-based health and safety firm, previously relied on manual methods for audits and inspections, which involved handwritten data collection and labor-intensive report generation. This process was time-consuming and prone to inefficiencies.
👉 GoAudits enabled them to conduct inspections via a user-friendly mobile app, significantly reducing the time required to complete reports from over an hour to approximately ten minutes.
In addition to faster reporting, Culham Consultancy benefited from tailoring audits to specific business processes and other GoAudits features such as photo annotations, dynamic dashboards, etc. This resulted in higher quality, more consistent information across various clients and sites, and improved data visualization and interpretation.

Free Checklists to Conduct Safety Observations
GoAudits offers a range of health and safety audit checklists. You can sign up for free and use these workplace inspection checklists to identify and report safety issues, prevent accidents, and ensure workplace safety.