The urgency of infection prevention and control (IPC) in care homes, to protect both residents and staff, has never been more evident than it was during the pandemic. The pandemic highlighted the need for effective isolation practices, stringent hygiene measures, and management of personal protective equipment (PPE). However, the unique environment of care homes, with their close community settings and high-risk populations, creates particular challenges when it comes to keeping everyone safe. These include managing the practicalities of isolation, preventing the introduction of infections, ensuring adherence to IPC protocols, and more. These challenges are compounded by the need for ongoing training and resource constraints.
So, how can care homes navigate these challenges effectively? Let’s explore the key principles for infection prevention and control in care homes, and actionable steps care homes can take to reduce infection risks.
- Common Sources of Infection in Care Homes
- What are Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Principles?
- CQC Requirements for Infection Control in Care Homes
- 7 Key Strategies for Infection Control in Care Homes
- Enhance Infection Control in Care Homes with GoAudits
- Care Home Infection Control Audit Templates
Common Sources of Infection in Care Homes
Understanding how infection spreads is crucial for implementing effective IPC measures. The chain of infection contains 6 links, with opportunities to break the chain at any link. The more links that are broken, the greater the protection.
The 6 links are:
- Pathogen
- Reservoir
- Portal of exit
- Means of transmission
- Portal of entry
- Susceptible host

Let’s address the common sources of infection in care homes that form part of the above chain of infection link.
Human Interaction
Close and regular contact between staff, residents, and visitors facilitates the transmission of infections. This includes the spread of respiratory viruses (such as influenza and COVID-19), gastrointestinal infections (like norovirus), and other common infections like MRSA.
Environmental Contamination
Surfaces, equipment, and shared facilities can become contaminated with pathogens. These include door handles, medical equipment, communal areas (like dining rooms and lounges), and residents’ personal items. Improperly cleaned and disinfected environments provide a reservoir for pathogens to survive and spread.
Inadequate Hand Hygiene
Failure to perform hand hygiene at key moments, such as before and after contact with a resident, after exposure to body fluids, and after removing gloves, significantly increases the risk of infection transmission.
Improper Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Incorrect use or failure to use PPE when necessary can lead to the spread of infections. This includes not changing gloves or aprons between tasks or residents and not wearing masks when required.
Waste Management
Improper disposal of healthcare waste (e.g., dressings, disposable clothing) can spread infection. Not segregating waste correctly or failing to dispose of it in a timely manner can lead to environmental contamination.
Lack of Resident Isolation
Not isolating residents with infectious diseases or symptoms promptly can result in widespread outbreaks within the facility. Cohorting symptomatic residents, when single-room isolation is not possible, is essential but also poses a risk if not managed properly.
Poor Ventilation
Inadequate ventilation in care homes can facilitate the airborne spread of pathogens, particularly in areas where residents and staff spend significant amounts of time together.
Shared Facilities and Equipment
The use of communal bathrooms, dining areas, and recreational facilities can contribute to the spread of infections. Similarly, if not properly cleaned between uses, shared equipment can be a transmission source.
Food Hygiene
Improper food handling and preparation can lead to outbreaks of foodborne illnesses. This includes not following proper cooking temperatures, cross-contamination, and inadequate storage of food items.
Water Systems
Legionella and other waterborne pathogens can proliferate in poorly maintained water systems, leading to infections among residents and staff.
What are Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Principles?
Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) is an essential aspect of healthcare, especially in care homes, where vulnerable populations reside.
Standard Infection Control Precautions (SICPs): 10 Principles of Infection Control
Standard infection control precautions (SICPs) are the basic IPC measures necessary to reduce the risk of spreading pathogens. According to NHS England, SICPs must be used by all staff at all times for all patients in all healthcare settings, whether the infection is present or not, to ensure the safety of the residents, staff, and visitors.
When implementing SICPs in care homes and other healthcare settings, it’s crucial to follow a comprehensive approach.
Here are the 10 principles of infection control:

- Patient Placement/Assessment of Infection Risk: Careful assessment of infection risk and patient placement is fundamental to preventing the spread of infections. This includes identifying individuals with a high risk of transmitting infections and arranging their care environment accordingly.
- Hand Hygiene: Proper hand hygiene is the cornerstone of infection prevention. Staff should use hand rubs containing emollients to prevent dermatitis and wash their hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds when visibly soiled or after using the bathroom.
- Respiratory and Cough Hygiene: Minimize cross-transmission of respiratory pathogens by using disposable tissues when coughing or sneezing and disposing of them properly. Encourage patients with respiratory symptoms to wear a surgical mask if it’s safe and tolerated.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): PPE must be accessible, stored properly to prevent contamination, and used correctly according to the task at hand. This includes gloves, aprons, full-body gowns, and eye or face protection, each having specific guidelines for use, changing, and disposal.
- Safe Management of the Care Environment: Maintaining a clean and safe environment is essential. Regular cleaning and disinfection practices should be in place, targeting high-touch surfaces and communal areas to reduce the risk of infection transmission.
- Safe Management of Care Equipment: All care equipment should be cleaned, disinfected, and maintained appropriately after each use and between patients, following the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure they do not become a source of infection.
- Safe Management of Healthcare Linen: Handle, transport, and process used linen in a manner that prevents the spread of infection, including using appropriate laundry protocols and ensuring linens are cleaned and stored properly.
- Safe Management of Blood and Body Fluids: Implement procedures for safely managing and disposing of blood, body fluids, and items contaminated with them, following proper protocols to minimize exposure risks.
- Safe Disposal of Waste (including Sharps): Waste and sharps must be disposed of in incorrectly labeled containers and according to local policies to prevent injuries and reduce the risk of infection spread.
- Occupational Safety/Managing Prevention of Exposure (including Sharps): Policies and procedures must be in place to protect staff from occupational exposure to infections. This includes vaccination, post-exposure prophylaxis, and clear guidelines on what to do in the event of an exposure incident.
Transmission Based Precautions (TBPs)
Transmission Based Precautions (TBPs) are essential strategies in preventing and controlling the spread of infections. TBPs complement SICPs and are implemented when caring for patients with known or suspected infections, to manage the routes of transmission specific to infectious agents. TBPs are categorized into Contact, Droplet, and Airborne precautions, each targeting different modes of transmission and requiring specific actions and protective measures.
Contact Precautions are used to prevent infections that spread through direct contact with the patient or indirectly from the patient’s immediate care environment. This includes using personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and aprons, and ensuring environmental cleanliness.
Droplet Precautions aim to prevent infections transmitted over short distances through droplets from the respiratory tract. Measures include wearing surgical masks and eye protection when within two meters of the patient, emphasizing the importance of patient placement, and assessing infection risks to manage space effectively in healthcare settings.
Airborne Precautions are necessary for diseases spread via aerosol transmission. This involves using higher levels of respiratory protection (e.g., FFP3 masks), ensuring adequate ventilation, and using isolation rooms with negative pressure where possible. Staff should assess the need for these precautions based on the infectious agent, the severity of the illness, and the setting in which care is provided.
CQC Requirements for Infection Control in Care Homes
The Care Quality Commission (CQC) plays a pivotal role in ensuring infection prevention and control in care homes, particularly in the wake of challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, care providers need to proactively ensure compliance with CQC requirements and get ready for CQC inspections.
CQC conducts detailed IPC inspections across care homes, evaluating eight specific areas: Visitors, Shielding, Admission, Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), Testing, Premises, Staffing, and Policies. These inspections aim to assess whether care homes are effectively preventing and controlling infections. Each area is judged on a scale of being “assured,” “somewhat assured,” or “not assured,” helping to pinpoint exactly where improvements are needed.
👉 Also Read:
→ CQC Quality Statements: A Complete Guide for Care Providers
→ How Health & Social Care Services Can Ensure CQC Compliance
→ A Care Provider’s Guide to CQC Registration Requirements
→ How to Prepare for CQC Inspections with Mock CQC Inspections
→ A Complete Guide to CQC Single Assessment Framework
→ CQC Inspection Checklists & Templates: Prepare CQC Visit
7 Key Strategies for Infection Control in Care Homes
Here are six best practices particularly crucial in the unique environment of care homes:
1. Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Correctly
Care home staff must be trained in the correct selection, use, and disposal of PPE, ensuring they understand when and how to use gloves, masks, gowns, and other protective gear. This also involves ensuring PPE is readily available and used appropriately based on the risk of exposure.
Use these free PPE checklists:
2. Infection Control During Resident Admissions
Assessing and managing infection risks during new resident admissions includes performing thorough risk assessments to identify potential infection sources and implementing isolation protocols if necessary.
3. Environmental Cleaning and Disinfection
Maintaining a clean and disinfected environment reduces the risk of infection spread. Routine and targeted cleaning should be prioritized, especially for high-touch areas and resident rooms. Care homes should use EPA-registered disinfectants and follow manufacturers’ instructions for effective use. This practice extends to the prompt cleaning of blood or other potentially infectious material spills.
4. Managing Outbreaks: Isolation and Cohorting Strategies
When outbreaks occur, quickly isolating symptomatic residents and employing cohorting strategies can help prevent further spread. This involves designated areas for infected individuals and careful management of staff and resources to avoid cross-contamination.
5. Engaging Residents and Visitors in Infection Prevention
Educating residents and their families about infection prevention practices helps create a community of care that supports IPC efforts. This includes teaching about hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and promptly reporting symptoms or concerns.
6. Regular Training and Education for Care Home Staff
Ongoing training and development for staff on IPC measures are essential. This should cover job-specific practices, emerging infection risks, and updates on guidelines and procedures.
7. Conduct frequent internal audits
Internal infection prevention and control audits are a helpful training tool that helps with all 6 strategies listed above. While it sounds like an additional administrative burden on your teams, using digital tools, you can make internal IPC audits part of day-to-day operations.
Keeping digital records of your regular internal checks also helps demonstrate due diligence and compliance when the time comes for CQC inspections.
Enhance Infection Control in Care Homes with GoAudits
While infection control is rightly considered a priority, embedding ICP measures into the day-to-day care home operations is often a challenge.
Using technology such as the GoAudits care home auditing app can prove effective and beneficial to streamline and enhance IPC protocols in care homes:
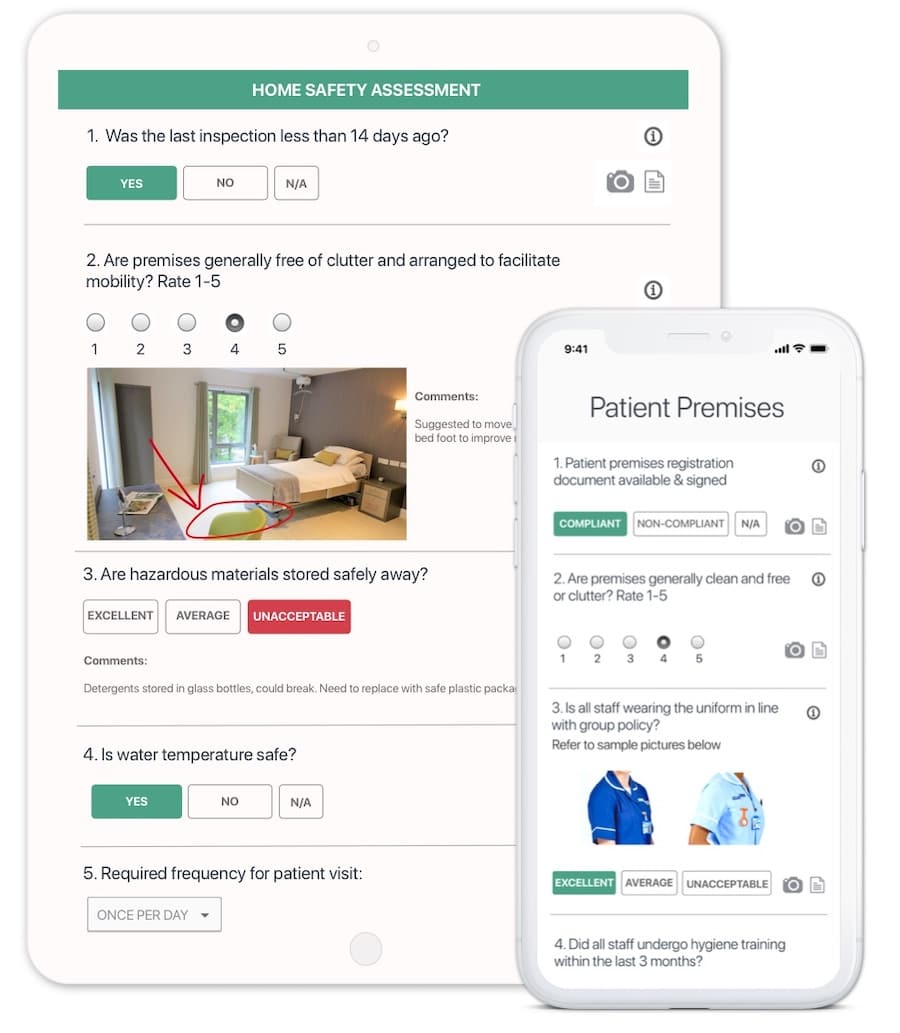
- Enable easy self-inspections with a user-friendly mobile app. Instant reports eliminate paperwork and manual administrative work.
- Start with IPC best practices and other care home audit templates. Easily update digital checklists in case of changes to IPC or local guidelines.
- Standardise IPC procedures and train staff. Create digital checklists for infection control compliance, hand hygiene, cleaning, and more, which all staff members can access on their mobile devices. Schedule regular checks to ensure IPC awareness and compliance.
- Assign corrective actions if issues are found during an IPC audit.
- Keep all digital records and inspection reports in one place. Easily demonstrate compliance during your next CQC inspection and ensure higher CQC ratings.
- The automatic scoring system gives you immediate insights into infection control compliance levels and areas requiring immediate attention.
Beyond infection control, you can also use GoAudits to streamline all internal care home audits.
Continue Reading: How GoAudits helped Careville comply with changing IPC requirements
Care Home Infection Control Audit Templates
GoAudits offers a comprehensive library of healthcare audit checklists designed to improve infection control compliance and quality of care across various healthcare settings, including care homes. These customizable infection prevention audit tools & templates cover a broad range of areas, from general care home audits to specific infection control measures.
- Infection Control Inspection Checklist
- Infection Control Audit Template
- Deep Cleaning for Infection Control
- Hand Hygiene Audit
- Infection Control Audit Template
- Care Home Audit Template
- Care Home Cleaning Checklist – Daily
- Daily Care Home Audit
- Care Home General Observation
- Care Home Audit Checklist
- MAR EMAR Audit Checklist





