Actively collecting and analyzing industrial hygiene data can help workplaces significantly decrease work-related injuries and illnesses. This highlights the importance of accurate monitoring and proactive decision-making. However, many workplaces still rely on manual systems, which make data collection and analysis not only time-consuming but also prone to error and difficult to scale. Industrial hygiene software can help overcome these challenges by replacing outdated methods with digital tools. With a reliable way to capture, analyze, and act on exposure data, organizations can improve workplace safety, enhance reporting accuracy, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
This article lists the top industrial hygiene software, industrial hygiene examples, steps & free checklists to perform internal audits, and more.
What is Industrial Hygiene in the Workplace & Why It Matters
Industrial hygiene in the workplace focuses on anticipating, recognizing, evaluating, and controlling environmental factors that may affect employee health and safety. It is a science-driven discipline that identifies potential hazards in the work environment and implements strategies to minimize or eliminate risks. Maintaining proper hygiene standards can protect workers from occupational illnesses, improve overall productivity, and ensure compliance with health and safety regulations.
Examples of Industrial Hygiene Hazards
| Categories | Industrial Hygiene Hazard Examples |
| Poor air quality | Dust, fumes, vapors, or gases can accumulate in enclosed spaces and cause respiratory problems, headaches, or long-term lung damage |
| Noise hazards | Continuous exposure to loud machinery or equipment can lead to hearing loss or stress-related conditions. |
| Extreme temperatures | Prolonged exposure to very hot or cold environments may result in heat stress, hypothermia, or dehydration |
| Chemical exposure and radiation | Contact with hazardous chemicals, solvents, or radiation sources can cause burns, poisoning, organ damage, or cancer |
| Biological hazards | Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other biological agents can spread in certain workplaces, especially in healthcare, laboratories, and food processing |
| Inadequate PPE | When workers lack suitable personal protective equipment, the risk of injury or illness increases significantly |
5 Importance of Industrial Hygiene in the Workplace
Here’s why industrial hygiene is important in the workplace:
- Identifying and controlling hazards prevents occupational illnesses and injuries. A healthier workforce means fewer absences and long-term well-being.
- Safe and clean environments reduce fatigue, errors, and disruptions. Workers perform tasks more efficiently when they are free from harmful exposures and physical discomfort.
- Preventing workplace hazards cuts expenses tied to medical treatment, compensation claims, and lost workdays. Investing in industrial hygiene also minimizes costs related to accidents and equipment damage.
- Meeting occupational health and safety standards protects organizations from fines, lawsuits, and shutdowns. Compliance also builds a framework for continuous safety improvement.
- A strong commitment to worker health demonstrates corporate responsibility. Businesses known for safe practices attract skilled employees, earn trust from clients, and strengthen long-term partnerships.
What are the 5 OSHA Requirements Relating to Industrial Hygiene?
OSHA requirements for industrial hygiene are built on the following five principles:
- Anticipation: Identify potential workplace health hazards in advance by analyzing job tasks, materials, and processes before exposure occurs.
- Recognition: Detect existing hazards such as chemicals, noise, or biological agents through inspections, employee feedback, and safety data sheets.
- Evaluation: Measure the severity and extent of hazards using tools like air sampling, noise monitoring, and exposure assessments.
- Hazards control: Implement engineering controls, administrative measures, or personal protective equipment to reduce risks to acceptable levels.
- Confirmation: Verify that controls are effective by conducting follow-up testing, monitoring exposures, and reviewing safety procedures regularly.
What is Industrial Hygiene Software?
Industrial hygiene software is a digital solution designed to identify, audit, and control workplace hazards that can affect employees’ health and safety. It centralizes data collection, exposure monitoring, and risk assessment in one platform. It helps you track environmental factors such as chemical, biological, and physical hazards. The software also supports regulatory compliance by maintaining accurate records, generating reports, and ensuring standards are consistently met.
Who Needs Industrial Hygiene Software and Why?
You need industrial hygiene software if your organization operates in industries where employees face occupational health risks. Sectors such as manufacturing, construction, oil and gas, mining, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals use this software to make informed decisions, safeguard employee health, comply with stringent safety regulations, and strengthen the overall safety culture. Relying on outdated, manual methods increases the risk for errors, delays, and non-compliance penalties.
Top 5 Industrial Hygiene Software in 2026
Here are our top 5 picks for industrial hygiene software.
| Pricing | Free trial & demo | |
| GoAudits | $10 per user per month; annual billing | 14-day free trial and personalized demo |
| VelocityEHS | – | Demo available |
| EHSInsight | Starting at $4,600 per year | Free trial |
| Cority | – | Demo available |
| Benchmark Gensuite | – | Demo available |
1. GoAudits Industrial Hygiene Management Software
Traditional safety and industrial hygiene audits often struggle with paper checklists, manual reporting, and inconsistent follow-ups. GoAudits safety inspection software solves these pain points by giving safety teams a mobile-first platform designed specifically for audits and inspections.
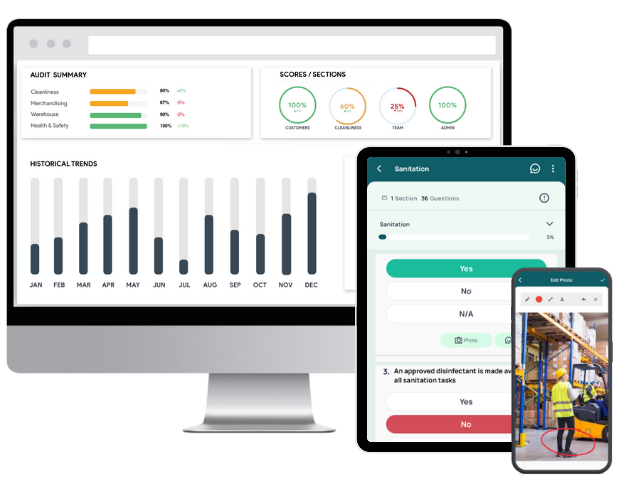
Key features & benefits of GoAudits:
- Access an extensive library of health & safety checklists or build your own with drag-and-drop tools. Upload existing forms and get them digitized quickly at no additional cost.
- Conduct inspections on any device, both online and offline. Easily capture photos, notes, e-signatures, timestamps, and geolocation for complete transparency.
- Generate and distribute instant, professional reports. Manual reporting can take days; GoAudits generates audit reports immediately, complete with scores, trends, and visual evidence.
- Track corrective actions to closure. Findings don’t just sit in a report: GoAudits turns them into tasks with deadlines and reminders, ensuring that hazards are actually fixed.
- Gain continuous compliance oversight. Smart dashboards highlight recurring issues, overdue actions, and risk trends across sites, helping managers stay on top of OSHA and other regulatory requirements.
👉 Result: Industrial hygiene audits that once took hours to compile and chase now happen in real time, with clear accountability and full visibility.
2. VelocityEHS Industrial Hygiene Software
VelocityEHS gives you the tools to build, manage, and improve an industrial hygiene (IH) program. It helps you assess and control workplace stressors, automate complex IH processes, and centralize program data. It streamlines sampling, surveillance, respirator fit testing, and exposure group management. With access to a chemical and OEL database, you can maintain a reliable IH program across your organization.
Key features of VelocityEHS:
- Standardize and centralize global IH activities for compliance and program oversight.
- Track IH samples and equipment to ensure reliable data collection and regulatory compliance.
- Monitor employee health for exposure to critical stressors, automating evaluations and record-keeping.
- Manage RFT schedules and protocols to protect employees with proper respiratory equipment.
- Leverage the chemical and OEL database, analyze sample data, and generate real-time reports.
3. EHS Insight Industrial Hygiene Database Software
EHS Insight provides a comprehensive solution for managing workplace exposure risks and sampling processes. The Industrial Hygiene Module streamlines data collection, scheduling, and analysis, reducing administrative work while improving compliance with OSHA, NIOSH, etc. It can help you identify hazards early, prioritize risks, and implement controls to protect employee health.
Key features of EHS Insight:
- Receive automated notifications for assessments, exceedances, and program updates.
- Pinpoint hazards using combined qualitative and quantitative assessments.
- Compare monitoring data with OELs/PELs and identify improvement areas.
- Leverage AI and technology to detect trends and optimize safety.
- Access tasks, reports, and analytics from any location.
4. Cority Industrial Hygiene Software
Cority unifies data collection, monitoring, and analysis in a single environment, enabling you to manage workplace exposures with precision and foresight. It offers predictive insights, streamlines workflows, and maintains regulatory compliance while protecting employee health. You can also detect hazards early, prioritize interventions, and drive measurable improvements in workplace safety.
Key features of Cority:
- Harmonize qualitative and quantitative data for accurate risk evaluation.
- Build, schedule, and track surveys across multiple hazards.
- Capture field data and trigger over-exposure notifications automatically.
- Instantly calculate exposure scores and highlight potential hazards.
- Manage equipment calibration and automate respirator/hearing tests.
5. Benchmark Gensuite Industrial Hygiene Software
Benchmark Gensuite helps you manage workplace hazards and protect employee health. You can identify, monitor, and mitigate industrial hygiene risks across your organization. It ensures compliance with regulatory standards while increasing visibility into your environmental health and safety programs with its mobile capabilities, robust analytics, and AI-driven insights.

Key features of Benchmark Gensuite:
- Auto-send notifications for assessments, exceedances, and summaries to ensure transparency.
- Combine qualitative and quantitative assessments to pinpoint potential hazards.
- Compare IH data with OELs/PELs and use analytics for informed decisions.
- Integrate AI to detect trends and optimize risk management.
- Access tasks on the go and visualize insights with Tableau-powered reports.
How to Choose the Best Industrial Hygiene Software?
Here are some points you should consider:
- Understand your business requirements and identify gaps in your current processes. Define the specific compliance standards, reporting needs, and operational challenges your organization faces to ensure the software addresses them directly.
- Look for essential features, such as customizable checklists, mobile auditing with offline access, instant report generation, corrective and preventive actions (CAPA), workflow automation, and data analytics for actionable insights.
- Check software reviews and testimonials from other organizations in your industry. Reviews highlight performance, reliability, and real-world user experiences that reveal strengths and weaknesses.
- Choose software that fits your current budget but also scales with business growth. A scalable solution adapts to new locations, users, or regulatory changes without requiring a complete system change.
- Ensure the interface is simple to navigate for all team members. An intuitive design reduces training time and boosts user adoption rates.
- Test the software through trials or demos to understand how it integrates with your workflows. Hands-on experience helps confirm if it meets your operational needs.
- Verify that the software complies with data protection regulations. Look for encryption, secure access controls, and regular system updates to safeguard sensitive information.
Industrial Hygiene Audits: An Overview
Industrial hygiene audits are systematic evaluations of workplace environments, processes, and practices to identify and control health hazards that may affect employees. These audits focus on physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic risks that can cause illness, injury, or long-term health problems. The goal is to ensure that workplaces comply with safety regulations and adopt preventive measures to protect workers.
Who Performs Industrial Hygiene Audits & Why
Industrial hygiene audits are typically conducted by certified industrial hygienists (CIHs), occupational health and safety professionals, or third-party specialists with expertise in workplace hazard assessment. In some cases, internal health and safety teams perform these audits if they have trained personnel with the required knowledge of occupational exposure standards, risk assessments, and regulatory compliance.
Common Industrial Hygiene Examples
Here are common industrial hygiene examples:
| Category | Description |
| Airborne contaminant control | Monitoring and reducing exposure to dust, fumes, vapors, and gases using ventilation systems and filtration units. |
| Noise exposure management | Measuring sound levels, installing noise barriers, and providing hearing protection devices in high-decibel areas. |
| Chemical safety practices | Using fume hoods, closed systems, or proper storage methods to minimize risks from solvents, acids, or reactive substances. |
| Heat stress prevention | Providing hydration stations, rest breaks, and cooling areas for employees in hot environments. |
| Biological hazard control | Implementing disinfection routines, protective clothing, and safe handling of biological materials. |
| Radiation monitoring | Using shielding, badges, and exposure limits in facilities that handle radioactive materials. |
| Respiratory protection programs | Supplying respirators, fit testing, and training to safeguard workers in environments with harmful particles. |
| Illumination checks | Ensuring adequate lighting to prevent accidents and reduce eye strain. |
| Confined space safety | Testing oxygen levels, monitoring toxic gases, and applying permit-to-work systems before entry. |
| Workplace housekeeping | Keeping floors, walkways, and storage areas clean to minimize slips, trips, and fire hazards. |
Steps to Perform Internal Industrial Hygiene Inspections
Follow these steps to perform a thorough inspection:
Plan and Prepare
Review your existing safety programs, policies, and procedures. Identify the scope of the audit, such as areas, processes, or tasks with higher risk potential. Collect previous inspection records, incident reports, and exposure data to understand recurring issues.
Use Checklists to Conduct the Audit
Use comprehensive checklists to standardize the process. Focus on hazard identification, risk assessment, and exposure monitoring. Evaluate physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic hazards present in the work environment. Ensure that sampling methods and monitoring equipment are properly calibrated.
👉 GoAudits offers a wide range of workplace inspection checklists tailored for different industries.
You can sign up for free and start using these checklists.
- Workplace Hygiene Checklist
- Personal Hygiene Checklist
- Canteen Hygiene Inspection
- Food Safety & Hygiene Checklist
- Hand Hygiene Checklist
- Cafe Cleaning Checklist – Daily
- Hygiene Standard
- Sanitation Inspection Checklist
- OHS Inspection Checklists & Templates
- OSHA Checklists & Audit Templates
Document and Evaluate Findings
Record observations systematically, including details such as the type of hazard, location, potential impact, and employees at risk. Assess the severity and likelihood of each hazard to prioritize corrective measures. Instead of vague notes, use specific and measurable information wherever possible.
Recommend and Assign Corrective Actions
Assign corrective actions that align with regulatory requirements and company policies to designated personnel with clear timelines. Recommendations should focus on eliminating hazards at the source, followed by engineering controls, administrative measures, and personal protective equipment.
Train and Engage Employees
Share findings with employees and provide targeted training. Involve workers in discussions about hazards and solutions to encourage accountability and compliance. Employee engagement improves the success rate of corrective actions and fosters a culture of safety.
Monitor and Verify Improvements
Revisit identified areas to confirm that corrective actions are implemented and effective. Conduct follow-up inspections and exposure monitoring when needed. Document progress and adjust control measures if risks persist.
Document Results and Share Reports with Management
Prepare a detailed inspection report summarizing findings, corrective actions, and follow-up status to ensure compliance and transparency. Share the report with management to support decision-making and resource allocation.
FAQs
Effective industrial hygiene practices include identifying workplace hazards, monitoring air quality, controlling exposure to harmful substances, and maintaining proper ventilation. You should also ensure the use of PPE, implement safe work procedures, and schedule regular health surveillance. Training employees on hazard recognition and enforcing strict housekeeping standards are equally important to minimize risks.
Occupational health and safety (OHS) focuses on protecting workers from injuries, illnesses, and accidents through policies, systems, and training. Industrial hygiene, on the other hand, specifically deals with anticipating, recognizing, evaluating, and controlling environmental factors such as chemicals, noise, and biological agents. OHS is broader, while industrial hygiene is a specialized branch within it.
The six key objectives of industrial hygiene are hazard anticipation, hazard recognition, hazard evaluation, hazard control, worker health protection, and regulatory compliance. They ensure you systematically prevent harmful exposures, safeguard employee well-being, and maintain a safe working environment. Meeting these goals helps workplaces reduce occupational risks.
Maintaining industrial hygiene can be challenging due to evolving workplace hazards, inadequate resources, and limited awareness among workers. You may also face difficulties with accurate exposure monitoring, implementing cost-effective controls, and keeping up with changing regulations. Additionally, balancing productivity with safety measures often creates practical constraints that make consistent hygiene management difficult.






