Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) is a key framework to improve healthcare quality and safety in nursing homes. It combines Quality Assurance (QA) and Performance Improvement (PI), using a clear, step-by-step approach. This methodology gets everyone involved – from nurses to managers – in making care better and solving problems.
This blog provides an overview of the key steps you need to take to implement QAPI, along with digital resources and compliance tools that you may find helpful.
- Introduction to QAPI
- STEP 1: Leadership Responsibility and Accountability
- STEP 2: Develop a Deliberate Approach to Teamwork
- STEP 3: Take your QAPI 'Pulse' with a Self-Assessment
- STEP 4: Identify Your Organization’s Guiding Principles
- STEP 5: Create Your QAPI Plan
- STEP 6: Conduct a QAPI Awareness Campaign
- STEP 7: Develop a Strategy for Collecting and Using QAPI Data
- STEP 8: Identify Your Gaps and Opportunities
- STEP 9: Prioritize Quality Opportunities and Charter PIPs
- STEP 10: Plan, Conduct, and Document PIPs
- STEP 11: Getting to the ‘Root’ of the Problem
- STEP 12: Take Systemic Action
- Key Elements of a QAPI Plan
- Implement a QAPI Plan with Healthcare Compliance Software
- Free & Customizable QAPI Templates and Healthcare Audits checklists
Introduction to QAPI
Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) is a comprehensive, strategic approach aimed at elevating your organization’s performance improvement initiatives. It’s created to align with and support the purpose, guiding principles, and scope of your QAPI efforts, determined through a reflective process.
QAPI plan is a framework for your organization’s continuous quality improvement in healthcare. It’s an actionable blueprint, laying out a systematic, data-driven methodology to enhance both the quality of life and the standard of care and services offered, especially in nursing homes. The plan underscores a proactive outlook, focusing on identifying and bridging gaps in systems through strategic interventions.

Let’s explore the steps to implement a QAPI plan.
STEP 1: Leadership Responsibility and Accountability
The successful implementation of QAPI hinges on strong leadership. Leaders play a crucial role in fostering a culture that not only supports but actively embraces QAPI efforts.
Leaders’ involvement should empower every caregiver in the organization to participate in this quality improvement journey.
Here’s what leaders should do:
- Allow residents, their families, and staff to have direct interactions with board members and executive leaders. This not only generates support for QAPI but also bridges the gap between management and caregivers.
- Engage with residents and caregivers in their spaces. This not only shows your commitment but also gives you first-hand insight into the everyday activities of care delivery.
- Collaborate with top management to appoint dedicated individuals who will lead the QAPI efforts.
Your action plan should include:
- Developing a Steering Committee: Their responsibilities are vast – from developing plans to setting priorities for Performance Improvement Projects (PIPs). This committee should be well-versed in systems thinking, reflecting the complex, multifaceted nature of a nursing home. Ensure the inclusion of key leadership roles like the Administrator and the Director of Nursing.
- Active Engagement of a Medical Director: The medical director’s role is crucial. They should not only be involved but actively engaged in the QAPI processes.
- Providing Resources: Acknowledge the need for resources – be it time, equipment, or training. Facilitate team meetings, provide necessary tools, and consider specialized training for team members.
- Fostering Open Communication: A climate of open communication is non-negotiable. You should: maintain an open-door policy, encourage cross-departmental communication, create a safe space for quality concerns, and recognize how your current culture aligns with QAPI goals.
👉 Audit and inspection software like GoAudits can enable leaders to monitor compliance in real-time. They can access custom dashboards to view key performance indicators, facilitating data-driven decision-making and resource allocation. With instant reporting, leaders are always informed and can act swiftly to address any issues.
STEP 2: Develop a Deliberate Approach to Teamwork
Teamwork is the backbone of effective QAPI. However, it’s more than about having people work together.
First, let’s address a common misconception: working together doesn’t automatically constitute a team. A functional team in QAPI has distinct characteristics:
- Every team member knows the team’s objective
- Each participant has a specific role, contributing their expertise
- All members are committed and contribute actively
Team roles often reflect members’ professional backgrounds, such as nurses, social workers, or physical therapists. However, in QAPI, this extends beyond conventional roles. Let’s see how:
- Task-Oriented Teams: These are formed for specific issues, their scope is limited and focused.
- Performance Improvement Project (PIP) Teams: They undertake longer-term challenges. When forming a PIP, consider the team’s purpose and the mix of skills needed. Here are some practical examples of PIP team composition:
- A PIP focusing on outdoor activities for residents included grounds personnel for insights on snow removal and outdoor seating.
- Simplifying medication regimens? A pharmacist, even at an additional cost, was vital for a PIP team.
- For a PIP targeting fall reduction, including housekeeping was crucial, recognizing that environmental factors like corridor clutter contribute to falls.
Teams should be interdisciplinary. For instance, a team addressing medication administration should include both nursing and pharmacy professionals. But don’t overlook the value that family members can bring. They offer unique perspectives, although confidentiality limitations may apply.
👉 GoAudits’ digital inspections app offers features like automated notifications and real-time communication. This can help ensure that all team members are aligned with their roles and responsibilities. It creates a transparent and efficient workflow and a unified approach for successful QAPI implementation.
STEP 3: Take your QAPI ‘Pulse’ with a Self-Assessment
The third step in implementing QAPI involves conducting a thorough self-assessment within your organization. Self-assessment reflects the true status of QAPI’s integration into your healthcare organization.
- Conducting the Self-Assessment: You can use the GoAudits QAPI self-assessment checklist to quarterly or bi-annually measure and evaluate how well various components of QAPI have been implemented in your organization. It’s vital to involve the entire QAPI team and organizational leadership in this process, ensuring that the assessment is a collective and honest reflection of your progress.
- Analyzing and Using Assessment Results: Upon completing the self-assessment, the results will highlight the specific areas that require further development. It helps you pinpoint the gaps in your current QAPI implementation and recognize opportunities for growth and improvement.
👉 Explore GoAudits’ library of healthcare checklists. You can use these customizable checklists to accurately gauge the quality of care, identify areas for improvement, and ensure compliance.
Practical Tips for Effective Self-Assessment
- Engage your entire QAPI team and leadership in the assessment process. Diverse perspectives ensure a more accurate and holistic evaluation.
- Encourage transparency and honesty in responses. The objective is to gauge real progress, not to paint an overly optimistic picture.
- Conduct these self-assessments regularly. Whether it’s annually or semiannually, consistent evaluation helps track progress and make timely adjustments.
- Use the findings of the assessment to create actionable plans. Identify the areas needing improvement and develop strategies to address them.
- Keep a record of each assessment and the subsequent action plans. Sharing these with the team maintains transparency and keeps everyone aligned and accountable.
STEP 4: Identify Your Organization’s Guiding Principles
Identifying your organization’s guiding principles is a crucial step for the successful implementation of QAPI.
Healthcare organizations, including nursing homes, hospices, home health agencies, etc., consist of various departments with interdependent functions. Guiding principles help you align the diverse functions of your facility with a core philosophy and maintain a cohesive approach to quality and performance improvement.
This step demands the collective insights of senior leadership and their involvement can ensure that the principles resonate with the broader vision and operational reality of the facility.
With these principles in place, you are better equipped to develop a comprehensive QAPI plan. It will guide your team in making informed decisions and setting programmatic priorities that align with your organization’s overarching objectives.
STEP 5: Create Your QAPI Plan
Every healthcare organization is distinct, with its own set of challenges and opportunities. Your QAPI plan should reflect this uniqueness. Whether it’s addressing the specifics of your sub-acute care unit, your dementia care unit, or your palliative care program, ensure that the plan includes all aspects of your facility.
The effectiveness of your plan hinges on its relevance to your specific setting and the diverse needs of your residents, including younger individuals who may require a different approach to quality of life.
If you’re part of a larger organization or corporation, you might already have access to a corporate quality plan. While it’s beneficial to align with broader organizational goals, your QAPI plan needs its own identity. It should provide enough flexibility to address local priorities and challenges while maintaining consistency with the overall quality objectives.
A successful QAPI plan requires regular assessment and refinement to stay relevant and effective. As your healthcare organization evolves, so should your QAPI plan. This ensures that your quality improvement efforts are always aligned with current needs and best practices in healthcare.
STEP 6: Conduct a QAPI Awareness Campaign
It’s essential to keep everyone informed about your QAPI plan, using varied methods and frequent updates. To foster a deep understanding, break down the QAPI material into digestible pieces, using relatable examples and interactive exercises. Consider using real scenarios from your facility to make the learning more relevant.
Demonstrate through examples how systems should either support quality care and sound business practices or be modified. Encourage caregivers to contribute their own examples and thoughts.
Also, extend this awareness to consultants, contractors, and collaborating agencies. They are part of your system and should be aligned with your QAPI approach. Emphasize the importance of every caregiver in raising quality concerns and thinking systemically.
Engage your team in exercises that cross disciplines and roles. For example, have activities personnel discuss how their work affects others and vice versa. Address real issues, like residents not being able to stay up late due to staffing limitations, and brainstorm solutions together.
Residents and their families are integral to your QAPI efforts. Make sure they know their perspectives are valued and crucial in decision-making and process improvements. Use resident and family councils and other forums to discuss and announce QAPI initiatives. Request their input on quality concerns, and use this feedback to identify and address areas for improvement proactively.
Try to understand issues from the residents’ perspective. For example, a 10-minute response time might seem adequate from a staff viewpoint but can feel interminable for a resident waiting for assistance.
Including QAPI information in routine communications with residents’ families can also help in keeping them informed and involved.
STEP 7: Develop a Strategy for Collecting and Using QAPI Data
The systematic collection and effective use of QAPI data is paramount for all healthcare organizations.
Your team’s first task involves deciding what data needs routine monitoring. This selection should include various areas, including clinical care (like pressure ulcers, patient fall risk, and infection control), medication management, resident satisfaction, patient care plans, state survey outcomes, and administrative processes. Even data on caregiver turnover, staffing patterns, and financial aspects are invaluable.
👉 GoAudits’ real-time insights and dashboards can provide a comprehensive overview of these metrics, offering immediate visibility of results and areas for improvement.
Merely collecting data won’t suffice. Collating and interpreting data systematically is key. An auditing software like GoAudits allows you to instantly generate detailed, engaging, and informative reports. These reports are automatically generated at the end of each inspection, pre-populated with attached photos, assigned actions, time stamps, geo-location, and user names, saving you time and ensuring accuracy.

Setting realistic yet challenging targets is your next step. GoAudits’ smart scoring functionality allows you to assess the overall outcome of an audit at a glance, as well as specific scores by section. This information helps you set progressive targets that align with both short and long-term objectives.
For instance, reducing unplanned rehospitalizations, maybe initially by 15% and subsequently by an additional 10%.
Benchmarking is equally essential. The most relevant benchmarks are often your past performances. GoAudits’ historical trends reports enable you to quickly see repeating issues and past audit results. This information allows you to set progressive targets based on your past performances and motivate your teams. For example, you can aim to improve hand-washing compliance from 66% to 90% in a quarter.
Paying attention to what happens post-discharge, whether in hospitals or homes, is important. Analyzing discharge rates, preventable hospitalizations, and post-hospitalization outcomes offers insights into the effectiveness of your care and areas needing improvement.
Finally, have a clear plan for the data review process. Determine who examines which data and how frequently. Data collection is fruitless unless it’s put to use. Assign responsibilities and define the frequency for review and interpretation. This ensures that the data you collect serves its purpose of enhancing care quality and efficiency.
👉 GoAudits’ tasks and workflows enable you to set up custom workflows and rules for report distribution, approvals, tasks, and reminders, involving the right people at the right time.
STEP 8: Identify Your Gaps and Opportunities
You must use a variety of data sources to pinpoint patterns or deficiencies in your systems of care that could lead to quality issues or, conversely, identify areas for improvement. GoAudits’ advanced analytics platform helps you pinpoint patterns or deficiencies in your systems of care that could lead to quality issues.
Here are some potential areas to consider when reviewing your data:
- Minimum data set (MDS) data to detect recurring problem patterns
- State survey results
- Resident care plans
- Trends in complaints
- Resident and family satisfaction
- Caregiver turnover patterns
- Patterns of ER and hospital usage
Discuss quality themes with residents and caregivers. Their unique perspectives might reveal patterns or root causes not previously considered. Host small group meetings with caregivers and arrange sessions with your Resident Council.
This step should naturally lead to the next steps involving the selection of PIPs. Target ‘high risk, high volume, problem-prone areas’ affecting quality of care or life.
Recognize your achievements; they are as important as identifying areas for improvement.
STEP 9: Prioritize Quality Opportunities and Charter PIPs
The next step in implementing QAPI is recognizing and prioritizing quality improvement opportunities. Distinguishing between what seems like a problem and what can be an opportunity for growth is key to performance improvement.
When prioritizing, focus on issues that are high-risk, frequent, or prone to problems. Problems leading to resident suffering shouldn’t be overlooked. It’s important to remember that all identified issues need attention, not all require PIPs.
Initiate PIPs with issues that seem solvable in the short term. It will help you ensure both immediate and long-term quality improvements.
The chartering of a PIP team signifies a formal commitment to addressing a specific problem. Include direct caregivers like nursing assistants, and if the issue is related to a specific area like dietary choices, include relevant department members in the team.
Chartering a PIP team signifies the seriousness of the assignment and mandates regular reporting to the Steering Committee.
👉 GoAudits’ task management and workflow automation features facilitate seamless collaboration and ensure timely reporting.
A leader, either appointed in the charter or elected by the team, steers the PIP team. Early in the process, the team should outline a timeline and budget. GoAudits’ intuitive interface allows for easy scheduling of audits and tracking of action completion, providing a clear overview of the project’s progress.
STEP 10: Plan, Conduct, and Document PIPs
The tenth step of implementing QAPI focuses on planning, conducting, and documenting PIPs.
Performance Improvement Projects or PIPs begin with a comprehensive data review, pinpointing areas that significantly impact resident care. By defining the scope of each PIP, you ensure manageable, targeted improvements.
Here’s how to implement PIPs successfully:
- Consider every PIP a learning process
- Determine what data and resources are required
- Set a realistic timeline for your PIP and communicate this to your Steering Committee
- Identify and acquire any necessary supplies or equipment for smooth implementation
- Select or create appropriate tools to measure progress
- Prepare and present the results of your PIP
- Use the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle for structured problem-solving
- Keep the Steering Committee informed about your progress and findings
Understanding the PDSA cycle
- Plan: Dive deep into the problem. Develop a strategy for improvement and decide on the metrics for measuring change.
- Do: Implement your plan and gather data.
- Study: Analyze the data. What did you learn? Did the changes have the desired effect?
- Act: Based on your findings, decide the next steps. Adapt, adopt, or abandon the changes. This decision shapes your future actions.

STEP 11: Getting to the ‘Root’ of the Problem
This step underscores the importance of understanding problems in their entirety before finding their solutions.
At the core of process improvement is the recognition that problems are often multifaceted and can be symptoms of deeper, systemic issues. It’s easy to fall into the trap of hastily developing solutions without fully grasping the problem. Such an approach can lead to temporary fixes rather than sustainable improvements. Problems in healthcare settings frequently involve multiple departments, each bringing its unique challenges and perspectives.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is the structured methodology designed to dig beneath the surface to uncover the true causes of performance issues. It encourages teams to look beyond the most immediate or apparent reasons for a problem.
👉 GoAudits reporting and analytics features help you dive deeper into data and trends, providing practical insights that are crucial for RCA.
It’s not uncommon to identify more than one root cause. By categorizing these causes and contributing factors, you can develop targeted actions for improvement.
To integrate RCA effectively into your QAPI efforts, consider the following steps:
- Begin by examining previous RCA examples
- Use RCA in response to an adverse event. Discuss and analyze these events with your team to gain practical insights.
- Make RCA a part of your team’s regular training sessions
STEP 12: Take Systemic Action
Taking systemic action goes beyond merely identifying root causes. It involves creating and executing strategies that not only address these causes but also bring about sustainable change.
When an issue arises, the instinctive response might be to urge caregivers to exercise greater caution. However, these approaches often fall short as they do not fundamentally alter the underlying systems or processes. The key lies in selecting actions directly tied to the root causes, leading to systemic changes rather than just supporting existing procedures.
For interventions to be truly effective, they must:
- Focus on eliminating the root cause behind the problem
- Provide long-term solutions rather than temporary fixes
- Ensure a greater positive than a negative influence on other processes
- Be practical, achievable, objective, and measurable
Before wide-scale implementation, consider a pilot test in a specific area of your facility.
The Department of Veterans Affairs National Center for Patient Safety categorizes corrective actions into three levels:
- Weak Actions: Relying on staff memory and training, enhancing existing processes. Examples include double-checks, warnings, and new policies.
- Intermediate Actions: Aid staff memory and modify processes. Examples include workload reduction, software modifications, and checklists.
- Strong Actions: Change or redesign processes, providing robust controls. Examples include physical changes like grab bars, forcing functions like the specific design of gas lines, and simplification like unit dosing.
👉 GoAudits enables healthcare organizations to create and manage corrective actions, ensuring that root causes are addressed and sustainable changes are implemented. Set up custom workflows to assign corrective actions, send reminders, and facilitate seamless collaboration between team members, from frontline caregivers to management.
GoAudits ensures strong accountability by assigning corrective actions to specific team members, making them aware of the issue, priority, and due date.
Now, let’s see how these steps are based on the five key elements of QAPI.
Key Elements of a QAPI Plan
CMS has defined five elements as the building blocks of effective QAPI. These building blocks provide a framework for the implementation of the QAPI program.

1. Design and scope
Beyond mere regulatory compliance, QAPI needs to involve the full spectrum of services and departments within your healthcare organization. It emphasizes not only clinical care but also the quality of life and resident choice. Incorporate best practices and evidence-based goals into your QAPI program.
2. Governance and leadership
Leadership involves the active participation of staff, residents, and their families. Adequate resources, including personnel, equipment, and training, are crucial. Leadership must also develop sustainable policies that maintain the integrity of QAPI, balancing resident rights and choices with safety and quality.
3. Feedback, data systems and monitoring
Effective QAPI programs are grounded in feedback and data systems. Your facility should have mechanisms to monitor a wide array of performance indicators and benchmarks for various care processes and outcomes. This involves collecting feedback from staff, residents and families, with particular attention to tracking, investigating, and preventing adverse events.
4. Performance improvement projects (PIPs)
PIPs are focused initiatives aimed at addressing specific problems, either in one area or facility-wide. They involve systematic information gathering to understand and resolve issues. Pinpoint problems, intervene effectively, and elevate the quality of care and services in a focused way.
5. Systematic analysis and systemic action
The final element is a systematic approach to understanding problems in their entirety, including their causes and implications. This involves root cause analysis to identify underlying issues and their causes. Systemic actions then span across all systems involved, ensuring not just the resolution of current issues but the prevention of future occurrences.
Learn More: A Complete Guide to QAPI in Healthcare
Differences Between QAPI Plan & QAPI Program
While often used interchangeably, a QAPI plan and a QAPI program are distinct elements in healthcare quality improvement.
- QAPI Plan
This is a formal document, a written representation of your organization’s commitment to quality improvement. It outlines the strategies, objectives, and actions your team will undertake. The QAPI plan is a dynamic entity, continually evolving as your organization grows and learns. It’s also a regulatory requirement, made available to management bodies like state agencies, federal surveyors, or the CMS upon request.
- QAPI Program
On the other hand, a QAPI program includes the broader, ongoing activities and initiatives undertaken within an organization to enhance quality. It refers to the actual implementation of the strategies and objectives outlined in the QAPI plan. The QAPI program integrates quality assurance—a reactive, retrospective process to ensure quality standards are met—and performance improvement—a proactive, forward-thinking approach to continually better care and services.
Implement a QAPI Plan with Healthcare Compliance Software
GoAudits is an all-in-one healthcare compliance software that offers a range of features to help you successfully implement QAPI.
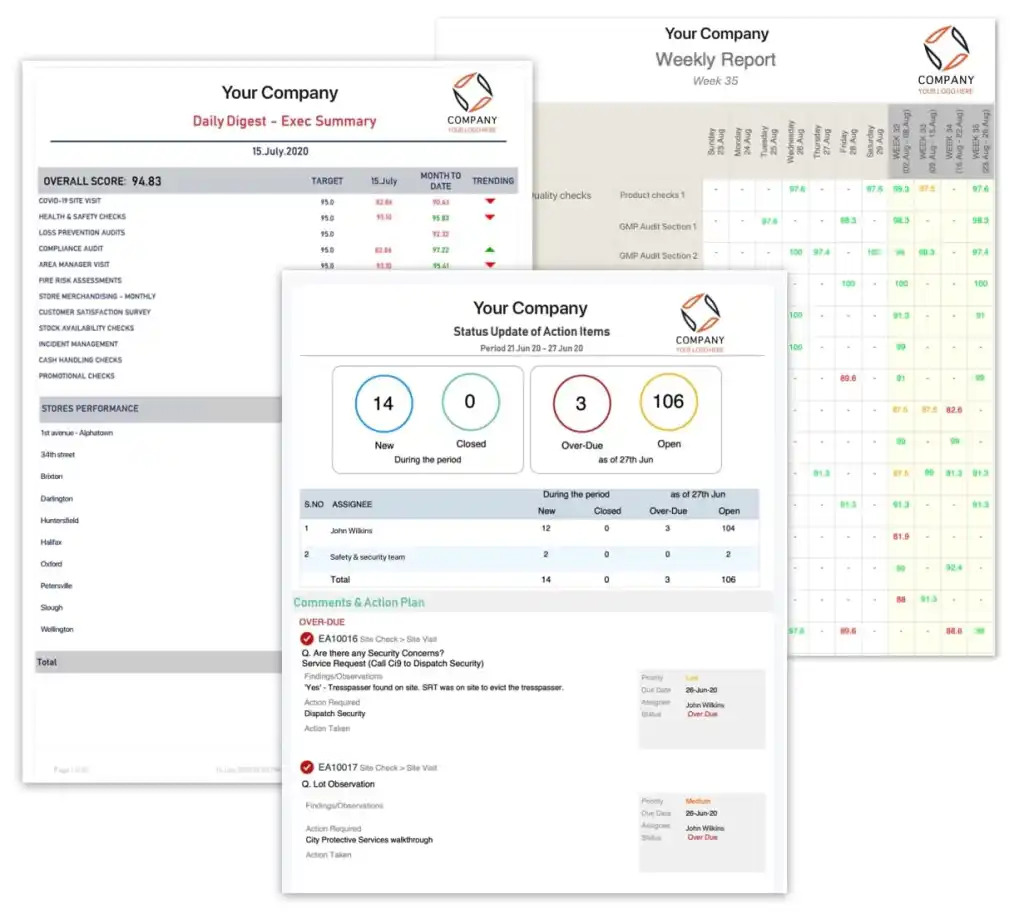
- With its comprehensive and customized checklists, identify the key aspects of care, treatment, and services that are important to monitor. Focus on clinical quality, patient safety, patient experience, or operational processes with GoAudits.
- Customize these checklists yourself or have the GoAudits team digitize them for you to ensure your checklists align perfectly with your healthcare facility’s specific QAPI requirements.
- Gain a real-time overview of your business performance metrics with smart dashboards. View audit scores across locations, teams, or specific topics, for valuable insights into your organization’s strengths and areas for improvement.
- Quickly identify trends, track progress, and make data-driven decisions to enhance the quality of care you deliver.
- Configurable daily, weekly, or monthly email summaries provide you with a snapshot of your organization’s performance, ensuring that you stay on top of things and can take necessary actions promptly.
- Instantly generate comprehensive reports at the end of each inspection. Customize them to fit your requirements, displaying historical data, trends, and recurring issues.
- Assign corrective actions during inspections, to specific team members, internally or externally, with clear details of priority and due dates.
- Track task completion status and overdue task reports are readily available in a centralized dashboard, ensuring that no issues slip through the cracks.
Free & Customizable QAPI Templates and Healthcare Audits checklists
In addition to the QAPI Plan Template and QAPI Self Assessment Tool, here are some additional healthcare checklists you can use to ensure high-quality care:




