The Supplier Ethical Data Exchange (Sedex) is a platform dedicated to enhancing transparency and accountability in supply chain operations. The Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit (SMETA) is a comprehensive audit methodology designed to assess labor standards, health and safety, environmental performance, and business ethics across various industries. SMETA 2 and SMETA 4 pillar audits are applicable across a broad spectrum of industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, food and beverage, apparel and textiles, pharmaceuticals, retail, logistics, hospitality, electronics, and chemicals. Sedex audits can enhance transparency across the supply chain, mitigate potential risks, ensure compliance with ethical standards, and build trust with consumers and partners.
This article will help you understand the scope and process of both SMETA 2 and SMETA 4 pillar audits, their importance in ensuring ethical supply chain practices, and the key differences between the two.
- SEDEX SMETA Requirements: 4 Pillars of SMETA
- What is a SMETA Audit?
- What are the Main Differences Between 2-Pillar and 4-Pillar SMETA Audits?
- How to Prepare for Sedex Audits?
- On-Site Sedex Audit Process
- What to Do After a Sedex Audit?
- Prepare for SMETA 2 & 4 Pillar Audits with Internal audits
- What are the Benefits of SEDEX Audits?
SEDEX SMETA Requirements: 4 Pillars of SMETA
To align your operations with global ethical standards, understanding the Sedex SMETA 4 pillar framework is essential. Developed by Sedex, SMETA audits assess compliance across 4 critical areas: Labor Standards, Health & Safety, Environment, and Business Ethics. These SMETA 4 pillars are grounded in the Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI) Base Code and International Labour Organization (ILO) conventions, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of ethical practices.
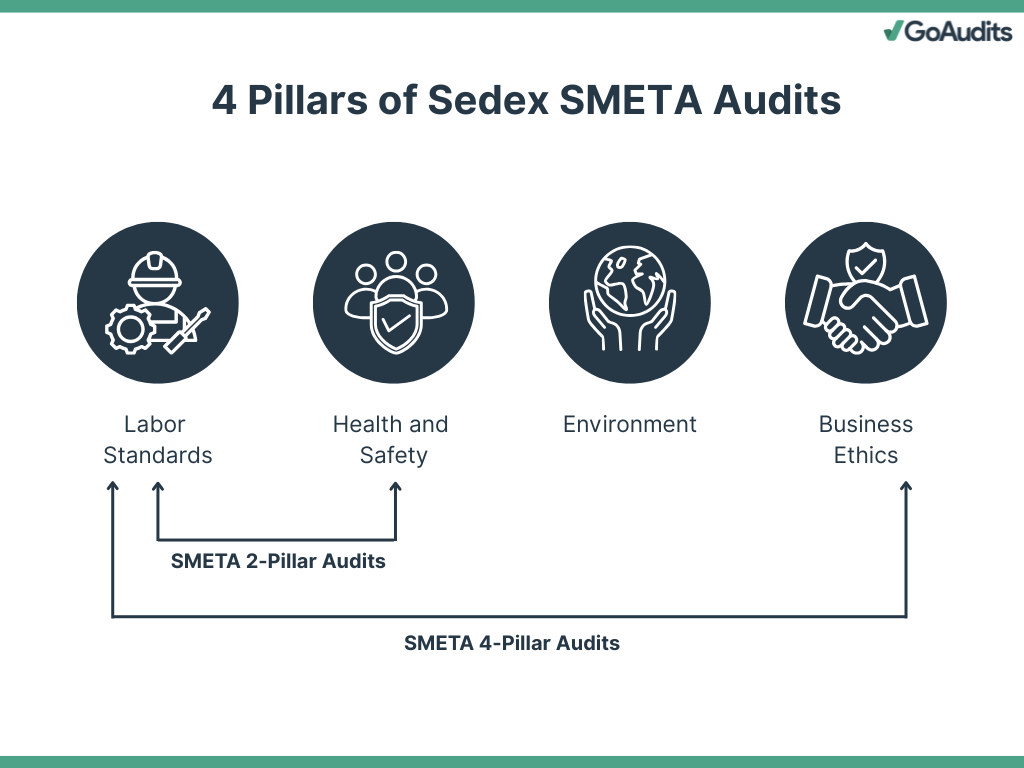
1. Labor Standards
It evaluates your adherence to fair labor practices, focusing on:
- Wages and Working Hours: Ensuring employees receive at least the minimum wage and work within legally mandated hours.
- Child and Forced Labor: Prohibiting employment of underage workers and any form of forced labor.
- Freedom of Association: Respecting workers’ rights to join unions and engage in collective bargaining.
- Non-Discrimination: Promoting equal opportunities regardless of race, gender, or other protected characteristics.
2. Health & Safety
The health & safety pillar examines the measures in place to protect workers’ well-being:
- Workplace Safety: Identifying and mitigating hazards to prevent accidents.
- Emergency Preparedness: Establishing procedures for emergencies, including fire drills and first aid.
- Sanitation and Hygiene: Maintaining clean facilities and access to potable water.
- Health Services: Providing necessary medical support and health education.
3. Environment
This pillar evaluates your organization’s environmental impact and sustainability efforts by reviewing environmental policies, monitoring data, and improvement plans:
- Resource Management: Efficient use of energy, water, and raw materials.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal and recycling practices to minimize pollution.
- Emissions Control: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and monitoring air quality.
- Compliance: Adhering to environmental laws and obtaining necessary permits.
4. Business Ethics
This is the last SMETA pillar, which assesses the integrity of your business practices. It involves the evaluation of codes of conduct, training programs, and reporting mechanisms to ensure ethical operations.
- Anti-Corruption Measures: Implementing policies to prevent bribery and corruption.
- Transparency: Ensuring accurate record-keeping and honest communication.
- Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive information and respecting privacy.
- Fair Competition: Engaging in lawful and ethical competitive practices.
What is a SMETA Audit?
SMETA is a globally recognized audit methodology designed to assess and improve ethical and responsible business practices within supply chains. SMETA is one of the most widely used social audit formats in the world, helping organizations evaluate and enhance standards.
There are two main types of Sedex SMETA audits, each varying in scope and depth.
SMETA 2 Pillar Audit
A SMETA 2 pillar audit focuses on two areas: labor standards and health & safety. It helps businesses identify and address ethical risks within their operations and supply chains. The SMETA 2 pillar audit can also include supplementary elements such as entitlement to work, homeworking, management systems, subcontracting, and a simplified environmental assessment.
The SMETA 2-pillar audit specifically covers labor and health & safety standards, as defined by the ETI Base Code. Other social audits, such as SA8000, BSCI, etc., may have different focuses, standards, or frameworks, and may not follow the ETI Base Code as their primary guideline. The SMETA 2-pillar audit is often a baseline requirement for suppliers in many global supply chains, while other social audits may be used for more specialized or comprehensive compliance needs.
The main difference between SMETA’s extended and shortened environment assessment is the depth and scope of the environmental review. The extended assessment in a 4-pillar audit provides a more comprehensive review, including local environmental impacts and responsible sourcing practices. The shortened assessment in a 2-pillar audit offers a preliminary review of environmental management practices.
Organizations across various industries may need a SMETA 2 pillar audit, particularly those:
- Supplying to retailers or brands that mandate ethical audits.
- Operating in regions with high risks related to labor and safety practices.
- Seeking to demonstrate commitment to ethical standards and improve supply chain transparency.
The timing for a SMETA 2 pillar audit depends on various factors:
- Client Requirements: If a client mandates an ethical audit, organizations should schedule it accordingly.
- Risk Assessment: Companies operating in high-risk regions or industries should consider regular 2 pillar SMETA audits to mitigate potential issues.
- Internal Policies: Organizations aiming to uphold high ethical standards may opt for periodic audits to ensure continuous compliance and improvement.
Typically, 2 pillar SMETA audits are conducted annually or biennially, but the frequency may vary based on specific organizational needs and stakeholder expectations.
SMETA 4 Pillar Audit
The SMETA 4 pillar audit is a comprehensive assessment framework designed to assess and improve a company’s ethical performance and evaluate its compliance with ethical trade practices across all four key areas discussed above.
- Labor Standards
- Health and Safety
- Environmental Management
- Business Ethics
The typical duration of a SMETA 4-pillar audit generally ranges from 1 to 4 days on-site, depending primarily on factors such as the number of employees, the size and complexity of the site, the number of buildings, and any special requirements like complex production processes or language barriers.
SMETA 4 pillar audits are particularly relevant for:
- Companies with complex supply chains
- Exporters and suppliers
- Organizations committed to corporate social responsibility (CSR)
The necessity and frequency of SMETA 4 pillar audits depend on various factors:
- Customer or Buyer Requirements: Some clients may mandate regular audits to ensure ongoing compliance with ethical standards.
- Industry Standards: Certain industries may have specific guidelines dictating the need for periodic audits.
- Risk Assessment Outcomes: Companies may choose to conduct audits based on identified risks within their operations or supply chains.
To maintain compliance and address any identified issues, it is advisable to schedule subsequent SEDEX audits annually or biennially, depending on the company’s risk profile and stakeholder requirements.
SMETA audits are performed by independent third-party auditors affiliated with Sedex. These auditors are trained to assess compliance with the ETI Base Code and relevant local laws. Organizations can select approved audit companies through the Sedex platform to conduct their assessments.
What are the Main Differences Between 2-Pillar and 4-Pillar SMETA Audits?
While 2-pillar audits cover the basics, the 4-pillar audit offers a deeper, more structured approach across multiple dimensions of the Sedex audit process.
| Aspect | SMETA 2-Pillar Audit | SMETA 4-Pillar Audit |
| Core Focus | Labor Standards, Health & Safety | Includes 2-pillar focus plus Environment and Business Ethics |
| Environmental Review | Simplified Assessment | Comprehensive Assessment |
| Business Ethics | Not Included | Included |
| Applicability | Suitable for organizations with limited environmental impact | Ideal for organizations with significant environmental and ethical considerations |
| Audit Depth | Foundational assessment | In-depth, comprehensive evaluation, making it more suitable for companies aiming for advanced sustainability and ethical standards |
How to Prepare for Sedex Audits?
Here’s a step-by-step guide to prepare for on-site SMETA audits.
1. Register with Sedex
Begin by registering on the Sedex platform. Choose the appropriate membership type (A or AB) based on your role in the supply chain. Upon registration, you will receive a Sedex Company Reference (ZC) number, which is essential for linking with your customers and accessing necessary tools like the self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ).
2. Link with Your Customers (Supplier Linking)
After registration, link your Sedex account with your customers by using their ZC numbers. This connection allows for the sharing of audit reports and SAQ responses.
3. Conduct a Gap Analysis
Perform a thorough gap analysis to identify discrepancies between your current practices and the requirements outlined in the Sedex audit criteria. It helps pinpoint areas that need improvement and ensure that you address potential non-compliances before the actual audit.
4. Complete the Sedex Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ)
Access and complete the SAQ on the Sedex platform. The SAQ gathers information about your company’s operations, labor standards, health and safety practices, and environmental management systems. Ensure that your responses are accurate and reflective of your current practices, as this information will be reviewed by the auditor.
5. Gather Necessary Documentation
Compile all relevant documents that demonstrate compliance with ethical standards, including employment contracts, payroll records, health and safety policies, environmental management procedures, training records, and any previous audit reports and corrective action plans.
6. Brief Staff and Management
Educate your staff and management about the upcoming audit. Ensure they understand the purpose of the audit, what it entails, and their roles during the process. Conduct training sessions if necessary to prepare them for potential interviews and to reinforce the importance of compliance with ethical standards.
7. Choose a Sedex-Approved Auditing Company
Select an auditing company that is approved by Sedex to conduct SMETA audits. Ensure that the auditor is familiar with your industry and understands the specific requirements of your operations. Coordinate with the auditor to schedule the audit at a time when your facility is fully operational, as audits should be conducted during periods of peak activity.
8. Determine the Scope: 2-Pillar or 4-Pillar SMETA Audit
Decide whether you require a 2 pillar SMETA audit or a 4-pillar audit. The choice depends on your customer’s requirements and the nature of your business operations.
9. Conduct a Pre-Audit
Before the official audit, consider conducting an internal pre-audit to assess your readiness. It helps in identifying any remaining gaps and allows you to address them proactively. Review your SAQ responses, verify the availability and accuracy of documentation, and ensure that staff are prepared for the audit process.
👉 Free & Customizable Audit Templates
GoAudits offers the following checklists to help you perform internal audits and prepare for 2-pillar and SMETA 4 pillar audits. You can sign up for free and start using these checklists.
→ SMETA Audit Checklist
→ SMETA 6.1 4-Pillar Audit Checklist
→ SMETA 7.0 Audit Checklist for 4-Pillar
→ SMETA 7.0 2-Pillar Audit Checklist
On-Site Sedex Audit Process
Let’s take a closer look at what the actual Sedex audit process looks like.
1. Opening Meeting
The Sedex audit commences with an opening meeting involving the site’s management and, where applicable, employee representatives. During this session, the auditor outlines the audit’s scope, objectives, and methodology, referencing standards such as the ETI Base Code and relevant local laws. The meeting also confirms logistical details, including the audit schedule, required documentation, and arrangements for site access and employee interviews.
2. Site Tour
Following the opening meeting, the auditor conducts a comprehensive tour of the facility. It covers all operational areas, including production zones, storage areas, employee amenities, and, if applicable, worker accommodations. This is done to observe working conditions firsthand, assess health and safety measures, and verify compliance.
3. Documentation Review
The auditor then examines relevant documentation to assess the site’s adherence to labor and ethical standards. Key documents include employment contracts, payroll records, working hour logs, health and safety policies, training records, and any permits or licenses required by law. It helps corroborate observations from the site tour and provides evidence of the site’s compliance with applicable standards.
4. Worker and Management Interviews
Interviews are conducted with both management and a representative sample of workers. Management interviews focus on understanding the site’s policies, procedures, and management systems. Worker interviews, conducted confidentially, aim to gather insights into actual working conditions, treatment by management, and awareness of rights and grievance mechanisms, validating information obtained through documentation and observation.
5. Closing Meeting
At the conclusion of the audit, a closing meeting is held with management and, where appropriate, employee representatives. The auditor presents the findings, highlighting areas of compliance and non-compliance. A corrective action plan report is prepared to ensure that the site understands the audit outcomes and the steps required for continuous improvement.

What to Do After a Sedex Audit?
Once the Sedex audits have been completed, here’s what you need to do.
1. Prepare and Submit the Audit Report and Corrective Action Plan (CAPR)
Upon receiving the audit report, review it thoroughly to understand the findings. Collaborate with your audit firm to develop a corrective action plan report (CAPR) that outlines specific actions to address each non-compliance issue, responsible parties, and timelines. Once finalized, upload both the audit report and the CAPR to the Sedex platform.
2. Address Non-Conformities
Implement the corrective actions as detailed in the CAPR. This may involve revising policies, enhancing training programs, or improving workplace conditions. Engage with your team to ensure that these changes are effectively integrated into daily operations. Regularly monitor progress and document evidence of improvements to demonstrate compliance.
3. Conduct Follow-Up Audits if Required
Depending on the severity of the non-conformities, a follow-up audit may be necessary to verify the implementation of corrective actions. Schedule this audit in coordination with your audit firm and ensure that all remedial measures are in place beforehand. The follow-up audit will assess the effectiveness of the actions taken and confirm compliance with SMETA standards.
4. Maintain Ongoing Compliance
Establish internal mechanisms to regularly review and update your practices in line with ethical standards. Use the Sedex platform to monitor compliance status, track improvements, and share updates with stakeholders. Engage in continuous training and development programs to foster a culture of ethical responsibility within your organization.
Prepare for SMETA 2 & 4 Pillar Audits with Internal audits
Are you preparing for a SMETA 2 or 4-pillar audit? GoAudits helps streamline the process from internal audits to corrective action, ensuring compliance, efficiency, and transparency every step of the way. GoAudits offers an intuitive mobile app designed specifically for auditors and site teams. No training is needed, just open the app and get started.
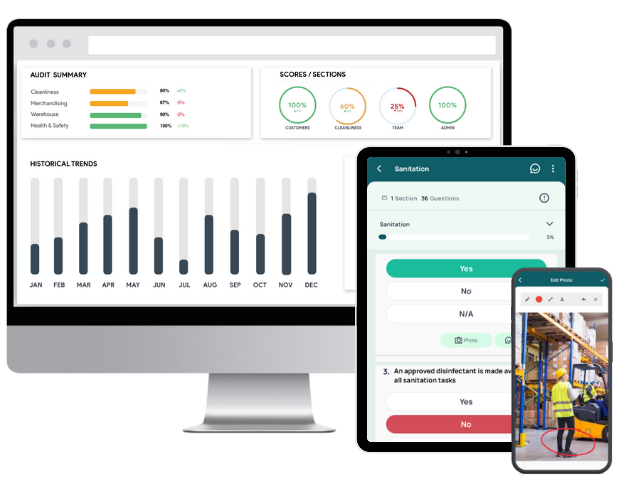
- Whether you’re aligning with the SMETA 2 pillar or extending to the SMETA 4 pillar audit scope, you can fully tailor your checklists. Use ready-made templates, build your own from scratch via drag-and-drop method, or send your existing checklist in any format and we’ll digitize it for you at no cost within 48 hours.
- Perform internal audits up to 5 times faster, even if you’re offline. Attach photos directly from your device, annotate them as needed, and capture other details with time stamps, geolocation, and e-signatures for complete traceability.
- Automatically generate comprehensive reports right at the end of each audit. Every report includes photos, assigned corrective actions, timestamps, and geolocation data. You can choose from several layouts, customize your audit reports, and share them with relevant stakeholders.
- Assign corrective actions on the spot, define priority levels and deadlines, and track them through to completion. Automatic reminders, escalations, and approval workflows ensure nothing is missed. The centralized dashboard offers real-time visibility into task status across sites and teams.
- Analyze trends over time and identify recurring issues with smart dashboards. Visualize audit scores and performance by site, and review historical data to assess systemic problems and inform your continuous improvement plans.
What are the Benefits of SEDEX Audits?
Implementing Sedex audits, particularly the comprehensive 4-pillar SMETA audit, offers numerous benefits that enhance your supply chain’s efficiency, transparency, and sustainability.
- The 4-pillar SMETA audit extends beyond labor and health & safety standards to include environmental performance and business ethics. It ensures that your operations align with international ethical standards.
- Sedex audits provide a clear view of your supply chain activities, enabling you to track, monitor, and understand every aspect of your operations. It facilitates early identification of potential risks or unethical practices, allowing for timely corrective actions and building trust with stakeholders.
- Regular Sedex audits help you assess and monitor supplier performance. It promotes accountability and encourages suppliers to maintain high standards, leading to an overall improvement in supply chain quality.
- Demonstrating commitment to ethical practices through Sedex audits enhances your organization’s reputation. Stakeholders, including customers and investors, are more likely to trust and engage with businesses that prioritize ethical sourcing and transparency.
- Sedex audits are globally recognized and widely accepted across industries, which brings several benefits, including standardized assessments, greater efficiency, and eliminating the need for multiple audits.
- Sedex audits help you mitigate compliance risks, safeguarding your organization against legal challenges and supply chain disruptions.
- Sedex audits provide detailed insights and recommendations, enabling you to develop and implement actionable improvement plans. They facilitate the continuous enhancement of your supply chain practices.
- Through the evaluation of environmental performance, Sedex audits encourage the adoption of sustainable practices. This includes efficient resource utilization, waste reduction, and responsible sourcing, contributing to environmental conservation and long-term business viability.
- Complying with Sedex 4 pillar requirements differentiates your brand in the global market, attracting customers and partners who value corporate responsibility.





