Local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems capture hazardous substances directly at the source before workers can inhale them. Studies show that portable or fixed LEV systems can reduce exposure to welding fumes and similar hazards by 40% to 50% compared with natural ventilation. However, simply installing a LEV system is not enough. They must be thoroughly inspected to remain effective. That’s why LEV inspections are a legal requirement under COSHH for any workplace using LEV systems. LEV inspections verify that the system performs as intended, complies with legal requirements, and continues to protect workers from harmful airborne contaminants. Without these checks, employees are at risk and businesses are exposed to costly non-compliance.
This article will list the key components of LEV systems, steps to inspect them, common issues identified during these inspections, and more.
What are Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV) Inspections?
Local exhaust ventilation (LEV) is an engineering control system that captures hazardous substances, such as dust, mist, fumes, vapors, and gases, at their source and transports them away, typically to a filter or a safe emission point. LEV inspections are periodic examinations and tests to verify the effectiveness, legal compliance, and maintenance needs of LEV systems. They ensure that these systems continue to protect workers from dangerous exposures at the workplace.
👉 What is the correct frequency of LEV inspections?
The legal maximum interval for a full LEV inspection and test is every 14 months under the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) regulations in the UK. Some higher-risk applications (e.g., metal casting, abrading, jute manufacturing) require more frequent inspections, either monthly or every 6 months, depending on the process. Daily, weekly, and monthly routine visual checks and basic maintenance are recommended in addition to statutory inspections. Employers are required to keep LEV inspection and test records for at least 5 years.
What are the Consequences of Neglecting LEV Inspections?
Here are the major consequences of neglecting LEV inspections:
- Employees may suffer from respiratory diseases, skin irritation, or long-term illnesses due to unfiltered exposure to hazardous fumes, dust, and airborne contaminants.
- Unchecked exposure can lead to frequent sickness, increasing staff absence, and reducing workforce reliability.
- Failure to comply with Health and Safety Executive (HSE) or equivalent regulatory requirements can result in fines, enforcement notices, or even prosecution.
- Non-compliance undermines your commitment to employee safety, harming trust with staff, clients, and stakeholders.
- Neglected LEV inspections may contribute to workplace illness, leading to employee claims and rising insurance premiums.
- Ineffective or damaged systems left unchecked deteriorate faster, requiring expensive maintenance or full replacement.
- Blockages, leaks, or poor airflow performance remain undetected, compromising contaminant control.
- Poor air quality reduces concentration, comfort, and efficiency, directly affecting output and work quality.
- Equipment breakdown or enforced shutdowns due to unsafe conditions interrupt production and deadlines.
👉 Poor recordkeeping is one of the most common reasons businesses fail HSE inspections. Instead of relying on paper logs, GoAudits automatically stores inspection records for 5+ years — ready for any compliance check.
Key Components to be Checked During LEV System Inspections
During LEV inspections, several key components must be assessed. These include:
Hoods or Enclosures
Hoods or enclosures capture contaminants directly at the point of release. The design and positioning of a hood determine how effectively fumes, dust, or vapors are contained before they spread. Enclosures offer maximum protection by fully surrounding the process, while capture hoods rely on airflow to draw pollutants away.
Ducting
Ducting carries the captured air from the hood to the filtration unit. The ductwork must be correctly sized and laid out to maintain airflow and prevent losses. Smooth interiors reduce resistance, while proper sealing minimizes leaks. Incorrect duct design can cause blockages or reduced efficiency.
Air Cleaner (Filters or Scrubbers)
Air cleaners remove hazardous substances from the extracted air. Filters trap dust and particulate matter, while scrubbers neutralize gases or vapors through chemical or liquid treatment. The type of air cleaner depends on the contaminants present.
Fan
The fan provides the energy to move air through the system. It must generate sufficient pressure to overcome resistance in the ductwork and filtration unit. Fan selection depends on the type of contaminant, the required airflow rate, and system pressure. Proper balancing ensures consistent and safe operation.
Discharge Point
It releases cleaned air back into the atmosphere or the workplace. Positioning is vital to avoid re-entry of contaminants into occupied areas. For outdoor discharges, the outlet height and direction must meet regulatory requirements. Recirculation systems require additional safeguards to protect workers.
System Point Indicators
System point indicators, such as pressure gauges or airflow monitors, verify that the LEV system is functioning within design parameters. They help identify blockages, leaks, or declining filter performance. Clear, accessible indicators allow workers and supervisors to check system performance at a glance.
Control Panel and Electrical Components
This manages the operation of the LEV system. It includes switches, alarms, and sometimes automated controls for variable airflow. Electrical components must be safe, reliable, and compliant with industrial standards. Integration with monitoring devices ensures early warnings of system faults.
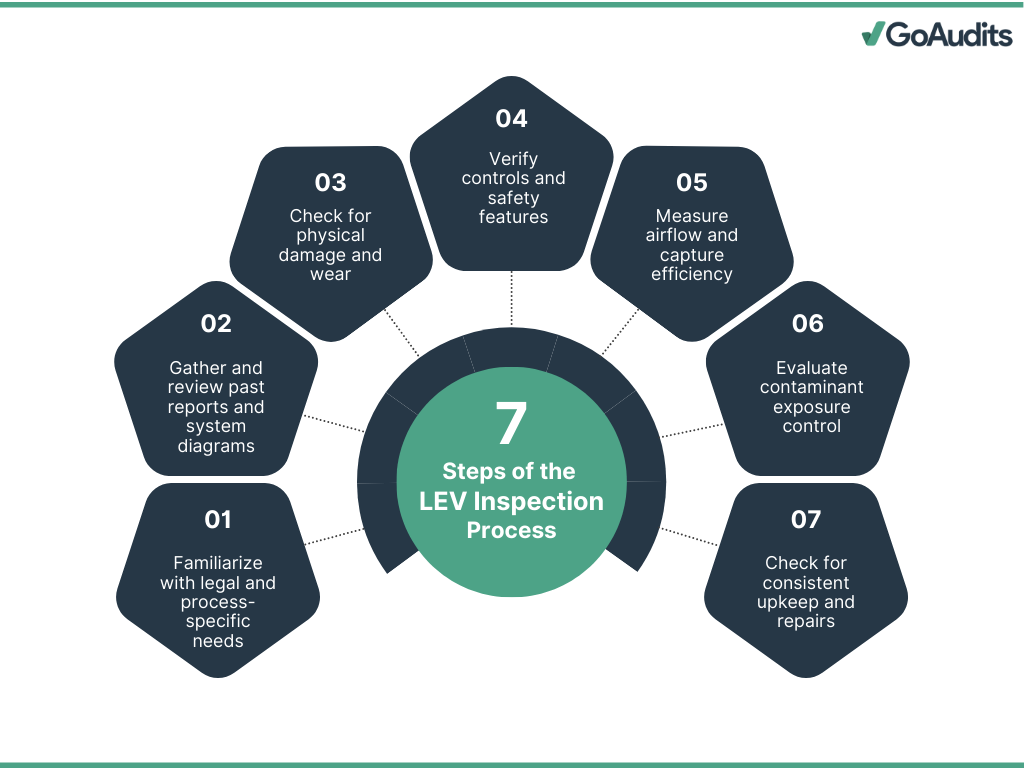
What are the Steps Involved in LEV Inspections?
Each LEV inspection follows a systematic process that involves the following steps.
Understanding LEV Inspection Requirements
Before conducting an inspection, you must be aware of the legal requirements. In most cases, LEV systems must undergo a Thorough Examination and Test (TExT) at least every 14 months. Certain high-risk processes, such as those involving respirable crystalline silica or asbestos, may require more frequent checks. You also need to maintain detailed records of each inspection, test results, and corrective actions for a minimum of five years. These documents are evidence of compliance and support ongoing system maintenance.
Pre-Inspection Preparation
Before the inspection, you should gather previous inspection reports, system diagrams, and maintenance records. Reviewing these documents helps identify recurring issues and system modifications. It is also essential to coordinate with site staff to arrange safe access to ducts, hoods, and filters without disrupting operations.
Visual Examination
The inspection begins with a detailed visual check of all system components. You should look for physical damage, corrosion, loose connections, leaks, blockages, and worn parts. A thorough visual check of key components discussed above often highlights early signs of failure that can compromise performance.
Functional Tests
Next, you must verify that all system controls and safety features operate as intended. This includes testing start/stop switches, airflow indicators, alarms, and interlocks with associated equipment. Functional tests confirm that operators receive timely warnings when the system is not performing properly.
Performance Testing
Performance tests measure whether the system achieves the required airflow and capture efficiency. Instruments such as anemometers, manometers, or smoke tubes are used to assess airflow rates, static pressure, and fume capture zones. Comparing the results with the design specifications ensures the system removes contaminants effectively.
Control Assessment
An LEV system is only effective if it controls worker exposure at the source. During this stage, you evaluate the system’s ability to keep contaminant concentrations below workplace exposure limits. Observing work practices and comparing measured airflow to occupational hygiene standards provides a clear assessment of risk control.
Examination of Maintenance Records
Finally, you must review the system’s maintenance records. Consistent filter replacements, duct cleaning, and fan servicing directly influence system reliability. Records should show scheduled maintenance, fault repairs, and any modifications. This review highlights gaps in upkeep that may affect long-term performance and compliance.
GoAudits all-in-one safety inspection software can help you perform LEV system inspections up to 5 times faster and ensure compliance with HSE regulations.
- Use ready-to-use, free LEV inspection checklists, or create custom ones tailored to your business needs.
- Capture inspection data directly on your device, even offline, with photos, e-signatures, timestamps, and geolocation.
- Instantly generate professional reports that include evidence, assigned actions, and scoring.
- Assign corrective actions in real time, track completion, and keep teams accountable with automated workflows, reminders, and notifications.
- Gain a complete view of inspection trends, recurring issues, and compliance levels, so you can identify risks quickly and prioritize improvements.
Common Issues Found During LEV Inspections
Understanding common issues highlighted by LEV inspections helps you address them proactively and maintain a safe working environment.
| Category | Examples of Common Issues & Failures |
| Operational and user-related issues | – Incorrect use of equipment, such as positioning materials outside the hood’s capture zone – Lack of operator training, leading to ineffective use – Obstructed hoods caused by storing tools or materials too close, reducing airflow and capture efficiency |
| System performance and mechanical issues | – Reduced airflow from blocked filters, worn fans, or damaged ductwork – Plugging and blockages in ducts handling dust or particulates – Leaks or loose duct connections causing suction loss – Mechanical failures such as broken fan blades or motor faults |
| Design and installation issues | – Complex duct runs or insufficient fan capacity making systems unreliable – Poor capture efficiency due to undersized or incorrectly positioned hoods – Incorrect duct sizing leading to low velocity and dust settlement – Inadequate or unsuitable filtration allowing contaminants back into the workspace |
| Maintenance and recordkeeping issues | – Neglected servicing of filters, fans, and ductwork reducing efficiency – Lack of routine airflow checks leading to unnoticed failures – Poor recordkeeping making compliance and performance demonstration difficult |
What to Do After an LEV System Inspection?
Here are the steps you should take after a LEV inspection.
Review the Inspection Report
Start by carefully reviewing the inspection report to understand the system’s current condition and the urgency of required actions. Focus on performance test results, identified deficiencies, and compliance with legal standards. Highlight any areas flagged as non-compliant or at risk.
Take Corrective Action
Address all issues noted in the report without delay. Replace worn parts, repair damaged ducting, and resolve airflow or capture efficiency problems. If immediate fixes are not possible, implement temporary controls to protect staff until permanent solutions are completed. Prompt action reduces risks of exposure and potential enforcement penalties.
Update Maintenance Records
Record every repair, adjustment, and replacement carried out following the inspection. Detailed documentation demonstrates compliance with regulatory requirements and provides a reliable history of system performance, supporting future inspections and helping you identify recurring issues.
Communicate with Staff
Share the inspection findings and corrective measures with affected staff to encourage proper system use and early reporting of performance issues. Clear communication ensures workers understand any changes in operating procedures or safety precautions.
Plan for Ongoing Monitoring
Establish a monitoring plan to check system performance between formal inspections. Simple, regular checks and monitoring can help detect early signs of failure and strengthen confidence in the system’s reliability.
Evaluate Overall Control Effectiveness
Finally, evaluate whether the LEV system is achieving its intended purpose, controlling exposure at the source. Review exposure measurements, health surveillance data, and worker feedback. If the system falls short, consider whether redesign, upgrade, or additional control measures are required.
FAQs
You can determine the need for local exhaust ventilation by assessing whether workers are exposed to hazardous substances. A risk assessment under COSHH should be carried out to identify exposure levels and whether general ventilation alone is insufficient. If airborne contaminants exceed workplace exposure limits or pose a significant health risk, an LEV system is required to capture contaminants at the source before they spread.
The five main components of an LEV system are: the hood, which captures contaminants at the source; the ducting, which safely carries them away; the air cleaner or filter, which removes hazardous particles or vapors; the fan, which provides the necessary airflow; and the discharge outlet, which safely releases clean or filtered air. Each component must function correctly to ensure the system operates effectively.
LEV systems must be tested every 14 months, as specified by COSHH regulations, to prevent testing from slipping beyond a year due to scheduling or operational delays. The additional two-month window ensures employers remain compliant and provides flexibility while maintaining consistent monitoring of system performance. This timeframe also accounts for the role LEV plays in safeguarding worker health, as even minor declines in efficiency can lead to unsafe exposure levels.
If an LEV system fails its statutory test, repairs must be prioritized based on the severity of the risk posed by the failure. Any fault that prevents the system from effectively controlling hazardous substances should be addressed immediately, and work involving exposure should be stopped until the system is safe. Non-critical issues that do not impact overall performance may be scheduled but must still be rectified promptly. Clear documentation of the test results and a structured action plan help ensure compliance and reduce health risks.




