Energy efficiency management is a global priority, especially when organizations worldwide are facing rising energy costs, regulatory pressures, and climate goals. ISO 50001 is a globally recognized standard that offers a structured and proven framework to implement, maintain, and improve an energy management system (EnMS). If 50% of the industrial and service sectors implement ISO 50001 by 2030, it could result in cumulative delivered energy savings of around 62 exajoules. This could save over $600 billion in energy costs and prevent 6,500 million metric tons of CO₂ emissions by the end of the decade. In the long term, ISO believes the standard has the potential to influence up to 60% of the world’s total energy use. ISO 50001 audits are assessments that confirm compliance, evaluate effectiveness, and reveal untapped opportunities for energy optimization.
This article will explore the importance of ISO 50001 audits in driving energy efficiency and performance, steps involved in the process, how to achieve certification, and more.
- Understanding ISO 50001 Audits
- What are the Key Components of an Energy Management System (EnMS)
- Steps to Prepare for and Perform ISO 50001 Audits
- ISO 50001 Certification Process
- Prepare for ISO 50001 Audits & Certification with GoAudits ISO Software
- What is ISO 50001 Software
- How to Choose the Right ISO 50001 Software?
- What are the Benefits of ISO 50001 Audits & Certification?
- FAQs
Understanding ISO 50001 Audits
ISO 50001 audits are formal evaluations conducted to assess an organization’s energy management system (EnMS) against the ISO 50001 standard. ISO 50001, developed by the International Organization for Standardization, provides organizations in all sectors a structured framework for managing energy use. It focuses on reducing energy consumption, improving efficiency, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
ISO 50001 audits verify whether the EnMS is effectively implemented, maintained, and capable of achieving continual improvement in energy performance. The audit process involves reviewing documentation, evaluating processes, and interviewing staff to ensure compliance with the standard’s requirements.
Any organization that has adopted or plans to adopt ISO 50001 must conduct regular audits. Regardless of size or sector, if your organization is pursuing energy efficiency, ISO 50001 audits are essential.
Types of ISO 50001 Audits
Two primary types of audits are conducted: internal and external.
Internal audits are conducted by your organization or a designated third party acting on your behalf. These audits help verify whether your EnMS complies with ISO 50001 requirements and your internal objectives. The main goal is to assess the effectiveness of your energy management system and the early detection of non-conformities. Internal audits ensure that energy planning, performance monitoring, and operational controls are functioning as intended.
External audits are carried out by independent certification bodies or regulatory authorities. These are required for ISO 50001 certification and ongoing compliance verification. The goal is to confirm that your EnMS aligns with the ISO 50001 standard and that you’re maintaining and improving energy performance as required.
Types of external audits include:
- Certification audit: Conducted in two stages to verify readiness and full compliance.
- Surveillance audit: Performed annually to ensure the EnMS is maintained effectively.
- Recertification audit: Occurs every three years to renew ISO 50001 certification.
What are the Key Components of an Energy Management System (EnMS)
To implement it effectively, you need to focus on the following key components:
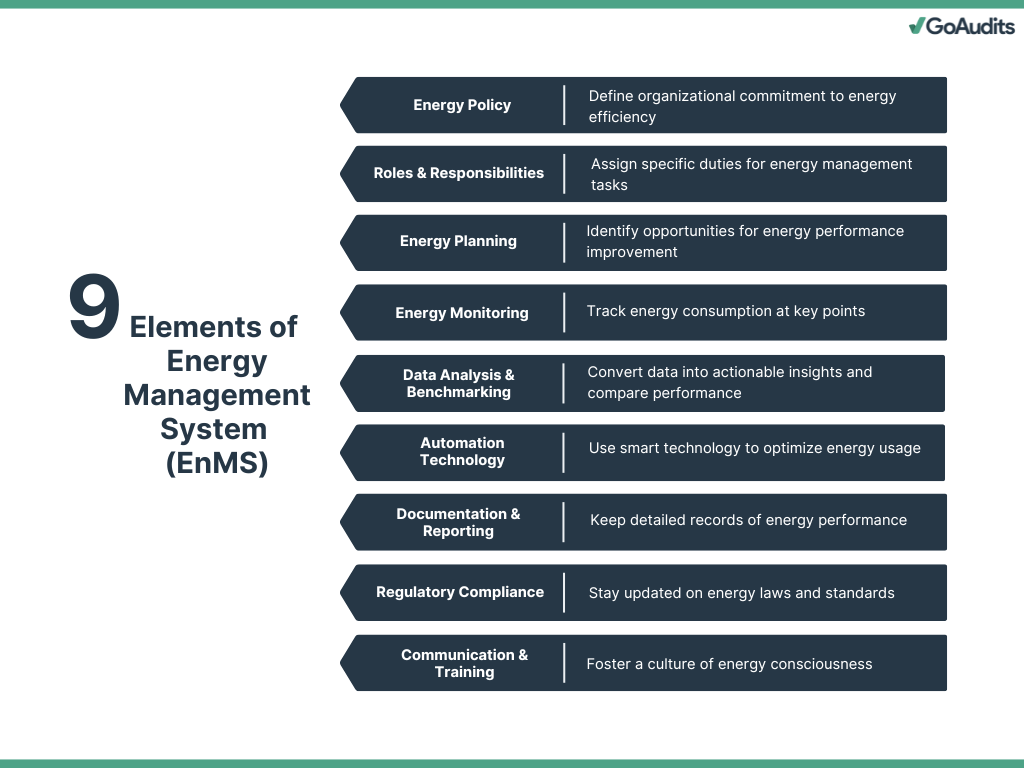
Energy Policy
When you begin the process of implementing an EnMS, the first step should be to establish a clear and actionable energy policy. It outlines your organization’s commitment to energy efficiency and continuous improvement. It is the guiding principle for all energy-related initiatives and should be endorsed by top management. Your energy policy must reflect your operational priorities, legal obligations, and sustainability goals.
Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure accountability across all levels, facilitate cross-departmental collaboration, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the EnMS. Assign specific duties to individuals or teams for tasks such as energy monitoring, compliance management, and performance evaluation.
Energy Planning
Energy planning identifies opportunities for energy performance improvement. It involves setting measurable objectives, conducting energy reviews, and developing action plans. By assessing significant energy uses (SEUs), you can prioritize efforts that deliver the greatest impact. The process of developing and implementing an EnMS also includes forecasting future energy demands and planning resources accordingly.
Energy Monitoring and Metering
Accurate monitoring and metering form the backbone of energy management as it helps you transition from reactive to proactive energy management. Track energy consumption at key points and use real-time data to identify anomalies, uncover wastage, and validate the effectiveness of energy-saving initiatives.
Data Analysis and Benchmarking
Data analysis helps convert raw energy data into actionable insights. Use analytics to track trends, identify inefficiencies, and quantify savings. Benchmarking against industry standards or internal baselines allows you to measure performance objectively, identify gaps, and drive continuous improvement.
Automation and Smart Technology
Smart systems enhance energy efficiency through automation and real-time control. Implement technologies such as Building Management Systems (BMS), IoT sensors, and AI-powered analytics. These tools optimize HVAC, lighting, and equipment usage based on actual demand, significantly reducing energy consumption.
Reporting and Documentation
Consistent documentation ensures transparency and traceability, supporting audits, traceability, and future planning. Maintain detailed records of energy performance, audits, improvements, and compliance efforts. Reporting should align with internal KPIs and external regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with energy regulations and standards is essential to avoid legal risks and demonstrate corporate responsibility. Stay updated on local, national, and international energy laws, including mandatory reporting, carbon emissions limits, and energy efficiency targets.
Communication, Training, and Awareness
Effective communication drives engagement across your organization and creates a culture of energy consciousness, which is key to long-term success. Provide regular training to build skills and reinforce energy-saving practices. Awareness campaigns ensure all employees understand their role in achieving energy goals.
Steps to Prepare for and Perform ISO 50001 Audits
Here’s a clear, step-by-step guide to help you successfully navigate the audit process.
1. Understand ISO 50001 Requirements
Start by studying the ISO 50001:2018 standard. Understand its structure, clauses, and intent. Focus on core elements like context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement. Pay attention to requirements for continuous energy performance enhancement, not just compliance.
2. Conduct a Gap Analysis
Before the audit, perform a thorough ISO 50001 gap analysis. Compare current practices with ISO requirements to identify missing elements. Use the findings to shape your implementation strategy and prioritize corrective actions.
3. Develop an Energy Policy
Revisit and refine your energy policy if necessary. Ensure it reflects current operational goals and regulatory requirements. Make the policy accessible to all stakeholders and reinforce its role as a guiding document. It should demonstrate top management’s commitment to energy efficiency and continual improvement.
4. Conduct an Energy Review
Carry out a comprehensive energy review to determine baseline energy performance. Evaluate energy sources, significant energy uses, and opportunities for improvement. Document findings and link them to performance objectives and targets.
5. Use Data to Make Energy Decisions
Collect and analyze energy consumption data across systems and processes. Identify major energy uses, patterns, and influencing factors. Use this data to prioritize actions, allocate resources effectively, and guide strategic decisions.
6. Set Energy Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establish relevant EnPIs for critical energy aspects. These KPIs should be quantifiable, meaningful, and aligned with your objectives. Monitor them regularly to measure performance improvements and ensure accountability.
7. Fix Targets and Objectives to Meet the Policy
Translate your energy policy into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. Assign responsibilities, timelines, and necessary resources. Objectives might include reducing energy intensity, lowering emissions, or increasing equipment efficiency.
8. Develop and Implement the EnMS
Design an energy management system tailored to your operations. Include documented procedures, roles, communication protocols, and control mechanisms. Ensure system integration with existing quality or environmental systems if applicable.
9. Measure the Results
Track performance against the set objectives and energy performance indicators. Use energy baselines and EnPIs (Energy Performance Indicators) to assess progress. Apply metering and monitoring tools to ensure data reliability and accuracy.
10. Review Policy Performance and Improve the EnMS
Conduct regular management reviews to evaluate the EnMS. Analyze results, identify gaps, and recommend changes. Incorporate lessons learned and feedback into system updates.
11. Define Audit Scope and Objectives
Clearly define the scope of the internal ISO 50001 audit. Determine which processes, departments, and locations are to be covered. Set objectives to assess compliance, identify risks, and evaluate the effectiveness of the EnMS.
The areas audited under ISO 50001 typically include:
- How the organization defines the scope of its EnMS and considers internal and external issues affecting energy performance.
- Top management’s involvement, energy policy, and assignment of roles and responsibilities.
- How the organization identifies energy aspects, sets objectives and targets, and establishes action plans for energy performance improvement.
- Resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information necessary for the EnMS.
- Operational controls, maintenance activities, and processes related to significant energy uses, including equipment efficiency and energy-saving practices.
- Monitoring, measurement, analysis, evaluation of energy performance, internal audits, and management reviews.
- How non-conformities are addressed, corrective actions taken, and continual improvement achieved.
12. Plan and Conduct the Internal Audit
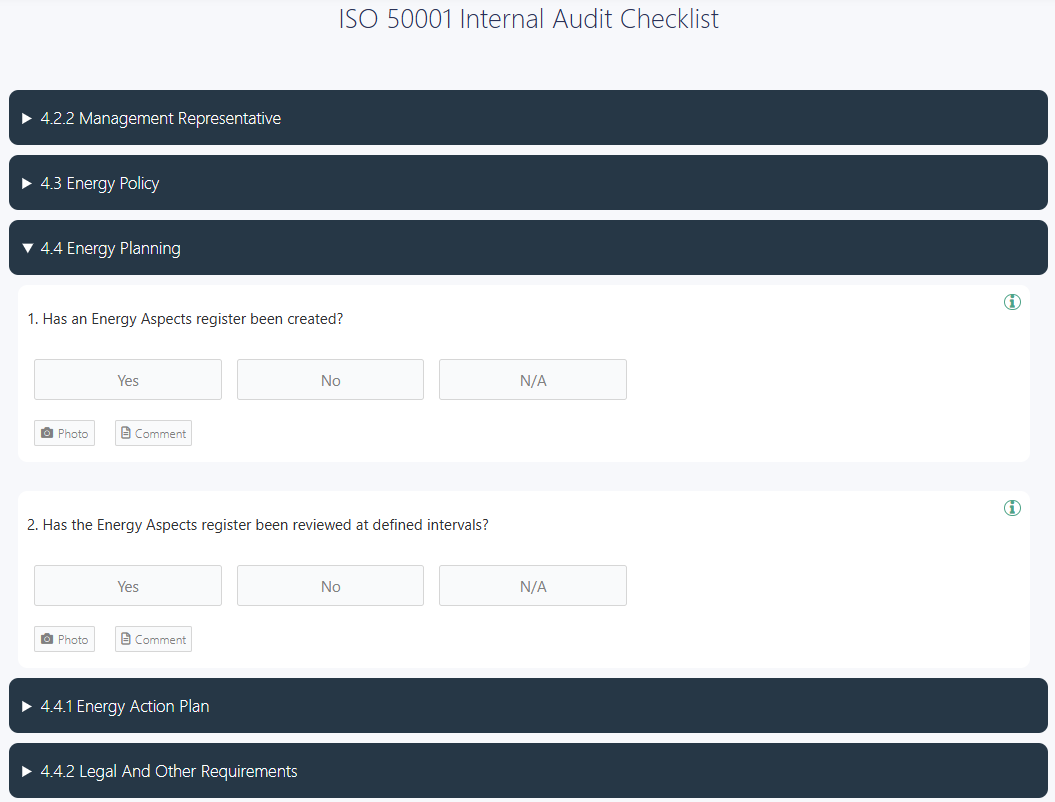
Create a detailed audit plan and use digital checklists based on ISO 50001 clauses to perform internal audits. Assign trained internal auditors who are independent of the areas they assess. Document observations, non-conformities, and strengths.
👉 GoAudits offers a free ISO 50001 checklist and an ISO 50001 internal audit checklist to streamline your internal ISO 50001 audits, ensure compliance with energy management standards, and identify opportunities for energy performance improvement.
13. Prepare and Share the ISO 50001 Audit Report
Compile a structured ISO 50001 audit report summarizing findings, evidence, and recommendations. Highlight non-conformities, potential improvements, and positive practices. Share the report with top management and relevant teams. Use it as a foundation for corrective actions and future planning.
ISO 50001 Certification Process
Here’s a clear breakdown of the certification process.
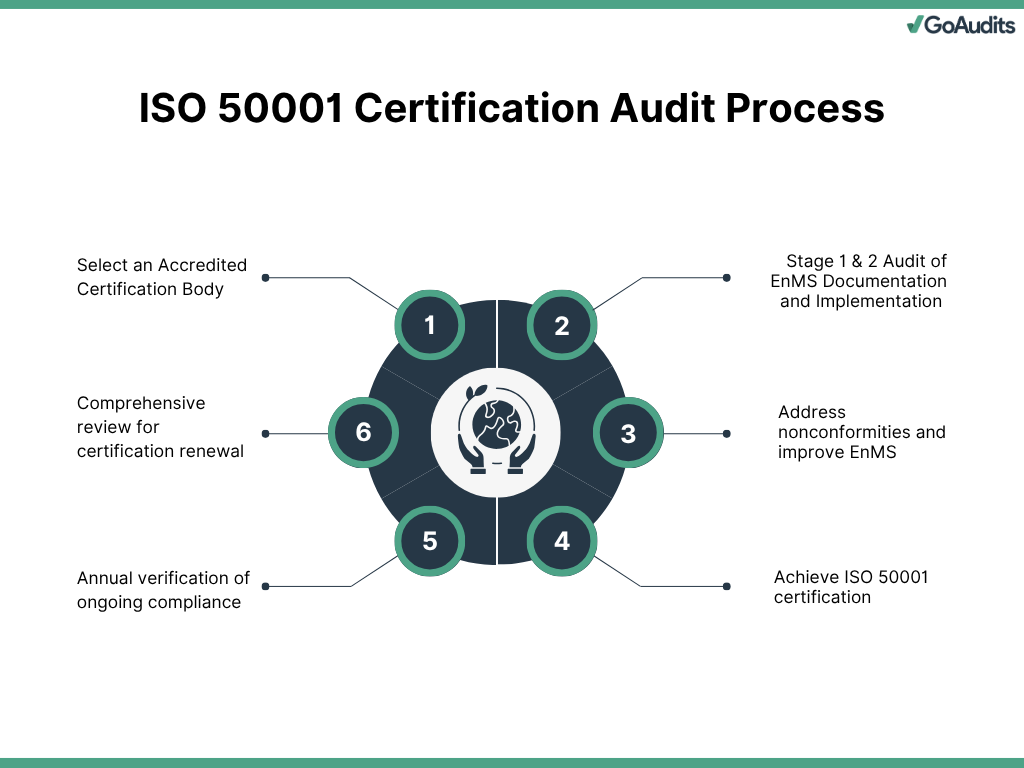
1. Select an Accredited Certification Body
Start by choosing a reputable, accredited certification body. Ensure the organization is recognized by a national accreditation authority and has relevant experience in your industry. An accredited body will offer credibility and ensure the certification process aligns with ISO requirements. Evaluate them based on their expertise, audit approach, and references from similar businesses.
2. Stage 1 and Stage 2 Audits
Once ready, the certification body conducts a two-stage audit:
Stage 1 audit is a preliminary review of your EnMS documentation. Auditors assess your readiness for Stage 2, identify gaps, and provide feedback. It focuses on your energy policy, objectives, legal compliance, and documentation control.
Stage 2 audit is an in-depth evaluation of how effectively your EnMS is implemented and maintained. Auditors examine operational controls, monitor energy performance indicators, and verify compliance with ISO 50001 requirements. They may also interview staff and review records and data.
3. Implement Corrective Actions and Improvements
Address all nonconformities found during the ISO 50001 audits. Develop and implement corrective action plans with clear responsibilities and deadlines. Continuous improvement is central to ISO 50001, so use audit feedback to strengthen your EnMS and drive energy performance.
Common non-conformities identified during ISO 50001 audits typically fall into several key categories. The most frequently observed non-conformities include:
- Many organizations fail to maintain comprehensive, up-to-date documentation required by ISO 50001. This includes missing or insufficient records of energy reviews, energy baselines, operational controls, and continual improvement processes. Auditors often find gaps in how energy sources, significant energy uses, and performance indicators are documented.
- Audit failures often result from a lack of visible leadership engagement. This is evidenced by inadequate resource allocation, poorly developed energy policies, and unclear assignment of roles and responsibilities for energy management. Without active support from top management, energy management systems lack the necessary organizational backing to function effectively.
- Weaknesses in the internal audit process are a common source of non-conformity. Issues include insufficient audit planning, untrained internal auditors, and failure to implement or verify corrective actions. This leads to recurring problems that are not addressed before external audits.
- Organizations frequently struggle with selecting appropriate energy performance indicators (EnPIs), which affects calibrating monitoring equipment accurately, and maintaining reliable data collection systems. They undermine the credibility of reported energy performance improvements and can result in certification failure.
- Non-conformities often arise when employees are not adequately trained or are unaware of their roles within the EnMS. This leads to inconsistent implementation and missed opportunities for energy performance improvement.
- Deviations from established procedures, such as not conducting required energy reviews or not updating documentation as processes change, are frequently cited non-conformities.
- Organizations sometimes fail to conduct comprehensive management reviews or do not include all required information, such as the measurement of quality objectives and review of non-conformities, which are mandatory under the standard.
Document every improvement to demonstrate compliance and support future evaluations.
4. Receive Certification
After successful completion of the Stage 2 audit and verification of corrective actions, your organization is granted ISO 50001 certification. This certificate is typically valid for three years. Display your certificate to build trust with stakeholders and meet regulatory or contractual requirements.
5. Surveillance Audit
Certification bodies conduct annual surveillance audits during the three-year certification cycle. These audits verify ongoing compliance and assess your progress toward energy performance improvement. Focus areas include:
- Maintenance of the EnMS
- Review of performance data
- Implementation of action plans
- Staff awareness and engagement
You should prepare for these audits just as thoroughly as the initial certification.
6. Recertification Audit
Before the certification expires, a recertification audit is required. It’s conducted every three years to renew certification. It evaluates the entire EnMS and confirms your continued commitment to the ISO 50001 standard. You must demonstrate continual improvement, provide evidence of energy performance gains, and show full implementation of the EnMS. If successful, your certification is renewed for another cycle.
Prepare for ISO 50001 Audits & Certification with GoAudits ISO Software
Achieving ISO 50001 certification demands consistent energy performance monitoring, strong documentation, and corrective actions aligned with the standard. GoAudits ISO compliance software is an all-in-one digital solution tailored to ISO 50001 audit preparation and certification. Whether you’re preparing for an initial ISO 50001 audit or maintaining ongoing compliance, it empowers your teams with structured workflows, instant reporting, and full accountability. From mobile inspections to automated reports and corrective action tracking, GoAudits enables you to stay audit-ready, reduce paperwork, eliminate the risk of non-compliance, and drive continual improvement in your EnMS.
- Access professionally built ISO 50001 checklists tailored for energy audits. Use them as-is or customize them to meet your specific organizational needs.
- Conduct audits anytime, anywhere, even offline, using an app that works across all devices. Attach photos, e-signatures, geotags, and timestamps for complete documentation
- Automatically generate ISO 50001 audit reports after each internal audit. These reports include smart data like timestamps, geo-tags, signatures, and corrective actions, and are ready to be reviewed and shared immediately.
- Assign tasks directly from the mobile app during audits. Track completion status, set priorities, and due dates. Ensure accountability with detailed task ownership and follow-through.
- Automate notifications and escalations, customize workflows for report approvals and task assignments, and keep everyone aligned with real-time updates and reminders.
- Access centralized dashboards to make data-informed decisions quickly, monitor energy performance trends over time, and identify recurring issues across audits and locations.

What is ISO 50001 Software
ISO 50001 software is designed to help organizations establish, implement, maintain, and improve their EnMS in accordance with the ISO 50001 standard. It streamlines this process by automating data collection, centralizing energy performance records, and simplifying reporting tasks.
By using ISO 50001 software, you can effectively track energy consumption, set energy objectives, and identify areas for improvement. It supports the continuous improvement cycle required by ISO 50001, enabling your organization to reduce energy costs, enhance operational efficiency, and meet regulatory requirements easily.
What are the Benefits of Using ISO 50001 Software?
Here are some of the benefits of using ISO 50001 software:
- Reduces manual effort and ensures easy access to required documentation.
- Brings all energy-related data into a single, organized platform.
- Streamlines planning, implementation, monitoring, and review processes.
- Provides instant visibility into energy usage and trends.
- Offers actionable insights backed by accurate, up-to-date data.
- Facilitates communication and accountability across departments.
How to Choose the Right ISO 50001 Software?
To make an informed decision, evaluate the ISO 50001 software based on essential features, usability, support, and pricing.
Prioritize Features That Support ISO 50001 Requirements
Start by assessing the core functionalities the software offers. It should align with the ISO 50001 requirements and your organization’s specific needs. Look for:
- Customizable checklists to tailor audits and inspections to your energy objectives.
- Mobile auditing capabilities to streamline on-site data collection and assessments.
- Instant report generation that offers quick insights and supports real-time decision-making.
- Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) tracking to manage non-conformities effectively.
- Workflow automation for managing approvals, reviews, and reminders without delays.
- Data analysis tools that help identify trends, inefficiencies, and opportunities for energy savings.
These features help you ensure continual improvement and seamless compliance with ISO 50001.
Ensure a User-Friendly Mobile App with Offline Access
ISO energy audits often happen on-site, where internet access may be limited. Choose ISO 50001 software with an intuitive mobile interface and offline functionality. This allows you to collect data, conduct audits, and sync results when you’re back online. It boosts efficiency and minimizes disruptions.
Consider Cost-Effectiveness
A feature-rich tool shouldn’t strain your budget. Look for ISO 50001 software that’s scalable and cost-effective, offering flexible pricing models that match your organization’s size and scope. Avoid paying for features you don’t need, and ensure there are no hidden fees in the subscription.
Evaluate Customer Reviews and Ratings
Read independent customer reviews to understand real-world performance. Look for feedback on usability, technical reliability, customer support, and updates. High ratings across different platforms often indicate a well-supported and functional tool.
Assess the Quality of Customer Support
Reliable technical support is essential, especially during implementation and audits. Choose vendors that offer multiple support channels, including live chat, email, and phone. Timely assistance ensures smooth onboarding and fast issue resolution.
Test the Software Before Committing
Always opt for free trials or live demos. These give you firsthand experience of the platform’s interface, features, and responsiveness. Use this period to test its compatibility with your existing systems and gather feedback from your team.
What are the Benefits of ISO 50001 Audits & Certification?
Here’s how your business benefits from ISO 50001 certification:
- ISO 50001 audits identify patterns in energy use and inefficiencies in your systems and optimize energy consumption across operations. It leads to significant reductions in energy bills and costs of 5% to 30% within the first few years. Some facilities reported annual savings from $36,000 to $938,000 and average energy cost reductions of 12% within 15 months
- Improved energy performance results in lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. ISO 50001 audits help you align with global sustainability goals, contributing to climate action initiatives, and enhancing your environmental responsibility.
- ISO 50001 audits uncover inefficiencies in equipment, systems, and practices. Addressing these gaps boosts operational performance and helps streamline workflows. The result is higher productivity with lower energy input.
- ISO energy audits help you anticipate and mitigate energy-related risks, including price volatility, energy supply disruption, or regulatory penalties, etc., by providing tools to assess these risks. You can implement preventative strategies and ensure business continuity.
- Staying compliant with national and international energy regulations becomes easier with ISO 50001, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties. Certification demonstrates that your organization follows a structured, auditable process for managing energy.
- ISO 50001 certification enhances your organization’s reputation in international markets. It signals to partners, clients, and regulatory bodies that you are committed to energy efficiency and sustainability. This can open new business opportunities and strengthen your global competitiveness.
- Transparency in energy performance builds trust among stakeholders, customers, investors, and employees alike. ISO 50001 audits demonstrate your proactive approach to sustainability and responsible resource management, reinforcing your brand’s credibility and integrity.
FAQs
The ISO 50001 lead auditor is a qualified professional responsible for overseeing and managing audits of EnMS to ensure compliance with the ISO 50001:2018 standard. Their primary role is to maximize the energy savings impact of ISO 50001 implementation across industrial, commercial, and public sector organizations. Key responsibilities include planning, leading, and managing audit teams, conducting audits, assessing conformance, documenting and reporting findings, communicating results, and more.
Internal auditors responsible for conducting ISO 50001 reviews must undergo specialized training to ensure they are competent in assessing and improving EnMS according to the ISO 50001 requirements. Essential ISO 50001 internal auditor training covers standard requirements, audit methodologies, practical skills, regulatory awareness, and best practices for reporting and continual improvement.
An effective ISO 50001 lead auditor should preferably have a technical degree in fields such as energy management, engineering, or science, combined with substantial professional experience that varies by education level (ranging from 48 months with a technical degree to 96 months for other backgrounds, plus a minimum of 15 audit days including roles as both lead auditor and team member on ISO 50001 audits). The role also requires completion of an accredited ISO 50001 lead auditor training course, successful passage of a recognized lead auditor exam, and documented audit experience.
Core competencies include a deep understanding of ISO 50001 requirements, proficiency in audit planning and execution according to ISO 19011, leadership and communication skills for managing audit teams and client relationships, and the technical expertise to assess energy management systems across various sectors. Practical experience in managing and participating in EnMS audits, as well as personal attributes like objectivity, integrity, and effective communication, are also essential.