ISO 14001 is the globally recognized standard for environmental management systems (EMS), designed to help organizations systematically manage their environmental responsibilities. It provides a structured approach to reducing environmental impact, improving resource efficiency, ensuring compliance with regulations, and minimizing legal risks. It emphasizes establishing an environmental policy, setting objectives, implementing controls, monitoring performance, and conducting management reviews. ISO 14001 audits are essential to ensure your business operations align with ISO 14001. They evaluate whether your EMS complies with the standard’s requirements, supports your environmental goals, functions effectively, and drives continuous improvement.
This blog will explore the entire process of ISO 14001 certification audit, including how to prepare, steps to take after the audit, and more. We have also listed free checklists to help you perform ISO environmental audits.
What is an ISO 14001 Audit?
An ISO 14001 audit is a systematic, documented process to evaluate an organization’s environmental management system (EMS) against the ISO 14001 standard. It helps determine whether the EMS meets the standard’s requirements, supports continuous improvement, and aligns with the organization’s environmental objectives. It assesses how well the organization identifies, manages, monitors, and controls its environmental issues. It ensures compliance not only with the ISO 14001 standard but also with applicable environmental laws and regulations.
You need to perform ISO 14001 audits if your organization is implementing or maintaining an environmental management system in line with the ISO 14001 standard. These audits are essential for businesses in:
- Manufacturing and construction
- Food production
- Agriculture and fishing
- Energy and utilities
- Transportation and logistics
- Healthcare
- Hospitality
- Public sector and government agencies
Types of ISO 14001 Audits
Understanding the types of audits is essential for maintaining compliance and driving continual improvement.
Internal Audits
Internal audits are conducted by your organization or by an independent party hired by you. The main goal is to prepare for external audits by assessing the effectiveness of your EMS and verifying compliance with the ISO 14001 standard, company policies, and environmental goals.
It assesses how well environmental policies are implemented, maintained, and followed in daily operations. Internal audits help you detect issues before they become regulatory violations or impact environmental performance. Internal audits should occur regularly, at planned intervals (e.g., quarterly or annually), based on the complexity of operations and environmental risks.
External audits
External audits are performed by a third-party certification body or regulatory authority to validate the effectiveness of your EMS and determine if it meets the ISO 14001 certification requirements. External audits follow a certification cycle, starting from initial certification and annual surveillance to full re-certification every three years.
- Certification Audits: Conducted when you’re seeking initial certification. It includes a detailed review of documentation and on-site inspections.
- Surveillance Audits: Periodic assessments (usually annually) after certification to ensure ongoing compliance and improvement.
- Recertification Audits: Performed at the end of the certification cycle (typically three years) to renew your ISO 14001 certification.
ISO 14001 Certification Audit Process
To prepare effectively for an ISO 14001 certification audit, you need to understand the audit’s structure, key focus areas, and what each stage entails, and more.

1. Understanding ISO 14001 Requirements and Audit Objectives
ISO 14001 provides a structured framework for managing environmental responsibilities. Its core objective is continual improvement of environmental performance, not just compliance.
Key areas assessed in an ISO 14001 audit include:
- Environmental policy and objectives
- Environmental aspects and impacts
- Legal and compliance obligations
- Operational controls and risk management
- Monitoring, measurement, and analysis
- Internal audits and management reviews
- Leadership commitment and employee awareness
- Continual improvement initiatives
ISO 14001 is structured around five fundamental elements that guide organizations in systematically improving their environmental performance. These elements are:
– Environmental Policy: Commitment and direction from top management for environmental performance
– Planning: Identification of impacts, legal requirements, and setting objectives
– Implementation & Operation: Execution of plans, assignment of roles, training, and operational controls
– Monitoring & Measurement: Performance tracking, audits, and corrective actions
– Review & Improvement: Management review and continual improvement of the EMS
Auditors evaluate whether your EMS is effectively implemented and maintained, and whether it delivers results aligned with environmental policy and objectives.
2. ISO 14001 Audit Plan
An audit plan outlines how the audit will be conducted. It’s an important document that ensures the process is systematic, transparent, and efficient. It includes:
- Audit Scope and Objectives: It defines the boundaries of the audit, including sites, activities, and processes. Objectives include verifying compliance with ISO 14001 and identifying improvement areas.
- Audit Criteria: These include ISO 14001:2015 clauses, your own EMS documentation, and relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
- Audit Methodology: Auditors use interviews, observations, and document reviews to gather objective evidence of conformity.
- Audit Schedule: It details the timeline and areas to be audited to minimize disruption while allowing sufficient time for a thorough assessment.
- Audit Team: Typically led by a certified lead auditor, the team may include technical experts. Independence and impartiality are crucial.
- Audit Reports and Summaries: Findings are documented, including nonconformities, observations, and opportunities for improvement.
- Reporting and Follow-Up: The final ISO 14001 audit report outlines any required corrective actions. A follow-up may be necessary to verify that actions are implemented and effective.
3. Self-Assessments Before Certification
Performing a self-assessment helps you identify gaps and strengthen your EMS before the formal audit. Key steps involve ensuring alignment with ISO 14001, conducting a gap analysis, and addressing any deficiencies identified during the review.
👉 Free Resources
GoAudits offers a wide range of free ISO audit checklists. You can sign up for free and start using these checklists, or you can digitize your ISO SOPs into actionable, digital checklists.
→ ISO 14001 Self-Assessment Checklist
→ ISO 14001 Internal Audit Checklist
→ ISO 14001:2015 Readiness Assessment
→ ISO 14001 Requirements Checklist
4. Stage 1 Audit
In Stage 1, auditors assess whether your EMS is ready for the full audit, focusing on documentation and preparedness. Objectives of Stage 1 audits:
- Evaluate EMS documentation
- Confirm compliance with ISO 14001 clauses
- Review site-specific conditions and legal obligations
- Identify areas of concern for Stage 2
A successful Stage 1 audit indicates you’re ready for the full system audit.
5. Stage 2 Audit
Auditors verify whether your EMS is effectively implemented and delivers results. During this stage, auditors:
- Assess the implementation of procedures and controls
- Verify legal and regulatory compliance
- Evaluate risk management and operational control
- Interview employees and observe activities
- Review records, monitoring, and internal audits
Nonconformities are classified as major or minor. You must address them before certification is granted.
Stage 1 audit does not assess the effectiveness of the EMS. It only checks if the EMS exists and is ready for the next step. Stage 2 audit verifies the EMS is fully implemented and operational, evaluates compliance with ISO 14001, and assesses its effectiveness. Nonconformities are identified, and certification is only granted if all major issues are resolved.
6. Certification Decision
Following the Stage 2 audit, the certification body reviews the audit findings. If your organization meets all requirements and has closed any nonconformities, certification is granted. You’ll receive:
- An ISO 14001 certificate (valid for three years)
- A formal ISO 14001 audit report
- Recommendations for continual improvement
The decision is based on objective evidence and the effectiveness of your EMS.
7. Surveillance Audits
Certification is not a one-time event. Surveillance audits are conducted at least once a year during the three-year cycle to:
- Monitor ongoing compliance
- Verify the effectiveness of corrective actions
- Ensure continual improvement
8. Recertification Audit
Before your certificate expires, a recertification audit is required to renew it for another three-year cycle. This audit:
- Reviews the full EMS
- Evaluates overall effectiveness and progress
- Confirms the system remains aligned with ISO 14001 requirements
- Identifies any systemic issues
Free ISO 14001 Audit Report Template
Here’s a free sample of an ISO 14001 internal audit report generated using GoAudits. GoAudits offers a full library of free ISO audit templates to get you started.
Prepare for ISO 14001 Certification Audits with GoAudits
ISO 14001 certification demands a structured, proactive approach to environmental management. GoAudits ISO compliance software streamlines every aspect of your compliance journey, minimizing paperwork and maximizing actionable insights. With the GoAudits mobile auditing app, you can capture real-time data on-site, generate detailed audit reports instantly, and assign corrective actions seamlessly. GoAudits helps you conduct mobile inspections, enforce accountability, align with ISO standards efficiently, and make data-driven decisions for environmental improvements.
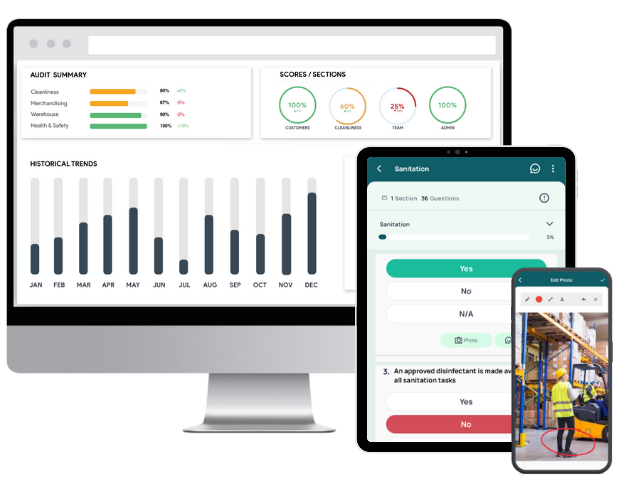
Here’s how:
- Access ready-to-use ISO audit checklists. Start immediately or customize to your specific needs using an intuitive drag-and-drop builder.
- Conduct inspections on any mobile device, even offline. Upload photos, add annotations, collect e-signatures, and ensure GPS-tagged records for full traceability.
- Generate branded internal audit reports automatically, complete with images, timestamps, user data, and scoring. Share them instantly with key stakeholders for faster action.
- Assign corrective actions directly during inspections. Include priority, deadlines, and responsibilities. Track resolution status to ensure nothing falls through the cracks.
- Set up workflows for escalations, reminders, and approvals. Notify the right people at the right time and monitor completion from a central dashboard.
- Access visual dashboards that summarize audit results across teams, locations, or topics. Identify recurring issues, monitor performance trends, and support strategic environmental planning.
What to Do After an ISO 14001 Audit
After completing an ISO 14001 audit, your next actions are important. The audit itself is only the starting point. What truly strengthens your EMS is how you respond. Here’s a structured approach to ensure post-audit actions lead to improvement.
Review the ISO 14001 Audit Report Carefully
Start by examining the audit report thoroughly. Focus on the non-conformities, observations, and opportunities for improvement. Make sure you understand the context of each finding. Look for patterns or recurring issues. This initial review helps you prioritize actions and assign responsibilities effectively.
Conduct a Root Cause Analysis
Addressing non-conformities without identifying their root causes leads to repeated issues. Use techniques such as the 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, or fault tree analysis. Aim to uncover system-level failures rather than just symptoms. Root cause analysis helps ensure corrective actions are both relevant and sustainable.
ISO 14001 audits frequently uncover both minor and major non-conformities within an environmental management system:
| Common issues | Examples |
| Documentation failures | Failure to document environmental procedures or process improvements, missing or incomplete required documentation, and documentation controls |
| Process and operational control issues | Not defining or following operating criteria for significant environmental aspects, process changes are not reviewed or approved by competent personnel, and non-adherence to documented procedures |
| Training and competence | Inadequate or missing training records and a lack of understanding of how work affects environmental performance |
| Compliance and legal obligations | Incomplete or outdated compliance records, failure to evaluate compliance, and non-compliance with legal requirements |
| Monitoring, measuring, and equipment | Inaccurate or incomplete equipment calibration and inadequate monitoring and measurement |
| Emergency preparedness and response | Lack of emergency plans or drills, and no review of the emergency plan’s effectiveness |
| Management review and corrective actions | Incomplete management reviews and a lack of documentation of corrective actions |
Develop and Implement a Corrective Action Plan
Based on your analysis, create a corrective action plan that clearly outlines:
- What needs to be fixed
- Who is responsible
- When will it be completed
- How will you measure success
Ensure actions are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound (SMART). Implement the actions promptly and monitor their progress closely.
Verify and Validate Effectiveness
Once corrective actions are implemented, verify their effectiveness. Conduct internal checks, reviews, or follow-up audits to confirm that the root cause has been addressed. Look for evidence of sustained improvement. If the issue persists, revisit the root cause analysis and refine the solution.
Revise Relevant Documents to Reflect the Change
Update all affected documents, such as procedures, work instructions, and process maps. Ensure changes are clearly documented and traceable. Maintain version control to prevent confusion and ensure everyone uses the most current information.
Update the Environmental Management System (EMS)
Integrate all valid changes into your EMS. Reflect lessons learned in your risk assessments, objectives, and compliance obligations. Strengthening your EMS after an audit is key to maintaining ISO 14001 certification and improving environmental performance over time.
Communicate with Stakeholders
Inform all relevant stakeholders, including employees, management, and external partners, about the outcomes and changes. Transparent communication helps build trust, reinforces commitment, and encourages active participation in the EMS.
Plan for Ongoing Surveillance and Continuous Improvement
Use the audit findings as input for future planning. Develop internal audit schedules, training programs, and performance reviews that target identified weak areas. Embed continuous improvement into your EMS by regularly reviewing objectives, targets, and metrics.
Why are ISO 14001 Audits Important?
ISO 14001 audits offer more benefits than ensuring an effective environmental management system within your organization. They are:
- They identify gaps in your EMS, allowing you to measure and improve your environmental impact. You can minimize waste, reduce emissions, and promote sustainable practices.
- ISO 14001 audits help you stay compliant by ensuring your EMS aligns with current legal requirements. Regular internal and external reviews reduce the risk of violations, fines, or shutdowns and demonstrate due diligence to authorities.
- They streamline processes by uncovering inefficiencies and resource waste. They push you to refine procedures, eliminate redundant steps, and optimize resource usage. This leads to smoother operations, clearer workflows, and reduced environmental and operational risks.
- ISO 14001 audits help identify energy-saving opportunities, lower raw material consumption, and reduce waste management costs. Over time, these cost reductions can have a significant impact on your bottom line.
- Environmental risks can threaten your operations. ISO 14001 audits highlight these risks early, enabling proactive mitigation. A robust EMS ensures that you’re prepared for environmental emergencies and regulatory inspections.
- Customers, investors, and partners increasingly favor environmentally responsible businesses. Certification through ISO 14001 audits showcases your commitment to sustainability. This can differentiate your brand and open access to new markets.
- Regular ISO 14001 audits reinforce accountability and strengthen your reputation as a responsible organization. In times of crisis or scrutiny, a well-audited EMS demonstrates your resilience and commitment to ethical, sustainable operations.
FAQs
ISO 14001 and EMAS both focus on environmental management, but they differ in scope and regulatory requirements. ISO 14001 is an international standard providing a framework for setting up an effective environmental management system. Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS), developed by the European Union, builds on ISO 14001 but adds stricter requirements, including legal compliance verification and the mandatory publication of a validated environmental statement. While ISO 14001 certifies that an EMS exists and functions, EMAS emphasizes transparency and continual improvement through external validation and public reporting.
ISO 14001 offers a globally recognized, flexible framework focused on continuous improvement and legal compliance within an EMS. Unlike sector-specific or performance-based standards, ISO 14001 does not prescribe environmental performance criteria but instead requires organizations to set, monitor, and meet their own objectives. It promotes a process-based approach integrated into business operations, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes and industries. This emphasis on system effectiveness rather than fixed benchmarks distinguishes it from more prescriptive or regional standards.
ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 both promote sustainability but address different aspects of environmental responsibility. ISO 14001 focuses broadly on environmental management, guiding organizations to minimize their ecological footprint and prevent pollution. ISO 50001, on the other hand, targets energy management specifically, helping organizations optimize energy use, improve energy performance, and reduce energy costs. While both follow a similar structure based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle and can be integrated, their scopes and performance metrics differ.






