In 2020, more than 125 American workers lost their lives, and nearly 2,400 others were injured due to electrical incidents in the workplace. According to OSHA, electrical hazards remain a leading cause of fatalities, particularly in industries like construction, where electrocution ranks among the top four fatal risks. Electrical audits are becoming essential not only to comply with industry regulations but also to ensure employee well-being. With the growing complexity of modern electrical systems and stringent regulations, organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of conducting thorough electrical assessments to identify potential electrical hazards, stay compliant, and safeguard their workforce.
This article will explore the role of electrical safety audits in workplace safety, why their relevance is expanding across industries, and how they provide a proactive approach to prevent accidents, legal liabilities, and expensive downtime.
- Electrical Audits: An Overview
- Types of Electrical Audits
- Key Components of Electrical Safety Audits
- What are the Key Steps Involved in Preparing for an Electrical Safety Audit?
- How Often Should Electrical Safety Audits Be Performed?
- Leverage GoAudits to Conduct Streamlined Electrical Audits
- Industry Standards and Guidelines for Electrical Safety Compliance
- What are the Main Benefits of Conducting Regular Electrical Safety Audits?
Electrical Audits: An Overview
Electrical audits are systematic evaluations of electrical systems, installations, and equipment within a facility or organization. Their primary purpose is to ensure safety, compliance with industry regulations, operational reliability, and energy efficiency. Electrical safety audits are typically conducted by electrical engineers, certified electrical safety auditors, specialized safety inspectors, and other experienced professionals.
What Specific Electrical Hazards Can Be Identified During an Electrical Audit?
During an electrical safety audit, several specific hazards can be identified that pose significant risks to both personnel and property. These include:
- Faulty Wiring: It is a prevalent hazard uncovered during audits. Issues such as damaged insulation, loose connections, and improper wire sizing can lead to short circuits, electrical fires, and equipment malfunctions.
- Inadequate Grounding: Electrical audits often reveal inadequate grounding systems, missing ground connections, or improper grounding practices. These deficiencies can result in electrical shock hazards and equipment damage.
- Overloaded Circuits: Overloading occurs when circuits carry more current than they are designed for, leading to overheating and potential fire hazards. This is often due to the addition of new equipment without proper circuit upgrades or excessive use of extension cords.
- Outdated Equipment: Electrical safety analysis frequently identifies outdated electrical equipment that no longer meets current safety standards. Components like old circuit breakers, fuses, and switches may be prone to failure, compromising system reliability and increasing the risk of accidents.
- Non-Compliance with Safety Standards: This is a significant hazard and includes improper installation practices, failure to adhere to electrical codes, and the use of non-compliant equipment.
- Exposed Electrical Parts: Exposed electrical components, such as live wires or uncovered junction boxes, pose a direct threat of electric shock or electrocution. These hazards are often overlooked but require immediate attention, with all electrical parts being properly enclosed and secured.
- Poor Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance of electrical systems can lead to the deterioration of components, increased wear and tear, and a higher likelihood of failures. Electrical assessments often reveal equipment that is not well-maintained, which can lead to breakdowns, malfunctions, and potential hazards.
Types of Electrical Audits
Here’s a detailed overview of different types of electrical audits:
Electrical Compliance Checks
Electrical compliance checks verify that electrical systems meet relevant national and international standards, preventing potential penalties. These electrical compliance checks include documentation review, testing, and verification of compliance with industry standards like NFPA 70E, OSHA, and IEC 60364.
Electrical Safety Audits
Electrical safety audits are comprehensive evaluations aimed at identifying potential hazards within electrical systems. These audits assess equipment, installations, and operational practices to prevent incidents such as shocks, arc flashes, and fires.
Key aspects include equipment inspection, risk assessments, and compliance verification. Regular electrical safety audits not only enhance worker safety but also contribute to the reliability and longevity of electrical systems.
Electrical Risk Assessments
Risk assessments systematically identify and evaluate potential hazards associated with electrical systems, creating a safe working environment and ensuring regulatory compliance. The process involves hazard identification, risk evaluation, and mitigation strategies.
Energy Audits
Energy audits focus on analyzing energy consumption patterns to identify opportunities for efficiency improvements, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. These audits involve load analysis, power quality assessment, and efficiency recommendations.
Reliability Assessments
Electrical reliability assessments proactively address potential issues with the aim of ensuring that electrical systems operate consistently without unexpected failures, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. These electrical assessments typically include system and equipment evaluation, remaining lifetime assessment, and asset health index calculation (quantifying the condition of assets to prioritize maintenance activities).
Key Components of Electrical Safety Audits
A comprehensive electrical safety audit involves the following core components.
Documentation Review
An effective electrical audit includes a thorough review of all technical and operational documentation, including single-line diagrams, system layouts, inspection reports, and equipment manuals. Proper documentation reflects the accuracy of system design and supports informed decision-making during risk assessments and maintenance planning.
Physical Inspection of Equipment and Infrastructure
Electrical safety audits also involve a detailed physical inspection of all electrical assets. This includes checking switchboards, panels, transformers, conductors, and grounding systems. The aim is to identify signs of overheating, corrosion, loose connections, or improper installations that could pose safety hazards.
Assessment of Safety Procedures and Practices
Another critical component is the evaluation of existing safety procedures and operational practices. It includes reviewing lockout/tagout processes, PPE usage, emergency protocols, and staff training programs. The goal is to ensure that safety measures are not only defined but actively followed.
Compliance Verification
Electrical safety audits involve verifying compliance with applicable national and international standards. They ensure that the organization complies with legal and regulatory requirements, minimizing the risk of violations and penalties.
Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification
An electrical assessment includes the identification of electrical hazards and the evaluation of associated risks. It involves analyzing system vulnerabilities like overloads, insulation failures, or proximity to water sources. It helps in prioritizing corrective actions based on risk severity and likelihood.
Review of Maintenance and Operational Records
It involves checking historical records related to equipment servicing, inspection routines, testing logs, and incident reports. Proper recordkeeping reflects whether maintenance is performed regularly and helps identify patterns that may indicate systemic issues.
Arc Flash and Short-Circuit Analysis
An electrical safety audit often includes arc flash and short-circuit analyses to determine potential energy levels and fault currents. It helps in calculating safe working distances, selecting appropriate PPE, and implementing mitigation measures to protect personnel.
Corrective Action Plan
The electrical safety assessment also includes the formulation of a corrective action plan. This outlines specific actions required to address identified deficiencies, mitigate risks, and enhance safety practices. It includes timelines, responsibilities, and follow-up mechanisms to ensure effective resolution.
Reporting and Recommendations
Finally, a detailed electrical inspection report is generated with audit findings, risk summaries, and practical recommendations. It act as a baseline for continuous improvement and supports future decision-making on electrical safety strategies.
What are the Key Steps Involved in Preparing for an Electrical Safety Audit?
Below are the key steps you should follow to effectively prepare for such an audit:
1. Define the Scope and Objectives
Begin by clearly outlining the scope of the electrical audit. Determine which areas, systems, and processes will be evaluated. Establish specific objectives, such as assessing compliance with safety standards, identifying potential hazards, or evaluating the effectiveness of existing safety measures.
2. Assemble the Audit Team
Form a team comprising individuals with expertise in electrical systems, safety regulations, and audit procedures. Include certified electricians, safety officers, and relevant stakeholders. Clearly define roles and responsibilities to facilitate efficient collaboration during the audit process.
3. Gather and Review Documentation
Collect all pertinent documents, including electrical schematics, maintenance records, safety protocols, and previous audit reports. Review these documents to understand the current state of the electrical systems and to identify any areas that may require special attention during the audit.
4. Develop Internal Electrical Audit Checklists
Create a comprehensive checklist that covers all aspects of the electrical systems to be evaluated. A well-structured internal audit checklist should be based on electrical SOPs that ensure consistency and thoroughness in the audit process.
👉 GoAudits offers a wide range of health and safety audit checklists tailored for electrical safety audits and inspections. You can sign up for free and start using these checklists.
- Electrical Safety Inspection Checklist
- Electrical Safety Checks
- Free Electrical Inspection Forms
- OSHA Electrical Safety Inspection Checklist
- Electrical Panel Maintenance Checklist
5. Plan and Schedule the Electrical Audit
Establish a detailed audit plan that outlines the timeline, specific areas to be audited, and the sequence of activities. Coordinate with relevant departments to schedule the audit at a time that minimizes disruptions to operations. Ensure that all necessary resources and personnel are available as per the schedule.
6. Conduct a Preliminary Inspection or Risk Assessment
Before the formal audit, perform a preliminary electrical assessment to identify obvious hazards or areas of concern. This may involve visual inspections, basic testing, and reviewing incident logs. Conducting an electrical assessment helps prioritize areas that require immediate attention during the audit.
7. Prepare the Facility and Staff
Inform all relevant personnel about the upcoming audit and its objectives. Ensure that the facility is accessible and that all areas to be audited are safe and ready for inspection. Provide necessary training or briefings to staff to facilitate their cooperation and understanding during the audit process.
8. Perform the Electrical Safety Audit
Execute the audit as per the established plan and checklist. This involves detailed inspections, testing of electrical components, and interviews with staff. Document all findings meticulously, noting any non-compliance issues, potential hazards, or areas for improvement.
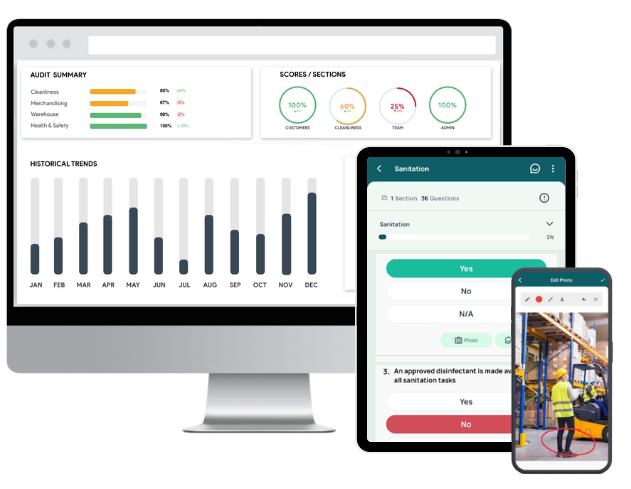
👉 GoAudits simplifies and streamlines the entire electrical safety audit process. With its intuitive mobile app, your teams can complete checklists and forms effortlessly, with minimal training. Visual elements such as annotated photos, e-signatures, timestamps, and geolocation ensure accuracy and accountability, while mandatory fields and embedded instructions help minimize mistakes. You can plan, schedule, and assign audits and inspections in bulk, monitor real-time progress, and manage follow-up actions by status, due date, or assignee.
9. Implement Measures for Improvement
Based on the audit findings, develop and implement corrective actions to address identified issues. This may include repairing faulty equipment, updating safety protocols, or providing additional training to staff. Prioritize actions based on the severity of the risks involved.
10. Review and Follow-Up
After implementing corrective measures, conduct a follow-up review to ensure that all issues have been adequately addressed. Evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken and make necessary adjustments. Regular reviews help maintain ongoing compliance and continuous improvement in electrical safety practices.
How Often Should Electrical Safety Audits Be Performed?
Most industry guidelines and regulations recommend conducting electrical safety audits at least once every year. The 2023 update to NFPA 70B specifically requires inspection of all electrical equipment at least every 12 months.
| Condition / Context | Recommended Audit Frequency |
| General compliance and hazard identification | Annually |
| High-risk facilities (e.g., hazardous materials, critical infrastructure) | Semi-annually or quarterly |
| Facilities with recent electrical incidents | Increase frequency until risks are mitigated |
| After major system changes (modifications, upgrades, expansions) | Immediate audit post-change |
| After an electrical incident, near miss, or accident | Immediate follow-up audit |
| Changes in operational profile (new equipment/processes) | Trigger a new electrical audit |
| Equipment with unresolved issues or alert history | Up to every 6 months or as needed |
Facilities with high-risk operations, such as those handling hazardous materials or operating in hazardous environments, or with critical electrical infrastructure, may require audits semi-annually or even quarterly. Even facilities with a record of electrical incidents should increase audit frequency until risks are mitigated.
Electrical audits should be conducted after any significant modifications, upgrades, or expansions to the electrical system. Any electrical incident, near miss, or accident should prompt a follow-up audit to ensure corrective actions are effective and no new hazards have been introduced. Changes in the facility’s operational profile, such as the introduction of new equipment or processes, should also trigger a new electrical audit.
Equipment with unresolved issues, continuous monitoring alerts, or missed maintenance cycles may also demand more frequent inspections, sometimes every six months.
Leverage GoAudits to Conduct Streamlined Electrical Audits
Electrical audits are often burdened with manual processes, fragmented documentation, and inconsistent reporting. Paper-based checklists increase the risk of human error, while traditional methods delay report generation and hinder timely corrective actions. Organizations frequently struggle with inefficient data entry, missing visual evidence, and poor traceability, all of which compromise compliance and safety standards. Without centralized tracking or accountability, recurring issues remain unresolved, and communication between teams breaks down, especially across multiple sites or departments.
GoAudits addresses these challenges with an all-in-one, intuitive, and user-friendly safety inspection app & software designed specifically to simplify and streamline audits, inspections, and compliance.
- Start with pre-built electrical audit templates or build your own using a drag-and-drop interface. Add timestamps and geolocation, and attach and annotate photos directly from the GoAudits app to provide visual evidence.
- Conduct electrical audits on any device even when you’re offline using the GoAudits mobile app. The data syncs automatically when
- Inspection reports are generated immediately after each audit or inspection. They include attached photos, scores, timestamps, geo-tags, and assigned actions. Customize audit reports to reflect your brand and share them instantly with relevant team members.
- Assign corrective actions during the electrical audit. Set task owners, priorities, and deadlines. Track overdue or incomplete tasks through a centralized dashboard to ensure timely resolution.
- Automate task assignments, report distribution, approvals, and reminders. Define workflows and set escalation paths based on your company’s hierarchy. Ensure the right people receive the right information at the right time to avoid delays and missed follow-ups.
- Get real-time visibility into audit scores and performance across locations, teams, or topics. Track trends, identify recurring issues, and monitor overall performance.
Industry Standards and Guidelines for Electrical Safety Compliance
Key standards and organizations play pivotal roles in shaping electrical safety protocols globally.
National Electrical Code (NEC)
The National Electrical Code (NEC), also known as NFPA 70, is a regionally adoptable standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. The NEC is widely recognized and adopted across various jurisdictions, providing comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safety of electrical installations.
NFPA 70E: Electrical Safety in the Workplace
NFPA 70E, developed by the National Fire Protection Association, focuses on electrical safety requirements to protect workers from electrical hazards in the workplace. It provides guidelines for safe work practices, including risk assessments, maintenance of electrical equipment, and the use of PPE. NFPA 70E complements OSHA regulations by offering detailed procedures to minimize the risk of electrical incidents.
NFPA 70 establishes the minimum requirements for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment to protect people and property from electrical hazards. NFPA 70E focuses specifically on electrical safety in the workplace. While NFPA 70 addresses how electrical systems should be built and maintained, NFPA 70E is concerned with how employees interact safely with electrical systems during operation, maintenance, and repair.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
OSHA’s electrical standards are designed to protect employees from electrical hazards such as shock, electrocution, fires, and explosions. These standards are codified in Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), particularly in parts 1910.302 through 1910.308 for general industry and 1910.331 through 1910.335 for electrical safety-related work practices. Compliance with OSHA standards is mandatory for employers to ensure workplace safety, and you can use these GoAudits free OSHA checklists to do so.
ISO 50001: Energy Management Systems
ISO 50001 is an international standard that provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an energy management system (EnMS). Its objective is to help organizations continually improve energy performance, including energy efficiency, use, and consumption. While ISO 50001 primarily focuses on energy management, it also contributes to electrical safety by promoting efficient and safe energy use practices.
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develops and publishes international standards for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. Key IEC standards related to electrical safety include:
- IEC 60364 covers the design, erection, and verification of electrical installations. It aims to ensure the safety of persons and property by providing guidelines for low-voltage electrical installations.
- IEC 61557 specifies requirements for equipment used to test, measure, or monitor protective measures in low-voltage distribution systems. It ensures the reliability and safety of electrical installations through proper testing and monitoring.
- IEC 61643-11 applies to surge protective devices (SPDs) connected to low-voltage power systems. It provides requirements and tests for SPDs to protect electrical installations from transient overvoltages, such as those caused by lightning.
What are the Main Benefits of Conducting Regular Electrical Safety Audits?
Electrical safety audits offer numerous benefits that contribute to the overall well-being of your organization.
- Regular electrical audits help identify potential electrical hazards. By detecting these issues early, you can implement corrective measures to prevent accidents, fires, and equipment failures, safeguarding your employees and assets.
- Adhering to electrical safety standards is essential. Regular electrical compliance checks ensure your electrical systems comply with industry standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties.
- Implementing regular safety audits fosters a culture of safety within your organization. It raises awareness among employees about electrical safety practices and encourages proactive behavior.
- Electrical safety audits contribute to operational efficiency by ensuring that all equipment functions optimally. Identifying and addressing issues like energy inefficiencies or equipment malfunctions can minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
- Proactive maintenance through regular electrical audits can lead to significant cost savings. By preventing major electrical failures and reducing energy consumption, your organization can avoid expensive repairs and lower operational costs.
- Regular electrical safety analysis extends the lifespan of electrical equipment. By addressing wear and tear promptly, you can ensure that your assets remain functional and efficient for a longer period.





